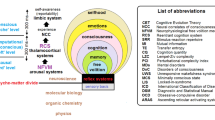
Abstract
This theoretical and speculative essay addresses a categorical distinction between neural events of sensory-motor cognition and those presumably associated with consciousness. It proposes to view this distinction in the framework of the branch of Statistical Physics currently referred to as Modern Critical Theory (Stanley, Introduction to phase transitions and critical phenomena, 1987; Marro and Dickman, Nonequilibrium phase transitions in lattice, 1999). Based on established landmarks of brain dynamics, network configurations and their role for conveying oscillatory activity of certain frequencies bands, the question is examined: what kind of state space transitions can systems with these properties undergo, and could the relation between neural processes of sensory-motor cognition and those of events in consciousness be of the same category as is characterized by state transitions in non-equilibrium physical systems? Approaches for empirical validation of this view by suitably designed brain imaging studies, and for computational simulations of the proposed principle are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acebron JA, Bonilla LL, Perez Vincente CJ, Ritort F, Spigler R (2005) The Kuramoto Model: simple paradigm for synchronization phenomena. Rev Mod Phys 77:137–185
Achard S, Salvador R, Whitcher B, Suckling J, Bullmore E (2006) A resilient, low frequency, small-world human brain functional networks with highly connected association cortical hubs. J Neurosci 26:63–72
Albert R, Barabasi AL (2002) Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev Mod Phys 74:47–97
Amaral LAN, Scala A, Barthelemy M, Stanley HE (2000) Classes of small world networks. Proc Natl Acad USA 97:11149–11152
Atkinson AP, Thomas MSC, Cleeremans A (2000) Consciousness: mapping the theoretical landscape. Trends Cogn Sci 4:372–382
Atmanspacher H, Kronz F (1999) Many realisms. In: Scott JC (ed) Modeling consciousness across the disciplines. University of America Press, New York, pp 281–306
Baars BJ (1988) A cognitive theory of consciousness. Cambridge University Press, New York
Baars BJ (1997) In the theater of consciousness. Oxford University Press, New York
Baars BJ (2002) The conscious access hypothesis. Trends Cogn Sci 6:47–52
Baars BJ, Ramsoy TZ, Laureys S (2003) Brain, conscious experience and the observing self. TINS 26:671–675
Baliki MN, Geha PY, Apkarian AV, Chialvo DR (2008) Beyond feeling: chronic pain hurts the brain, disrupting the default-mode network dynamics. J Neurosci 28:1398–1403
Barahona M, Pecora LM (2001) Synchronization in small-world systems. Phys Rev Lett 89:054101
Bassett DS, Bullmore ET (2006) Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist 12:512–523
Bassett DS, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Achard S, Dule T, Bullmore E (2006) Adaptive reconfiguration of fractal small-world human brain functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:19518–19523
Batterman RW (2002) The devil in the details. Oxford University Press
Bedeau M (2002) Downward causation and the autonomy of weak emergence. Principia 6(1):5–50
Beggs JM, Plenz D (2003) Neuronal avalanches in neocortical circuits. J Neurosci 23:11167–11177
Beggs JM, Plenz D (2004) Neuronal avalanches are diverse and precise activity patterns that scale for many hours in cortical tissue slice cultures. J Neurosci 24:5216–5229
Bibbig A, Traub RD, Miles A, Whittington MA (2002) Long-range synchronization of gamma and beta oscillations and the plasticity of excitatory and inhibitory synapses: a network model. J Neurophysiol 88:1634–1654
Bienenstock EA (1995) A model of neocortex. Network Comput Neural Syst 6:179–224
Bollobas B (1985) Random graphs. Academic Press, London
Braeutigam S, Stins JF, Rose SPR, Swithenby SJ, Ambler T (2001) Magneto-encephalographic signals identify stages in real-life decision processes. Neural Plast 8:241–252
Braeutigam S, Rose SPR, Swithenby SJ, Ambler T (2004) The distributed neural systems supporting choice-making in real-life sitiations: differences between men and women when choosing groceries detected using magneto-encephalography. Eur J Neurosci 1–10
Breakspear M, Williams LM, Stam CJ (2004) A novel method for the topographic analysis of neural activity reveals formation and dissolution of ‘dynamic cell assemblies’. J Comput Neurosci 16:49–68
Breitmeyer BG, Ogmen H (1984/2006) Visual masking: time slices through consciousness and unconscious vision. Oxford University Press, UK
Bressler SL, Kelso JAS (2001) Cortical coordination dynamics and cognition. Trends Cogn Sci 5:26–36
Breskin I, Soriano J, Moses E, Tlustry T (2006) Percolation in living neural Networks. Phys Rev Lett 97:188102
Brovellli A, Ding M, Ledberg A,Chen Y, Nakamura R, Bressler SL (2004) Beta oscillations in a large scale sensorimotor cortical network: directional Influences revealed by Granger causality. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9849–9854
