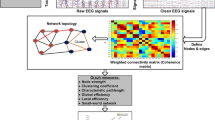
Abstract
Developmental Dyslexia is a neuro-developmental disorder that often refers to a phonological processing deficit regardless of average IQ. The present study investigated the distinct functional changes in brain networks of dyslexic children during arithmetic task performance using an electroencephalogram. Fifteen dyslexic children and fifteen normally developing children (NDC) were recruited and performed an arithmetic task. Brain functional network measures such as node strength, clustering coefficient, characteristic pathlength and small-world were calculated using graph theory methods for both groups. Task performance showed significantly less performance accuracy in dyslexics against NDC. The neural findings showed increased connectivity in the delta band and reduced connectivity in theta, alpha, and beta band at temporoparietal, and prefrontal regions in dyslexic group while performing the task. The node strengths were found to be significantly high in delta band (T3, O1, F8 regions) and low in theta (T5, P3, Pz regions), beta (Pz) and gamma band (T4 and prefrontal regions) during the task in dyslexics compared to the NDC. The clustering coefficient was found to be significantly low in the dyslexic group (theta and alpha band) and characteristic pathlength was found to be significantly high in the dyslexic group (theta and alpha band) compared to the NDC group while performing task. In conclusion, the present study shows evidence for poor fact-retrieval mechanism and altered network topology in dyslexic brain networks during arithmetic task performance.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data
Data will be made available based on reasonable request.
Code availability
Code will be made available based on reasonable request.
References
Akbarian B, Erfanian A (2020) A framework for seizure detection using effective connectivity, graph theory, and multi-level modular network. Biomed Signal Process Control 59:101878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101878
Arbabshirani MR, Calhoun VD (2011) Functional network connectivity during rest and task: comparison of healthy controls and schizophrenic patients. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2011:4418–4421
Arns M, Peters S, Breteler R, Verhoeven L (2007) Different brain activation patterns in dyslexic children: evidence from EEG power and coherence patterns for the double-deficit theory of dyslexia. J Integr Neurosci 6:175–190
Ashkenazi S, Black JM, Abrams DA et al (2013) Neurobiological underpinnings of math and reading learning disabilities. J Learn Disabil 46:549–569. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219413483174
Bailey SK, Aboud KS, Nguyen TQ, Cutting LE (2018) Applying a network framework to the neurobiology of reading and dyslexia. J Neurodev Disord 10:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11689-018-9251-z
Balasubramanian G, Kanagasabai A, Jagannath M, Seshadri NPG (2018) Music induced emotion using wavelet packet decomposition—an EEG study. Biomed Signal Process Control 42:115–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2018.01.015
Bastos AM, Schoffelen J-M (2016) A tutorial review of functional connectivity analysis methods and their interpretational pitfalls. Front Syst Neurosci 9:175
Boets B, Op de Beeck HP, Vandermosten M et al (2013) Intact but less accessible phonetic representations in adults with dyslexia. Science 342(80):1251 LP – 1254. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1244333
Bullmore E, Sporns O (2009) Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:186–198. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2575
Bullmore E, Sporns O (2012) The economy of brain network organization. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:336–349
Cho S, Metcalfe AWS, Young CB et al (2012) Hippocampal-prefrontal engagement and dynamic causal interactions in the maturation of children’s fact retrieval. J Cogn Neurosci 24:1849–1866. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_00246
Cohen JR, D’Esposito M (2016) The segregation and integration of distinct brain networks and their relationship to cognition. J Neurosci 36:12083–12094
De Clercq-Quaegebeur M, Casalis S, Vilette B et al (2018) Arithmetic abilities in children with developmental dyslexia: performance on French ZAREKI-R test. J Learn Disabil 51:236–249. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219417690355
De Smedt B, Boets B (2010) Phonological processing and arithmetic fact retrieval: evidence from developmental dyslexia. Neuropsychologia 48:3973–3981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.10.018
De Smedt B, Grabner RH, Studer B (2009) Oscillatory EEG correlates of arithmetic strategy use in addition and subtraction. Exp Brain Res 195:635–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1839-9
