Abstract
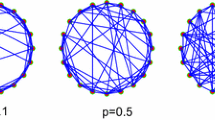
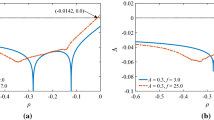
Electric fields, which are ubiquitous in the context of neurons, are induced either by external electromagnetic fields or by endogenous electric activities. Clinical evidences point out that magnetic stimulation can induce an electric field that modulates rhythmic activity of special brain tissue, which are associated with most brain functions, including normal and pathological physiological mechanisms. Recently, the studies about the relationship between clinical treatment for psychiatric disorders and magnetic stimulation have been investigated extensively. However, further development of these techniques is limited due to the lack of understanding of the underlying mechanisms supporting the interaction between the electric field induced by magnetic stimulus and brain tissue. In this paper, the effects of steady DC electric field induced by magnetic stimulation on the coherence of an interneuronal network are investigated. Different behaviors have been observed in the network with different topologies (i.e., random and small-world network, modular network). It is found that the coherence displays a peak or a plateau when the induced electric field varies between the parameter range we defined. The coherence of the neuronal systems depends extensively on the network structure and parameters. All these parameters play a key role in determining the range for the induced electric field to synchronize network activities. The presented results could have important implications for the scientific theoretical studies regarding the effects of magnetic stimulation on human brain.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews-Zwilling Y, Gillespie AK, Kravitz AV, Nelson AB, Devidze N, Lo I, Yoon SY, Bien-Ly N, Ring K, Zwilling D, Potter GB, Rubenstein JL, Kreitzer AC, Huang Y (2012) Hilar GABAergic interneuron activity controls spatial learning and memory retrieval. PLoS ONE 7(7):e40555
Barth DS, MacDonald KD (1996) Thalamic modulation of high-frequency oscillating potentials in auditory cortex. Nature 383:78–81
Bassett DS, Bullmore ET (2006) Small world brain networks. Neuroscientist 12:512–523
Bédard C, Kröger H, Destexhe A (2006) Model of low-pass filtering of local field potentials in brain tissue. Phys Rev E 73:051911
Bikson M, Inoue M, Akiyama H, Deans JK, Fox JE, Miyakawa H, Jefferys JG (2004) Effects of uniform extracellular DC electric fields on excitability in rat hippocampal slices in vitro. J Physiol 557:175–190
Börgers C, Kopell N (2008) Gamma oscillations and stimulus selection. Neural Comput 20:383–414
Buhl EH, Cobb SR, Halasy K, Somogyi P (1995) Properties of unitary IPSPs evoked by anatomically identified basket cells in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 7:1989–2004
Bullmore E, Sporns O (2009) Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:186–198
Buzsaki G, Leung L, Vanderwolf CH (1983) Cellular bases of hippocampal EEG in the behaving rat. Brain Res Rev 6:139–171
Cheyne D, Bells S, Ferrari P, Gaetz W, Bostan AC (2008) Self-paced movements induce high frequency gamma oscillations in primary motor cortex. Neuroimage 42:332–342
Cook CM, Thomas AW, Prato FS (2004) Resting EEG is affected by exposure to a pulsed ELF magnetic field. Bioelectromagnetics 25:196–203
Correa A, Nobre AC (2008) Spatial and temporal acuity of visual perception can be enhanced selectively by attentional set. Exp Brain Res 189:339–344
Deans JK, Powell AD, Jefferys JGR (2007) Sensitivity of coherent oscillations in rat hippocampus to AC electric fields. J Physiol 583(2):555–565
Devos D, Lefebvre L (2006) Effect of deep brain stimulation and L-dopa on electrocortical rhythms related to movement in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Brain Res 159:331–349
Di Lazzaro V, Oliviero A, Pilato F, Saturno E, Dileone M, Mazzone P, Insola A, Tonali PA, Rothwell JC (2004) The physiological basis of transcranial motor cortex stimulation in conscious humans. Clin Neurophysiol 115:255–266