Bullmore E, Fadili J, Maxim V, Sendur L, Whitcher B, Suckling J, Brammer M, Breakspear M (2004) Wavelets and functional magnetic resonance imaging of the human brain. NeuroImage 23:S234–S249
Buschman TJ, Miller EK (2007) Top-own versus bottom-up control of attention in the prefrontal and posterior parietal cortices. Science 315:1860–1862
Buzsaki G (2006) Rhythms of the brain. Oxford University Press
Changeux J-P, Michel CM (2006) Mechanisms of neural integration at the brain-scale level. In: Grillner S, Graybiel AM (eds) Microcircuits—the interface between neurons and global brain function. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 347–370
Chialvo DR (2006) The brain near the edge. 9th Granada seminar on computational physics, Granada, Spain
Chialvo DR, Balenzuela P, Fraiman D (2008) The brain: what is it critical about? Proceedings of the American Institute of Physics in print
Chiel HJ, Beer RD (1997) The brain has a body: adaptive behavior emerges from interaction of nervous system, body and environment. TINS 20:553–557
Churchland PM (1989) A neurcomputational perspective. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Churchland PM (2006) Inner space and outer spaces: the new epistemology. In: Hetherington SS (ed) Epistemology futures. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 48–70
Craig AD (2002) How do you feel? Interoception: the sense of the physiological condition of the body. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:655–666
Damasio AR (1994) Descarts error: emotions, reason and the human brain. Grosset/Putnam, New York
Damasio AR (1999) The feeling of what happens: body and emotion in the making of consciousness. Harcourt, New York
Damasio AR (2001) Fundamental feelings. Nature 413:781
Damasio AR (2003) Looking for Spinoza: joy, sorrow and the feeling brain. Harcourt, New York
Damasio AR, Grabowski TJ, Bechara A, Damasio H, Ponto LBJ, Parvizi J, Hichwa RD (2000) Subcortical and cortical brain activity during the feeling of self-generated emotions. Nat Neurosci 3:1049–1056
Dehaene S, Changeux J-P (1989) A simple model of prefrontal cortex in delayed response tasks. J Cogn Neurosci 1:244–261
Dehaene S, Changeux J-P (1991) The Wisconsin card sorting test: theoretical analysis and simulation of a reasoning task in a model neuronal network. Cereb Cortex 1:62–79
Dehaene S, Changeux J-P (1997) A hierarchical neuronal network for planning behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:13293–13298
Dehaene S, Nagacche l (2002) Towards a cognitive neuroscience of consciousness: basic evidence and a workspace framework. Cognition 79:1–37
Dehaene S, Chageux J-P, Naccache L, Sackur J, Sergent C (2006) Conscious, preconscious and subliminal processing: a testable taxonomy. Trends Cogn Sci 10:204–211
Dehaene S, Sregent T, Changeux J-P (2003) A neuronal network model linking subjective reports and objective physiological data during conscious perception. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8520–8525
Del Cul A, Baillet S, Dehaene S (2007) Brain dynamics underlying the nonlinear threshold for access to consciousness. PLoS Biol 5:e260
Dickman R, Vespignani A, Zapperi S (1998) Self-organized criticality as an absorbing state phase transition. Phys Rev E 57:5095–5105
Dorogovtsev SN, Mendes JFF (2003) Evolution of networks. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Dorogovtesev SN, Mendes JFF, Samukhin AN (2000) Structure of growing networks with preferential linking. Phys Rev Lett 85:4633–4636
Dosenbach NUF, Visscher KM, Palmer E, Miezin FM, Wenger KK, Kang HC, Burgund ED, Grimes AL, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE (2006) A core system for the implementation of task sets. Neuron 50:799–812
Dosenbach NUF, Fair DA, Miezin FM, Cohen AL, Wenger KK, Dosenbach RAT, Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Raichle ME, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE (2007) Distinct brain networks for adaptive and stable task controls in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11073–11078
Edelman GM (2003) Naturalizing consciousness: a theoretical framework. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5520–5524
Eguiluz VM, Chialvo DR, Cecchi GA, Baliki M, Apkarian AV (2005) Scale-free brain functional networks. Phys Rev Lett 94:018102-1
Fair DA, Dosenbach NUF, Church JA, Cohen AL, Brahmbhatt S, Miezin FM, Barch DM, Raichle ME, Petersen SE, Schlaggar BL (2007) Development of distinct control networks through segregation and integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13507–13512
Fell J (2004) Identifying neural correlates of consciousness: the state space approach. Conscious Cogn 13:709–729
Fingelkurts AnA, Fingelkurts AlA (2001) Operational architectonics of the human brain biopotential field: towards solving the mind-brain problem. Brain Mind 2(3):261–296
Fingelkurts AnA, Fingelkurts AlA (2005) Mapping of the brain operational archi-textonics. In Chen FJ (ed) Focus on brain mapping research. Nova Science Pub., Inc.