De Smedt B, Taylor J, Archibald L, Ansari D (2010) How is phonological processing related to individual differences in children’s arithmetic skills? Dev Sci 13:508–520. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7687.2009.00897.x
Dehaene S (1992) Varieties of numerical abilities. Cognition 44:1–42
Dehaene S, Piazza M, Pinel P, Cohen L (2003) Three parietal circuits for number processing. Cogn Neuropsychol 20:487–506. https://doi.org/10.1080/02643290244000239
Dimitrakopoulos GN, Member S, Kakkos I (2018) Fatigue reveals different network topological. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 26:740–749
Dushanova JA, Tsokov SA (2020) Small-world EEG network analysis of functional connectivity in developmental dyslexia after visual training intervention. J Integr Neurosci 19:601–618
Evans TM, Flowers DL, Napoliello EM et al (2014) The functional anatomy of single-digit arithmetic in children with developmental dyslexia. Neuroimage 101:644–652
Fowler AE, Liberman AM, Shankweiler D et al (1995) Cognitive profiles of reading-disabled children: comparison of language skills in phonology, morphology, and syntax. Psychol Sci 6:149–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.1995.tb00324.x
Fraga González G, Van der Molen MJW, Žarić G et al (2016) Graph analysis of EEG resting state functional networks in dyslexic readers. Clin Neurophysiol 127:3165–3175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2016.06.023
Gao JF, Yang Y, Huang WT et al (2016) Exploring time-and frequency-dependent functional connectivity and brain networks during deception with single-trial event-related potentials. Sci Rep 6:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37065
Gauba H, Kumar P, Roy PP et al (2017) Prediction of advertisement preference by fusing EEG response and sentiment analysis. Neural Netw 92:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2017.01.013
Geary DC, Hoard MK (2001) Numerical and arithmetical deficits in learning-disabled children: relation to dyscalculia and dyslexia. Aphasiology 15:635–647. https://doi.org/10.1080/02687040143000113
Geethanjali B, Adalarasu K, Jagannath M, Guhan Seshadri NP (2019) Music-induced brain functional connectivity using EEG sensors: a study on Indian music. IEEE Sens J 19:1499–1507. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2018.2873402
Grabner RH, Brunner C, Leeb R et al (2007) Event-related EEG theta and alpha band oscillatory responses during language translation. Brain Res Bull 72:57–65
Grabner RH, De Smedt B (2012) Oscillatory EEG correlates of arithmetic strategies: a training study. Front Psychol 3:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00428
Güntekin B, Emek-Savaş DD, Kurt P et al (2013) Beta oscillatory responses in healthy subjects and subjects with mild cognitive impairment. NeuroImage Clin 3:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2013.07.003
Hanslmayr S, Sauseng P, Doppelmayr M et al (2005) Increasing individual upper alpha power by neurofeedback improves cognitive performance in human subjects. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 30:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-005-2169-8
Hecht SA, Torgesen JK, Wagner RK, Rashotte CA (2001) The relations between phonological processing abilities and emerging individual differences in mathematical computation skills: a longitudinal study from second to fifth grades. J Exp Child Psychol 79:192–227. https://doi.org/10.1006/jecp.2000.2586
Hensel S, Rockstroh B, Berg P et al (2004) Left-hemispheric abnormal EEG activity in relation to impairment and recovery in aphasic patients. Psychophysiology 41:394–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8986.2004.00164x
Hinault T, Lemaire P (2016) What does EEG tell us about arithmetic strategies? A review. Int J Psychophysiol 106:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2016.05.006
Johnstone IM, Silverman BW (1997) Wavelet threshold estimators for data with correlated noise. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol 59:319–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9868.00071
Kamat VV (1967) Measuring intelligence of Indian children. Oxford University Press, London
Klimesch W, Doppelmayr M, Pachinger T, Ripper B (1997) Brain oscillations and human memory: EEG correlates in the upper alpha and theta band. Neurosci Lett 238:9–12
Klimesch W, Schack B, Sauseng P (2005) The functional significance of theta and upper alpha oscillations. Exp Psychol 52:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1027/1618-3169.52.2.99
Koerte IK, Willems A, Muehlmann M et al (2016) Mathematical abilities in dyslexic children: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Brain Imag Behav 10:781–791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-015-9436-y
Lushchekina EA, Khaerdinova OY, Novototskii-Vlasov VY et al (2016) Synchronization of EEG rhythms in baseline conditions and during counting in children with autism spectrum disorders. Neurosci Behav Physiol 46:382–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-016-0246-5
