Abstract
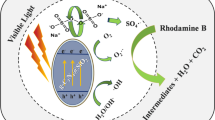
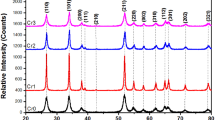
In this work, we report the results of the electrodeposition of MnO2 film on stainless steel (SS) electrode in aqueous MnSO4 solution which was used as photocatalyst to degrade the Rhodamine B (RhB). Different techniques such as field emission gun scanning electron microscopy (FEG-SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Braunauer Emett and Teller (BET), and UV-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (UV-vis DRS) were used to characterize the deposited MnO2 film. It was found that MnO2 is electrodeposited as a γ-MnO2 nanoparticle film with a low rate of crystallinity and high specific surface area of about 140 m2 g−1. The particle size is less than 20 nm. In addition, the diffuse reflectance measurements show that the γ-MnO2 presents a direct band gap of about 1.41 eV. The Mott-Schottky plot confirms that γ-MnO2 is a n-type semiconductor with the flat band potential VFB = 0.016 V vs. Ag/AgCl and the electron concentration ND = 0.8 × 1020 cm−3. The conduction and valence energy band values were estimated at Ec = 4.498 eV and Ev = 5.908 eV, respectively. It was shown also that these films exhibit good ability for the degradation of RhB especially under visible light irradiation. Indeed, degradation rates of about 90 and 55% were obtained after 60 min of visible and UV light irradiation, respectively. Finally, the degradation process mechanism of RhB is discussed.

ᅟ
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao S, Li J, Wang L, Wang X (2010) Degradation of rhodamine B and safranin-T by MoO3: CeO2 nanofibers and air using a continuous mode. CLEAN–Soil, Air, Water 38:268–274
Konstantinou IK, Albanis TA (2004) TiO2-assisted photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous solution: kinetic and mechanistic investigations: a review. Appl Catal B Environ 49(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.11.010
Houas A, Lachheb H, Ksibi M, Elaloui E, Guillard C, Herrmann J-M (2001) Photocatalytic degradation pathway of methylene blue in water. Appl Catal B Environ 31(2):145–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(00)00276-9
Zhang H, Duan L, Zhang D (2006) Decolorization of methyl orange by ozonation in combination with ultrasonic irradiation. J Hazard Mater 138(1):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.05.034
Stylidi M, Kondarides DI, Verykios XE (2003) Pathways of solar light-induced photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. Appl Catal B Environ 40(4):271–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(02)00163-7
Makowski A, Wardas W (2001) Photocatalytic degradation of toxins secreted to water by cyanobacteria and unicellular algae and photocatalytic degradation of the cells of selected microorganisms. Curr Top Biophys 25:19–25
Weidenkaff A, Reller A, Wokaun A, Steinfeld A (2000) Thermogravimetric analysis of the ZnO/Zn water splitting cycle. Thermochim Acta 359(1):69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-6031(00)00508-6
Chan Y-L, Pung S-Y, Sreekantan S, Yeoh F-Y (2016) Photocatalytic activity of β-MnO2 nanotubes grown on PET fibre under visible light irradiation. J Exp Nanosci 11(8):603–618. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2015.1102342
M. D. C. Cotto-Maldonado, Heterogeneous catalysis applied to advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for degradation of organic pollutants, 2012
Cotto-Maldonado MDC, Campo T, Elizalde E, Gomez-Martínez A, Morant C, Márquez F (2013) Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine-B under UV-visible light irradiation using different nanostructured catalysts. Am Chem Sci J 3:178–202
Das M, Bhattacharyya KG (2014) Oxidation of rhodamine B in aqueous medium in ambient conditions with raw and acid-activated MnO2, NiO, ZnO as catalysts. J Mol Catal A Chem 391:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2014.04.019
E. TC, Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine-B under UV-visible light irradiation using different nanostructured catalysts, 2013
Ai Z, Zhang L, Kong F, Liu H, Xing W, Qiu J (2008) Microwave-assisted green synthesis of MnO2 nanoplates with environmental catalytic activity. Mater Chem Phys 111(1):162–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.03.043
Chan YL, Pung SY, Hussain NS, Sreekantan S, Yeoh FY (2013) Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B using MnO2 and ZnO nanoparticles. In: Materials Science Forum, pp 167–174