Dlabač-De Lange JJ, Knegtering R, Aleman A (2010) Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for negative symptoms of schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 71(4):411
Ermentrout GB (1996) Type I membranes, phase resetting and synchrony. Neural Comput 8:979–1001
George MS, Lisanby SH, Avery D, McDonald WM, Durkalski V, Pavlicova M, Anderson B, Nahas Z, Bulow P, Zarkowski P, Holtzheimer PE III, Schwartz T, Sackeim HA (2010) Daily left prefrontal transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy for major depressive disorder: a sham-controlled randomized trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67(5):507–516
Giannì M, Liberti M, Apollonio F, D’Inzeo G (2006) Modeling electromagnetic fields detectability in a HH-like neuronal system: stochastic resonance and window behavior. Biol Cybern 94:118–127
Gielen S, Krupa M, Zeitler M (2010) Gamma oscillations as a mechanism for selective information transmission. Biol Cybern 103(2):151–165
Goldman DE (1943) Potential impedence and rectification in membranes. J Gen Physiol 27:37–60
Gu Y, Liljenström H (2007) A neural network model of attention-modulated neurodynamics. Cogn Neurodyn 1(4):275–285
Haenschel C, Bittner R, Waltz J, Haertling F, Wibral M, Singer W (2009) Cortical oscillatory activity is critical for working memory as revealed by deficits in early-onset schizophrenia. J Neurosci 29:9481–9489
Hansel D, Mato G, Meunier C (1995) Synchrony in excitatory neural networks. Neural Comput 7:307–335
Hilgetag CC, Kaiser M (2004) Clustered organisation of cortical connectivity. Neuroinformatics 2:353–360
Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF (1952) A quantitative description of membrane and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol 117:500–544
Hodgkin AL, Katz B (1949) The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid. J Physiol 108:37–77
Honey CJ, Kotter R, Breakspear M, Sporns O (2007) Network structure of cerebral cortex shapes functional connectivity on multiple time scales. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:10240–10245
Jiao X, Wang R (2010) Synchronous firing patterns of neuronal population with excitatory and inhibitory connections. Int J Non Linear Mech 45:647–651
Kaiser J, Rahm B, Lutzenberger W (2009) Temporal dynamics of stimulus-specific gamma-band activity components during auditory short-term memory. Neuroimage 44:257–264
Kamitani Y (2011) A model of magnetic stimulation of neocortical neurons. Neurocomputing 38–40:697–703
Kobayashi M, Pascual-Leone A (2003) Transcranial magnetic stimulation in neurology. Lancet Neurol 2:145–156
Koenig T, Prichep L, Dierks T, Hubl D, Wahlund LO, John ER, Jelic V (2005) Decreased EEG synchronization in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 26:165–171
Kotnik T, Miklavcic D (2000) Theoretical evaluation of the distributed power dissipation in biological cells exposed to electric fields. Bioelectromagnetics 21(5):385–394
Kotnik T, Bobanović F, Miklavčič D (1997) Sensitivity of transmembrane voltage induced by applied electric fields—A theoretical analysis. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 43:285–291
Kotnik T, Miklavčič D, Slivnik T (1998) Time course of transmembrane voltage induced by time-varying electric fields—a method for theoretical analysis and its application. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 45:3–16
Kullmann DM (2011) Interneuron networks in the hippocampus. Curr Opin Neurobiol 21(5):709–716
Lakatos P, Karmos G, Mehta AD, Ulbert I, Schroeder CE (2008) Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection. Science 320:110–113
Lee KH, Williams LM, Haig A, Goldberg E, Gordon E (2001) An integration of 40 Hz Gamma and phasic arousal: novelty and routinization processing in schizophrenia. Clin Neurophysiol 112(8):1499–1507
Legros A, Corbacio M, Beuter A et al (2010) Human exposure to a 60 Hz, 1800 microtesla magnetic field: a neuro-behavioral study. Revue de l’Électricité et de l’Électronique (REE) 5:44–55