Teplan M (2002) Fundamentals of EEG measurement. Meas Sci Rev 2:1–11
Majerus S, Cowan N (2016) The nature of verbal short-term impairment in dyslexia: the importance of serial order. Front Psychol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01522
Mallat G (1989) A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell II:674–693
Mamun M, Al-Kadi M, Marufuzzaman M (2013) Effectiveness of wavelet denoising on electroencephalogram signals. J Appl Res Technol 11:156–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1665-6423(13)71524-4
Maslov S, Sneppen K (2002) Specificity and stability in topology of protein networks. Science 296(80):910–913
Mather N, Goldstein S, Eklund K (2001) Learning disabilities and challenging behaviors. Balt MD Brookes
Norton ES, Beach SD, Gabrieli JDE (2015) Neurobiology of dyslexia. Curr Opin Neurobiol 30:73–78
Ortiz-Mantilla S, Cantiani C, Shafer VL, Benasich AA (2019) Minimally-verbal children with autism show deficits in theta and gamma oscillations during processing of semantically-related visual information. Sci Rep 9:1–12
Papagiannopoulou EA, Lagopoulos J (2016) Resting state EEG hemispheric power asymmetry in children with dyslexia. Front Pediatr. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2016.00011
Penolazzi B, Spironelli C, Angrilli A (2008) Delta EEG activity as a marker of dysfunctional linguistic processing in developmental dyslexia. Psychophysiology 45:1025–1033. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8986.2008.00709.x
Perera H, Shiratuddin MF, Wong KW (2018a) Review of EEG-based pattern classification frameworks for dyslexia. Brain Informatics. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40708-018-0079-9
Perera H, Shiratuddin MF, Wong KW, Fullarton K (2018b) EEG signal analysis of passage reading and rapid automatized naming between adults with dyslexia and normal controls. Proc IEEE Int Conf Softw Eng Serv Sci ICSESS 2017–Novem:104–108. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSESS.2017.8342874
Peters L, De Smedt B (2018) Arithmetic in the developing brain: a review of brain imaging studies. Dev Cogn Neurosci 30:265–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2017.05.002
Peterson RL, Pennington BF (2012) Seminar: developmental dyslexia. Lancet 379:1997–2007. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60198-6.Seminar
Phinyomark A, Ibanez-Marcelo E, Petri G (2017) Resting-state fMRI functional connectivity: big data preprocessing pipelines and topological data analysis. IEEE Trans Big Data 3:415–428. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbdata.2017.2734883
Pugh KR, Mencl WE, Jenner AR et al (2000) Functional neuroimaging studies of reading and reading disability (developmental dyslexia). Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev 6:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-2779(2000)6:3%3c207::AID-MRDD8%3e3.0.CO;2-P
Ramus F (2004) Neurobiology of dyslexia: a reinterpretation of the data. Trends Neurosci 27:1–9
Raven J, Raven J, Court J (1998) Coloured progressive matrices. Oxford Psychologists Press, Oxford
Richlan F, Kronbichler M, Wimmer H (2013) Structural abnormalities in the dyslexic brain: a meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. Hum Brain Mapp 34:3055–3065. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22127
Richlan F, Kronbichler M, Wimmer H (2011) Meta-analyzing brain dysfunctions in dyslexic children and adults. Neuroimage 56:1735–1742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.02.040
Richlan F, Kronbichler M, Wimmer H (2009) Functional abnormalities in the dyslexic brain: a quantitative meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Hum Brain Mapp 30:3299–3308. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20752
Rivera SM, Reiss AL, Eckert MA, Menon V (2005) Developmental changes in mental arithmetic: evidence for increased functional specialization in the left inferior parietal cortex. Cereb Cortex 15:1779–1790. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhi055
Rourke BP, Conway JA (1997) Disabilities of arithmetic and mathematical reasoning: perspectives from neurology and neuropsychology. J Learn Disabil 30:34–46. https://doi.org/10.1177/002221949703000103
Rubinov M, Sporns O (2010) NeuroImage complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 52:1059–1069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.10.003
Sauseng P, Hoppe J, Klimesch W et al (2007) Dissociation of sustained attention from central executive functions: local activity and interregional connectivity in the theta range. Eur J Neurosci 25:587–593
Shah HR, Sagar JKV, Somaiya MP, Nagpal JK (2019) Clinical practice guidelines on assessment and management of specific learning disorders. Indian J Psychiatry 61:211
Simmons FR, Singleton C (2007) Do weak phonological representations impact on arithmetic development? A review of research into arithmetic and dyslexia. Dyslexia 239:234–239. https://doi.org/10.1002/dys