Cheng J-H, Shao G, Yu H-J, Xu J-J (2010) Excellent catalytic and electrochemical properties of the mesoporous MnO2 nanospheres/nanosheets. J Alloys Compd 505(1):163–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.05.169
Cui H-J, Huang H-Z, Yuan B, Fu M-L (2015) Decolorization of RhB dye by manganese oxides: effect of crystal type and solution pH. Geochem Trans 16:1
Liang S, Teng F, Bulgan G, Zong R, Zhu Y (2008) Effect of phase structure of MnO2 nanorod catalyst on the activity for CO oxidation. J Phys Chem C 112(14):5307–5315. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0774995
Liu C, Pan D, Tang X, Hou M, Zhou Q, Zhou J (2016) Degradation of rhodamine B by the α-MnO2/peroxymonosulfate system. Water Air Soil Pollut 227:1–10
Sun H, Xu K, Huang M, Shang Y, She P, Yin S, Liu Z (2015) One-pot synthesis of ultrathin manganese dioxide nanosheets and their efficient oxidative degradation of rhodamine B. Appl Surf Sci 357:69–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.258
Sun S, Wang W, Shang M, Ren J, Zhang L (2010) Efficient catalytic oxidation of tetraethylated rhodamine over ordered mesoporous manganese oxide. J Mol Catal A Chem 320(1-2):72–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2010.01.006
Yu C, Li G, Wei L, Fan Q, Shu Q, Jimmy CY (2014) Fabrication, characterization of β-MnO2 microrod catalysts and their performance in rapid degradation of dyes of high concentration. Catal Today 224:154–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2013.11.029
Zhang H, Chen W-R, Huang C-H (2008) Kinetic modeling of oxidation of antibacterial agents by manganese oxide. Environ Sci Technol 42(15):5548–5554. https://doi.org/10.1021/es703143g
Zhang W, Yang Z, Wang X, Zhang Y, Wen X, Yang S (2006) Large-scale synthesis of β-MnO2 nanorods and their rapid and efficient catalytic oxidation of methylene blue dye. Catal Commun 7(6):408–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2005.12.008
Baral A, Das DP, Minakshi M, Ghosh MK, Padhi DK (2016) Probing environmental remediation of RhB organic dye using α-MnO2 under visible-light irradiation: structural, photocatalytic and mineralization studies. Chem Select 1(14):4277–4285. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201600867
Messaoudi B, Joiret S, Keddam M, Takenouti H (2001) Anodic behaviour of manganese in alkaline medium. Electrochim Acta 46(16):2487–2498. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(01)00449-2
Zhang Y, Sun C, Lu P, Li K, Song S, Xue D (2012) Crystallization design of MnO2 towards better supercapacitance. CrystEngComm 14(18):5892–5897. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ce25610j
Mimi N, Messaoudi B, Takenouti H, Pillier F (2009) Synthese de nouveaux materieux de structure nanometrique pour electrode de piles. Ann Chim 34(3):187–199. https://doi.org/10.3166/acsm.34.187-199
Paul R, Cartwright A (1986) The mechanism of the deposition of manganese dioxide: part II. Electrode impedance studies. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 201(1):113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0728(86)90091-4
Cherchour N, Deslouis C, Messaoudi B, Pailleret A (2011) pH sensing in aqueous solutions using a MnO2 thin film electrodeposited on a glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim Acta 56(27):9746–9755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2011.08.011
Zhang Q, Cheng X, Zheng C, Feng X, Qiu G, Tan W, Liu F (2011) Roles of manganese oxides in degradation of phenol under UV-vis irradiation: adsorption, oxidation, and photocatalysis. J Environ Sci 23(11):1904–1910. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60655-9
Moulai F, Cherchour N, Messaoudi B, Zerroual L (2017) Electrosynthesis and characterization of nanostructured MnO2 deposited on stainless steel electrode: a comparative study with commercial EMD. Ionics 23:1–8
Kozawa A, Powers R (1967) Cathodic reduction of Beta-MnO2 and gamma-MnO2 in NH4CI and KOH electrolytes. Electr Technol 5:535
Chou S, Cheng F, Chen J (2006) Electrodeposition synthesis and electrochemical properties of nanostructured γ-MnO2 films. J Power Sources 162(1):727–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.06.033
Chabre Y, Pannetier J (1995) Structural and electrochemical properties of the proton/γ-MnO2 system. Prog Solid State Chem 23(1):1–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/0079-6786(94)00005-2