Li X, Morita K, Robinson HPC, Small M (2011) Impact of gamma-oscillatory inhibition on the signal transmission of a cortical pyramidal neuron. Cogn Neurodyn 5:241–251
Lisanby SH, Luber B, Perera T, Sackeim HA (2000) Transcranial magnetic stimulation: applications in basic neuroscience and neuropsychopharmacology. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 3:259–273
Liu Y, Wang R, Zhang Z, Jiao X (2010) Analysis on stability of neural network with inhibitory neurons. Congn Neurodyn 4(1):61–68
Lytton WW, Sejnowski TJ (1991) Simulations of cortical pyramidal neurons synchronized by inhibitory interneurons. J Neurophysiol 66:1059–1079
Meunier D, Lambiotte R, Bullmore ET (2010) Modular and hierarchically modular organization of brain networks. Front Neurosci 4:200
Ozer M, Perc M, Uzuntarla M (2009) Stochastic resonance on Newman-Watts networks of Hodgkin-Huxley neurons with local periodic driving. Phys Lett A 373:964–968
Pashut T, Wolfus S, Friedman A, Lavidor M, Bar-Gad I, Yeshurun Y (2011) Mechanisms of magnetic stimulation of central nervous system neurons. PLoS Comput Biol 7(3):18
Pauly H, Schwan HP (1959) Uber die Impedanz einer suspension von kugelformigen Teilchen mit einer Schale. Z Naturforsch B 14:125–131
Perc M (2005) Spatial decoherence induced by small-world connectivity in excitable media. New J Phys 7:252
Perc M (2007) Stochastic resonance on excitable small-world networks via a pacemaker. Phys Rev E 76:6
Perc M (2008) Stochastic resonance on weakly paced scale-free networks. Phys Rev E 78:3
Perkel DH, Mulloney B, Budelli RW (1981) Quantitative methods for predicting neuronal behavior. Neuroscience 6:823–827
Pinault D, Deschênes M (1992) Voltage-dependent 40-Hz oscillations in rat reticular thalamic neurons in vivo. Neuroscience 51:245–258
Radman T, Ramos RL, Brumberg JC, Bikson M (2009) Role of cortical cell type and morphology in sub- and suprathreshold uniform electric field stimulation. Brain Stimulat 2(4):215–228
Reijneveld JC, Ponten SC, Berendse HW, Stam CJ (2007) The application of graph theoretical analysis to complex networks in the brain. Clin Neurophysiol 118:2317–2331
Rojas-Líbano D, Kay LM (2008) Olfactory system gamma oscillations: the physiological dissection of a cognitive neural system. Cogn Neurodyn 2(3):179–194
Scannell JW, Blakemore C, Young MP (1995) Analysis of connectivity in the cat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience 15(2):1463–1483
Schroeder CE, Lakatos P (2009) Low-frequency neuronal oscillations as instruments of sensory selection. Trends Neurosci 32:9–18
Schwan HP (1957) Electrical properties of tissue and cell suspensions. Adv Biol Med Phys 5:147–209
Sederberg PB, Schulze-Bonhage A, Madsen JR, Bromfield EB, McCarthy DC, Brandt A, Tully MS, Kahana MJ (2007) Hippocampal and neocortical gamma oscillations predict memory formation in humans. Cereb Cortex 17:1190–1196
Sporns O, Chialvo DR, Kaiser M, Hilgetag CC (2004) Organization, development and function of complex brain networks. Trends Cogn Sci 8:418–425
Stam CJ, Reijneveld JC (2007) Graph theoretical analysis of complex networks in the brain. Nonlinear Biomed Phys 1:3
Stam CJ, Jones BF, Nolte G, Breakspear M, Scheltens PH (2007) Small-world networks and functional connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. Cereb Cortex 17:92–99
Strogatz SH (2001) Exploring complex networks. Nature 410:268–276
Sun X, Perc M, Lu Q, Kurths J (2008) Spatial coherence resonance on diffusive and small-world networks of Hodgkin-Huxley neurons. Chaos 18:023102
Tallon-Baudry C (2009) The roles of gamma-band oscillatory synchrony in human visual cognition. Front Biosci 14:321–332
Terao Y, Ugawa Y (2002) Basic mechanisms of TMS. J Clin Neurophysiol 19:322–343
Traub RD, Whittington MA, Colling SB, Buzsáki G, Jeffreys JGR (1996a) Analysis of gamma rhythms in the rat hippocampus in vitro and in vivo. J Physiol 493:471–484
Traub RD, Whittington MA, Stanford IM, Jefferys JGR (1996b) A mechanism for generation of long-range synchronous fast oscillations in the cortex. Nature 383:621–624