Simmons FR, Singleton C (2006) The mental and written arithmetic abilities of adults with dyslexia. Dyslexia 12:96–114. https://doi.org/10.1002/dys.312
Sinha UK (2007) Specific learning disability- screening questionnaire (SLD-SQ). Psychomatrix Corporation 2012, New Delhi
Skagenholt M, Träff U, Västfjäll D, Skagerlund K (2018) Examining the triple code model in numerical cognition: An FMRI study. PLoS One 13:e0199247
Soltanlou M, Artemenko C, Dresler T et al (2019) Oscillatory EEG changes during arithmetic learning in children. Dev Neuropsychol 44:325–338. https://doi.org/10.1080/87565641.2019.1586906
Soltanlou M, Artemenko C, Ehlis AC et al (2018) Reduction but no shift in brain activation after arithmetic learning in children: a simultaneous fNIRS-EEG study. Sci Rep 8:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20007-x
Spironelli C, Penolazzi B, Angrilli A (2008) Dysfunctional hemispheric asymmetry of theta and beta EEG activity during linguistic tasks in developmental dyslexia. Biol Psychol 77:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2007.09.009
Stipacek A, Grabner RH, Neuper C et al (2003) Sensitivity of human EEG alpha band desynchronization to different working memory components and increasing levels of memory load. Neurosci Lett 353:193–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2003.09.044
Sun S, Li X, Zhu J et al (2019) Graph theory analysis of functional connectivity in major depression disorder with high-density resting state EEG data. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 27:429–439. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2894423
Achenbach TM (1991) Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4-18 and 1991 profile. VT Univ Vermont, Dep Psychiatry, Burlington
Ting W (2008) EEG feature extraction based on wavelet packet decomposition for brain computer interface. Measurement 41:618–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2007.07.007
Träff U, Passolunghi MC (2015) Mathematical skills in children with dyslexia. Learn Individ Differ 40:108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2015.03.024
van der Mark S, Klaver P, Bucher K et al (2011) The left occipitotemporal system in reading: Disruption of focal fMRI connectivity to left inferior frontal and inferior parietal language areas in children with dyslexia. Neuroimage 54:2426–2436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.002
Vandermosten M, Boets B, Wouters J, Ghesquière P (2012) A qualitative and quantitative review of diffusion tensor imaging studies in reading and dyslexia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36:1532–1552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.04.002
Virgilio GCD, Sossa AJH, Antelis JM, Falcón LE (2020) Spiking neural networks applied to the classification of motor tasks in EEG signals. Neural Netw 122:130–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2019.09.037
von Stein A, Sarnthein J (2000) Different frequencies for different scales of cortical integration: from local gamma to long range alpha/theta synchronization. Int J Psychophysiol 38:301–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8760(00)00172-0
Wang J, Wang X, Xia M et al (2015) GRETNA: a graph theoretical network analysis toolbox for imaging connectomics. Front Hum Neurosci 9:386
Xia M, Wang J, He Y (2013) BrainNet viewer: a network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PLoS ONE 8:e68910
Yu H, Zhu L, Cai L et al (2020) Variation of functional brain connectivity in epileptic seizures: an EEG analysis with cross-frequency phase synchronization. Cogn Neurodyn 14:35–49
Zarjam P, Epps J, Chen F, Lovell NH (2013) Estimating cognitive workload using wavelet entropy-based features during an arithmetic task. Comput Biol Med 43:2186–2195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2013.08.021
Zikov T, Bibian S, Durnont GA, et al (2002) A wavelet based de-noising technique. Proc Second Jt EMBS/BMES Conf 98–105
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the children and their parents for their participation. The authors are also grateful to the Principals and psychologists of special schools who had participated in this study.
Funding
The authors did not receive any funding for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This research protocol has been approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee, National Institute of Technology Raipur (NITRR/IEC/2019/02) and informed consent was obtained from all the participants/their parents.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seshadri, N.P.G., Geethanjali, B. & Singh, B.K. EEG based functional brain networks analysis in dyslexic children during arithmetic task. Cogn Neurodyn 16, 1013–1028 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-021-09769-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-021-09769-9