Fingelkurts AnA, Fingelkurts AlA (2006) Timing in cognition and EEG brain dynamics: discreteness vs. continuity. Cogn Process 7:135–162
Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Corbetta M, Van Essen D, Raichle ME (2005) The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional Networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9673–9678
Fox MD, Corbetta M, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Reichle ME (2006) Spontaneous neural activity distinguishes human dorsal and ventral attention systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:10046–10051
Franovic I, Miljkovic V (2007) Fractal properties of percolation clusters in Euclidean neural networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals. doi:10.1016/j.chaos.2007.06.026
Freeman WJ (1975) Mass action in the nervous system. Academic Press, New York
Freeman WJ (2004a) Origin, structure and role of background EEG activity: Part 1. Analytic amplitude. Clin Neurophysiol 115:2077–2088
Freeman WJ (2004b) Origin, structure and role of background EEG activity: Part 2. Analytic phase. Clin Neurophysiol 115:2089–2107
Freeman WJ (2005a) Origin, structure and role of background EEG activity: Part 3. Clin Neurophysiol 116:1118–1129
Freeman WJ, Holmes MD (2005b) Metastability, instability and state transitions in neocortex. Neural Netw 18:497–504
Freeman WJ, Holmes MD, West GA, Vanhatalo S (2006) Dynamics of human neocortex that optimizes its stability and flexibility. Int J Intell Syst 21:881–901
Fries P (2005) A mechanism for cognitive dynamics: neuronal communication through neural coherence. Trends Cogn Sci 9:474–480
Friston KJ (2000) The labile brain I. Neuronal transients and nonlinear coupling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 355:215–236
Gade PM, Sinha S (2006) How crucial is small world connectivity for dynamics? Int J Bifurcat Chaos 16:2767–2775
Ganis G, Thompson WL, Kosslyn SM (2004) Brain areas underlying visual mental imagery and visual perception. Cogn Brain Res 20:226–241
Gervasoni D, Lin SH, Ribeirao S, Soares ES, Pantoja J, Nicolelis MAL (2004) Global forebrain dynamics predict rat behavioral states and their transitions. J Neurosci 24:11137–1147
Gewaltig MO, Diesman M, Aertsen A (2001) Propagation of cortical synfire activity: survival probability in single trials and stability in the mean. Neural Netw 14:657–673
Giunti M (1997) Computation, dynamics and cognition. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Gladwell M (2000) The Tipping Point: how little things can make a big difference. Little Brown, Boston
Goldenfeld N, Martin O, Ooono Y (1989) Intermediate asymptotics and renormalization group theory. J Scientific Comput 4:355–372
Gong P, Nikolaev AR, van Leeuwen C (2003) Scale invariant fluctuations of the dynamical synchronization in human brain electrical activity. Neurosci Lett 336:33–36
Grinstein G, Linsker R (2005) Synchronous neural activity in scale free network models versus random network models. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:9948–9953
Gusnard DA, Raichle ME (2001) Searching for a baseline: functional imaging and the resting human brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:685–694
Haldeman C, Beggs JM (2005) Critical branching captures activity in living neural networks and maximizes the number of metastable states. Phys Rev Lett 94:058101
Hilgetag CC, O’Neill MA, Young MP (2000) Hierarchical organization of macaque and cat cortical sensory systems explored with a novel network processor. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 355:71–89
Hilgetag CC, Koetter R, Stephan KE, Sporns O (2002) Computational methods for the analysis of brain connectivity. In: Ascoli GA (ed) Computational neuroanatomy. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Hinrichsen H (2006) Non-equilibrium phase transitions. Physica A 369:1–28
Hobson JA, Pace-Schott EF, Stickgold R (2000) Dreaming and the brain: toward a cognitive neuroscience of conscious states. Behav Brain Sci 23:793–1121
Hohenberg PC, Halperin BI (1977) Theory of dynamical critical phenomena. Rev Mod Phys 49:435–479
Honey CJ, Koetter R, Breakspear M, Sporns O (2007) Network structure of cerebral cortex shapes functional connectivity on multiple time scales. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:10240–10245