Traub RD, Bibbig A, Fisahn A, LeBeau FEN, Whittington MA, Buhl EH (2000) A model of gamma-frequency network oscillations induced in the rat CA3 region by carbachol in vitro. Eur J Neurosci 12:4093–4106
Uhlhaas PJ, Singer W (2010) Abnormal neural oscillations and synchrony in schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci 11(2):100–113
Uhlhaas PJ, Linden DEJ, Singer W, Haenschel C, Lindner M, Maurer K, Rodriguez E (2006) Dysfunctional long-range coordination of neural activity during Gestalt perception in schizophrenia. J Neurosci 26:8168–8175
Van den Heuvel MP, Stam CJ, Boersma M, Hulshoff Pol HE (2008) Small-world and scale-free organization of voxel-based resting-state functional connectivity in the human brain. Neuroimage 43(3):528–539
van Vreeswijk C, Abbott LF, Ermentrout GB (1995) When inhibition, not excitation synchronizes neural firing. J Comput Neurosci 1:313–322
Ventriglia F (2008) The engram formation and the global oscillations of CA3. Cogn Neurodyn 2(4):335–345
Wang XJ, Buzsáki G (1996) Gamma oscillation by synaptic inhibition in a hippocampal interneuronal network model. J Neurosci 16:6402–6413
Wang X-J, Rinzel J (1993) Spindle rhythmicity in the reticularis thalami nucleus: synchronization among mutually inhibitory neurons. Neuroscience 53:899–904
Wang R, Zhang Z (2011) Phase synchronization motion and neural coding in dynamic transmission of neural information. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 22(7):1097–1106
Wang QY, Duan ZS, Perc M, Chen GR (2008a) Synchronization transitions on small-world neuronal networks: effects of information transmission delay and rewiring probability. EPL 83:50008
Wang R, Zhang Z, Chen G (2008b) Energy function and energy evolution on neural population. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 19(3):535–538
Wang QY, Perc M, Duan ZS, Chen G (2010a) Impact of delays and rewiring on the dynamics of small-world neuronal networks with two types of coupling. Phys A 389:3299–3306
Wang QY, Perc M, Duan ZS (2010b) Spatial coherence resonance in delayed Hodgkin-Huxley neuronal networks. Int J Mod Phys B 24(9):1201–1213
Wang QY, Chen G, Perc M (2011) Synchronous bursts on scale-free neuronal networks with attractive and repulsive coupling. PLoS ONE 6:e15851
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 393:440–442
Whittington MA, Traub RD, Jeffreys JGR (1995) Synchronized oscillations in interneuron networks driven by metabotropic glutamate receptor activation. Nature 373:612–615
Whittington MA, Jefferys JGR, Traub RD (1996) Effects of intravenous anaesthetic agents on fast inhibitory oscillations in the rat hippocampus in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 118:1977–1986
Wilson TW, Rojas DC, Reite ML, Teale PD, Rogers SJ (2007) Children and adolescents with autism exhibit reduced MEG steady-state gamma responses. Biol Psychiatry 62:192–197
Yener GG, Başar E (2010) Sensory evoked and event related oscillations in Alzheimer’s disease: a short review. Cogn Neurodyn 4(4):263–274
Zamora-López G, Zhou C, Kurths J (2010) Cortical hubs form a module for multisensory integration on top of the hierarchy of cortical networks. Front Neuroinform 4:1
Zhang X, Wang R, Zhang Z, Qu J, Cao J, Jiao X (2010) Dynamic phase synchronization characteristics of variable high-order coupled neuronal oscillator population. Neurocomputing 73:2665–2670
Zhou CS, Zemanova L, Zamora G, Hilgetag CC, Kurths J (2006) Hierarchical organization unveiled by functional connectivity in complex brain networks. Phys Rev Lett 97:238103
Ziemann U, Rothwell JC (2000) I-waves in motor cortex. J Clin Neurophysiol 17:397–405
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61072012), the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 60901035 and 50907044).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, K., Wang, J., Deng, B. et al. Synchronization of neuron population subject to steady DC electric field induced by magnetic stimulation. Cogn Neurodyn 7, 237–252 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-012-9233-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-012-9233-x