Abstract
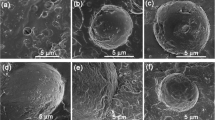
Dielectric relaxation spectroscopy (DRS) was used to investigate the effect of morphological evolution on conductivity behavior of PLA/PCL blends containing P[MPEGMA-IL]. The morphology of blends changes from sea-island morphology into co-continuous morphology with increasing P[MPEGMA-IL] content. P[MEPGMA-IL] could mainly localize in PCL domains and expand to the interface layer between the PLA and PCL phase because of the low viscosity of PCL phase and the high affinity of MEPGMA groups for both polymer phases. The dielectric results were discussed in terms of α relaxation that corresponds to normal and segmental mode movement, interfacial polarization that corresponds to interfacial aggregation of charge carriers, and ac conductivity that originates from conductive network of mobile charge carriers. Co-continuous morphology and high ions concentration lead to the enhancement of segment movement and ion conductive channel in PCL phase, which correspond to high conductivity and low activation energy of PLA/PCL/8P[MEGMA-IL] blend.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rasal RM, Janorkar AV, Hirt DE (2010) Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog Polym Sci 35:338–356
Supthanyakul R, Kaabbuathong N, Chirachanchai S (2016) Random poly(butylene succinate-co-lactic acid) as a multifunctional additive for miscibility, toughness, and clarity of PLA/PBS blends. Polymer 105:1–9
Finotti PFM, Costa LC, Chinelatto MA (2016) Effect of the chemical structure of compatibilizers on the thermal, mechanical and morphological properties of immiscible PLA/PCL blends. Macromol Symp 368:24–29
Zhang K, Mohanty AK, Misra M (2012) Fully biodegradable and biorenewable ternary blends from polylactide, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and poly(butylene succinate) with balanced properties. ACS Appl Mater Inter 4(6):3091–3101
Nampoothiri KM, Nair NR, John RP (2010) An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA) research. Bioresour Technol 101(22):8493–8501
Forouharshad M, Gardella L, Furfaro D, Galimberti M, Monticelli O (2015) A low-environmental-impact approach for novel biocomposites based on PLLA/PCL blends and high surface area graphite. Eur Polym J 70:28–36
Lai SM, Liu YH, Huang CT, Don TM (2017) Miscibility and toughness improvement of poly(lactic acid)/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) blends using a melt-induced degradation approach. J Polym Res 24:102
Chavalitpanya K, Phattanarudee S (2013) Poly(lactic acid)/polycaprolactone blends compatibilized with block copolymer. Energy Procedia 34:542–548
Labet M, Thielemans W (2009) Synthesis of polycaprolactone: a review. Chem Soc Rev 38:3484–3504
Lopez-Rodriguez N, Lopez-Arraiza A, Meaurio E, Sarasua JR (2006) Crystallization, morphology, and mechanical behavior of polylactide/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) blends. Polym Eng Sci 46(9):1299–1308
Lv QL, Wu DF, Xie H, Peng S, Chen Y, Xu CJ (2016) Crystallization of poly(ε-caprolactone) in its immiscible blend with polylactide: insight into the role of annealing histories. RSC Adv 6(44):37721–37730
Issaadi K, Habi A, Grohens Y, Pillin I (2015) Effect of the montmorillonite intercalant and anhydride maleic grafting on polylactic acid structure and properties. Appl Clay Sci 107:62–69
Issaadi K, Habi A, Grohens Y, Pillin I (2016) Maleic anhydride-grafted poly(lactic acid) as a compatibilizer in poly(lactic acid)/graphene oxide nanocomposites. Polym Bull 73:2057–2071
Zhang C, Zhai TL, Turng LS, Dan Y (2015) Morphological, mechanical, and crystallization behavior of polylactide/polycaprolactone blends compatibilized by L-lactide/caprolactone copolymer. Ind Eng Chem Res 54(38):9505–9511
Jeon O, Lee SH, Kim SH, Lee YM, Kim YH (2003) Synthesis and characterization of poly(l-lactide)-poly(ε-caprolactone) multiblock copolymers. Macromolecules 36(15):5585–5592
Peponi L, Navarro-Baena I, Báez JE, Kenny JM, Marcos-Fernández A (2012) Effect of the molecular weight on the crystallinity of PCL-b-PLLA di-block copolymers. Polymer 53(21):4561–4568
Zeng J-B, Li K-A (2015) Compatibilization strategies in poly (lactic acid)-based blends. RSC Adv 5(41):32546–32565
Odent J, Leclère P, Raquez JM, Dubois P (2013) Toughening of polylactide by tailoring phase-morphology with P [CL-co-LA] random copolyesters as biodegradable impact modifiers. Eur Polym J 49(4):914–922
Odent J, Habibi Y, Raquez JM, Dubois P (2013) Ultra-tough polylactide-based materials synergistically designed in the presence of rubbery ε-caprolactone-based copolyester and silica nanoparticles. Compos Sci Technol 84:86–91