Saravanakumar K, Muthuraj V, Vadivel S (2016) Constructing novel Ag nanoparticles anchored on MnO2 nanowires as an efficient visible light driven photocatalyst. RSC Adv 6(66):61357–61366. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA10444D
Dewald J (1960) The charge and potential distributions at the zinc oxide electrode. Bell Labs Tech J 39(3):615–639. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1960.tb03935.x
A. Loucif, Caractérisation photoélectrochimique des oxydes formés sur alliages base nickel en milieu primaire des réacteurs à eau pressurisée, Grenoble, 2012
Nakayama M, Mito S, Mohri Y (2014) Enhanced photocurrent in Birnessite–type MnO2 thin films in the visible and near-infrared regions by scaffolding multi-wall carbon nanotubes. J Electrochem Soc 161(6):H355–H358. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.017406jes
Ali GA, Yusoff MM, Shaaban ER, Chong KF (2017) High performance MnO 2 nanoflower supercapacitor electrode by electrochemical recycling of spent batteries. Ceram Int 43(11):8440–8448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.03.195
Pinaud BA, Chen Z, Abram DN, Jaramillo TF (2011) Thin films of sodium birnessite-type MnO2: optical properties, electronic band structure, and solar photoelectrochemistry. J Phys Chem C 115(23):11830–11838. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp200015p
Varela F, Gassa L, Vilche J (1993) Characterization of passive layers formed on lead by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J Electroanal Chem 353(1-2):147–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0728(93)80293-Q
Di Paola A, Shukla D, Stimming U (1991) Photoelectrochemical study of passive films on stainless steel in neutral solutions. Electrochim Acta 36(2):345–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4686(91)85260-E
Gassa L, Mishima H, de Mishima BL, Vilche J (1997) An electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of electrodeposited manganese oxide films in borate buffers. Electrochim Acta 42(11):1717–1723. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(96)00371-4
Belhadi A, Boudjellal L, Boumaza S, Trari M (2017) Hydrogen production over the hetero-junction MnO2/SiO2. Int J Hydrog Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.06.086
Bessekhouad Y, Trari M, Doumerc J-P (2003) CuMnO2, a novel hydrogen photoevolution catalyst. Int J Hydrog Energy 28(1):43–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3199(02)00023-X
Belabed C, Haine N, Benabdelghani Z, Bellal B, Trari M (2014) Photocatalytic hydrogen evolution on the hetero-system polypyrrol/TiO2 under visible light. Int J Hydrog Energy 39(31):17533–17539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.08.107
Yu K, Yang S, He H, Sun C, Gu C, Ju Y (2009) Visible light-driven photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B over NaBiO3: pathways and mechanism. J Phys Chem A 113(37):10024–10032. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp905173e
Fu H, Zhang S, Xu T, Zhu Y, Chen J (2008) Photocatalytic degradation of RhB by fluorinated Bi2WO6 and distributions of the intermediate products. Environ Sci Technol 42(6):2085–2091. https://doi.org/10.1021/es702495w
Sun M, Li D, Chen Y, Chen W, Li W, He Y, Fu X (2009) Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of calcium antimony oxide hydroxide for the degradation of dyes in water. J Phys Chem C 113(31):13825–13831. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp903355a
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from General Direction of Scientific Research and of Technological Development of Algeria (DGRSDT/MESRS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• RhB photodegradation by γ-MnO2 film electrodeposited as photocatalyst.
• Eg and specific surface area of γ-MnO2 are about 1.41 eV and 140 m2 g−1, respectively.
• γ-MnO2 film is more photocatalytically efficiency under visible light than UV light.
• The highest photodegradation rate (90%) is obtained under visible light after 60 min.
• The photodegradation under visible light occurs via photocatalytic oxidation and/or photosensitization processes.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 337 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moulai, F., Fellahi, O., Messaoudi, B. et al. Electrodeposition of nanostructured γ-MnO2 film for photodegradation of Rhodamine B. Ionics 24, 2099–2109 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2440-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2440-7