Abstract
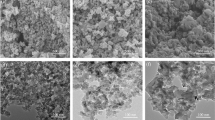
Silica aerogel (SiO2 aerogel) was prepared by sol–gel method from tetraethyl orthosilicate hydrolyzation and has been characterized by scanning electron microscopy and N2 adsorption for its surface structure, surface area, and pore-size distribution. Constant current charge–discharge technique, cyclic voltammetry, and electrochemical impedance spectrum were employed for its specific capacitance and equivalent series resistance. The results showed that the maximum specific capacitance of SiO2 aerogel electrode in 1 M Et4NBF4/PC electrolyte was 62.5 F g−1. In addition, the SiO2 aerogel capacitor exhibits excellent long-term stability with no significant degradation after 500 charging and discharging cycles. Therefore, the application of high surface area SiO2 aerogel as electrodes in supercapacitor devices is promising.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conway BE (1999) Electrochemical supercapacitors. Kluwer, New York
Burke A (2000) J Power Sources 91:37–50
Frackowiak E, Béguin F (2001) Carbon 39:937–950
Hrubesh LW (1998) J Non-Cryst Solids 225:335–342
Yang HL, Ni W, Sun CC et al (2006) Aerospace Materials and Technology 2:18–22
Gibiat V, Lefeuvre O et al (1995) J Non-Cryst Solids 186:244–255
Schmidt M, Schwertfeger F (1998) J Non-Cryst Solids 225:364–368
Sousa A, Souca EMB (2006) J Non-Cryst Solids 352:3451–3456
Scherer GW (1998) J Colloid Interface Sci 202:399–410
Scherer GW, Calas S, Sempere R (1998) J Colloid Interface Sci 202:411–416
Pekala RW, Farmer JC, Alviso CT et al (1998) J Non-Cryst Solids 225:74–80
Dong W, Sakamoto JS, Dunn B (2003) Sci Technol Adv Mater 4:3–11
Anappara AA, Rajeshkumar S, Mukundan P et al (2004) Acta Materialia 52:369–375
Shi H (1996) Electrochim Acta 41:1633–1639
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW et al (1985) Pure Appl Chem 57:603–619
Rassy HE, Buisson P, Bouali B et al (2003) Langmuir 19:358–363
Chen WC, Wen TC, Teng HS (2003) Electrochim Acta 48:641–649
Arulepp M, Permann L, Leis J et al (2004) J Power Sources 133:320–328
Li J, Wang X, Huang Q et al (2006) J Power Sources 158:784–788
Wang DW, Li F, Liu M et al (2008) Angew. Chem 47:373–376
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Zhi-ping Ge for the surface area measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, X., Wang, C., Li, T. et al. Studies on the performances of silica aerogel electrodes for the application of supercapacitor. Ionics 15, 561–565 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-009-0315-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-009-0315-7