Abstract
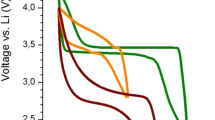
LiFePO4-C was prepared by the solid-state reaction using LiH2PO4, Fe2O3, and glucose as raw materials, which is a green and low-cost method. Thermogravimetry, differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray diffraction, and element analyzer were used to study the phase and carbon content of the synthesized samples. The optimum conditions for synthesizing LiFePO4 are identified. The discharge capacity of 120 mAh g−1 was achieved at a current density of 100 mA g−1 between 2.5 and 4.2 V during the first 50 cycles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Padhi AK, Nanjundaswamy KS, Goodenough JB (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:1188–1194
Yonemura M, Yamada A, Takei Y, Sonoyama N et al (2004) J Electrochem Soc 151:A1352–A1356
Chung SY, Bloking JT, Chiang YM (2002) Nat Matters 1:123–128
Herle PS, Ellis B, Coombs N et al (2004) Nat Matters 3:147–152
Delacourt C, Poizot P, Tarascon JM et al (2005) Nat Matters 4:254–260
Huang H, Yin SC, Nazar LF (2001) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 4:A170–A172
Mi CH, Cao GS, Zhao XB (2005) Nat Matters 59:127–130
Ruan YL, Tang ZY, Huang BM (2005) Chin J Chem Eng 13:686–690
Wang YQ, Wang BL, Yang J et al (2006) Adv Funct Mater 16:2135–2140
Xu ZH, Xu L, Lai QY et al (2007) Mater Chem Phys 105:80–85
Wang YG, Wang YR, Hosono E et al (2008) Angew Chem Int Edit 47:7461–7465
Croce F, Epifanio AD, Hassoun J et al (2002) Electrochem Solid-State Lett 5:A47–A50
Park KS, Son JT, Chung HT et al (2004) Solid State Commun 129:311–314
Wagemaker M, Ellis BL, Luetzenkirchen-Hecht D et al (2008) Chem Mater 20:6313–6315
Li LJ, Li XH, Wang ZX et al (2009) J Phys Chem Solids 70:238–242
Kang HC, Jun DK, Jin B et al (2008) J Power Sources 179:340–346
Arnold G, Garche J, Hemmer R et al (2003) J Power Sources 119:247–251
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Chinese Ministry of Education (No. NECT-07-0307) and New Teacher Fund of Ministry of Education of China (No.20070561032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Liu, Q. & Wang, H. Synthesis of LiFePO4-C cathode materials using a green and low-cost method. Ionics 15, 689–692 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-009-0389-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-009-0389-2