Wu DF, Zhang YS, Zhang M, Zhou W (2008) Phase behavior and its viscoelastic response of polylactide/poly(ε-caprolactone) blend. Eur Polym J 44(7):2171–2183
Wu DF, Lin DP, Zhang J, Zhou W, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Wang D, Lin B (2011) Selective localization of nanofillers: effect on morphology and crystallization of PLA/PCL blends. Macromol Chem Phys 212(6):613–626
Laredo E, Grimau M, Bello A, Wu DF, Zhang YS, Lin DP (2010) AC conductivity of selectively located carbon nanotubes in poly(ε-caprolactone)/polylactide blend nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules 11(5):1339–1347
Wang P, Xu P, Wei HB, Fang HG, Ding YS (2018) Effect of block copolymer containing ionic liquid moiety on interfacial polarization in PLA/PCL blends. J Appl Polym Sci 135(16):46161
Singh MP, Singh RK, Chandra S (2014) Ionic liquids confined in porous matrices: physicochemical properties and applications. Prog Mater Sci 64(10):73–120
Park K, Ha JU, Xanthos M (2010) Ionic liquids as plasticizers/lubricants for polylactic acid. Polym Eng Sci 50:1105–1110
Park KI, Xanthos M (2009) A study on the degradation of polylactic acid in the presence of phosphonium ionic liquids. Polym Degrad Stab 94(5):834–844
Leroy E, Jacquet P, Coativy G, Reguerre AL, Lourdin D (2012) Compatibilization of starch-zein melt processed blends by an ionic liquid used as plasticizer. Carbohydr Polym 89(3):955–963
Yousfi M, Livi S, Duchet-Rumeau J (2014) Ionic liquids: a new way for the compatibilization of thermoplastic blends. Chem Eng J 255(6):513–524
Megevand B, Pruvost S, Lins LC, Livi S, Gérard JF, Duchet-Rumeau J (2016) Probing nanomechanical properties with AFM to understand the structure and behavior of polymer blends compatibilized with ionic liquids. RSC Adv 6(98):96421–96430
Wang P, Zhang D, Zhou YY, Li Y, Fang HG, Wei HB, Ding YS (2018) A well-defined biodegradable 1,2,3-triazolium-functionalized PEG-b-PCL block copolymer: facile synthesis and its compatibilization for PLA/PCL blends. Ionics 24(3):787–795
Corrales TP, Laroze D, Zardalidis G, Floudas G, Butt HJ, Kappl M (2013) Dynamic heterogeneity and phase separation kinetics in miscible poly(vinyl acetate)/poly(ethylene oxide) blends by local dielectric spectroscopy. Macromolecules 46(18):7458–7464
Ren JD, Adachi K (2003) Dielectric relaxation in blends of amorphous poly(DL-lactic acid) and semicrystalline poly(L-lactic acid). Macromolecules 36(36):5180–5186
Bharati A, Wübbenhorst M, Moldenaers P, Cardinaels R (2016) Effect of compatibilization on interfacial polarization and intrinsic length scales in biphasic polymer blends of PαMSAN and PMMA: a combined experimental and modeling dielectric study. Macromolecules 49(4):1464–1478
Xu P, Gui H, Yang S, Ding Y (2014) Dielectric and conductivity properties of poly(L-lactide) and poly(L-lactide)/ionic liquid blends. Macromol Res 22(3):304–309
Calandrelli L, Calarco A, Laurienzo P, Malinconico M, Petillo O, Peluso G (2008) Compatibilized polymer blends based on PDLLA and PCL for application in bioartificial liver. Biomacromolecules 9(6):1527–1534
Noroozi N, Schafer LL, Hatzikiriakos SG (2012) Thermorheological properties of poly (ε-caprolactone)/polylactide blends. Polym Eng Sci 52(11):2348–2359
Laoutid F, François D, Paint Y, Bonnaud L, Dubois P (2013) Using nanosilica to fine-tune morphology and properties of polyamide 6/poly(propylene) blends. Macromol Mater Eng 298(3):328–338
Brás AR, Viciosa MT, Wang YM, Dionísio M, Mano JF (2006) Crystallization of poly(L-lactic acid) probed with dielectric relaxation spectroscopy. Macromolecules 39(19):6513–6520
Sengwa RJ, Dhatarwal P, Choudhary S (2014) Role of preparation methods on the structural and dielectric properties of plasticized polymer blend electrolytes: correlation between ionic conductivity and dielectric parameters. Electrochim Acta 142:359–370
Starkweather HW, Peter A (1992) Conductivity and the electric modulus in polymers. J Polym Sci Polym Phys 30:637–641
Mudarra M, Diaz-Calleja R, Belana J, Canadas JC, Diego JA, Sellares J, Sanchis MJ (2004) Sublinear dispersive conductivity in polymethyl methacrylate at temperatures above the glass transition. Polymer 45(8):2737–2742
Ye YS, Sharick S, Davis EM, Winey KI, Elabd YA (2013) High hydroxide conductivity in polymerized ionic liquid block copolymers. ACS Macro Lett 2(7):575–580
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51603060) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JD2016JGPY0001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Zhou, Y., Xu, P. et al. Effect of P[MPEGMA-IL] on morphological evolution and conductivity behavior of PLA/PCL blends. Ionics 25, 3189–3196 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02871-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02871-3