Humphries MD, Gurney K, Precott TJ (2006) The brain stem reticular formation is a small-world, not scale-free network. Proc R Soc B 273:503–511
Jirsa VK (2004) Connectivity and dynamics of Neural Information processing. Neuroinformatics 2:1–22
John ER (2002) The neurophysics of consciousness. Brain Res Rev 39:1–28
Just W, Schmueser F (2005) On phase transitions in coupled map lattices. Lect Notes Phys 671:33–61
Kelso JAS, Engstrom DA (2006) The complementary nature. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Kelso K, Bressler SL, DeGuzman GC, Ding M, Fuchs A, Holroyd T (1992) A phase transition in human brain and behavior. Phys Lett A 169:134–144
Kim J (1999) Making sense of emergence. Philos Perspect 11:185–207
Koenig T, Prichep L, Lehmann DL, Sosa PV, Braeker E, Kleinlogel H, Isenhart R, John ER (2002) Millisecond by millisecond, year by year: normative EEG microstates and developmental stages. NeuroImage 16:41–48
Koenig T, Studer D, Hubl D, Melie L, Strik WK (2005) Brain connectivity at different time scales measured with EEG. Philos Trans R Soc B 360:1015–1023
Koetter R (2001) Neuroscience databases: tools for exploring brain structure function relationships. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Biol Sci 356:1111–1120
Kosslyn SM, Ganis G, Thompson WL (2001) Neutral foundations of imagery. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:635–642
Kossly SM, Thompson WL, Alpert NM (1997) Neural systems aherd by visual imagery and visual perception: a positron emission tomography study. NeuroImage 6:320–334
Kozma R, Puljic M, Balister P, Bollobas B, Freeman WJ (2004) Neuropercolation: a random cellular automata approach to spatio-temporal neurodynamics. Lect Notes Comput Sci 3305:435–443
Kozma R, Puljic M, Balister P, Bollobas B, Freeman WJ (2005) Phase transitions in the neuropercolation model of neural populations with mixed local and non-local interactions. Biol Cybern 92:367–379
Kuznetsov SP (1992) Universality and scaling in two-dimensional coupled map lattices. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2:281–301
Lachaux J-P, Rodriguez E, Martineri J, Varela FJ (1999) Measuring phase synchrony in brain signals. Hum Brain Mapp 8:194–208
Lago-Fernandez LF, Huerta R, Corbacho F, Siguenza JA (2000) Fast response and temporal coherent oscillations in small-world networks. Phys Rev Lett 84:2758–2761
Lakatos I (1978) The methodology of scientific research programs. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Lamme VAF (2003) Why visual attention and awareness are different. Trends Cogn Sci 7:12–18
Lamme VAF (2006a) Zap! Magnetic tricks on conscious and unconscious vision. Trends Cogn Sci 10:193–195
Lamme VAF (2006b) Towards a true neural stance on consciousness. N Cogn Sci 10:494–501
Lamme VAF, Roelfsema PR (2000) The distinct modes of vision offered by feedforward and recurrent processing. TINS 23:571–579
Latora V, Marchiori M (2001) Efficint behavior of small-world networks. Phys Rev Lett 87:198701-1-4
Laughlin RB (2005) A different universe: reinventing physics from the bottom down. Basic Books, New York
Lehmann D, Strik WK, Henggeler B, Koenig T, Koukkou M (1998) Brain electric microstates as building blocks of spontaneous thinking. Int J Psychophysiol 29:1–11
Lehmann D, Faber PL, Gianotti LRR, Kochi K, Pascual-Marqui RD (2006) Coherence and phase locking in the scalp EEG and between LORETTA model sources, and microstates as putative mechanisms o brain temporo-spatial functional organization. J Physiol Paris 99:29–36
Le VanQuyen M (2003) Disentangling the dynamic core: a research program for a neurodynamics at the large scale. Biol Res 36:67–88
Linkenkaer-Hansen K, Nikouline VV, Palva JM, Ilmoniemi RJ (2001) Long-range temporal correlations and scaling behavior in human brain oscilations. J Neurosci 21:1370–1377
Luebeck S (2004) Universal scaling behavior of non-equilibrium phase transtitions. Int J Mod Phys B 18:3977
Marcq P, Chate H, Manneville P (1996) Universal critical behavior in two-dimensional coupled map lattices. Phys Rev Lett 77:4003–4006
Marro J, Dickman R (1999) Nonequilibrium phase transitions in lattice models. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Mason MF, Norton MI, van Horn JD, Wegner DM, Grafton ST, Macrae CN (2007) Wandering Minds: the default network and stimulus-independent thought. Science 315:393–395
Masuda N, Aihara K (2004) Global and local synchrony of coupled neurons in small-world networks. Biol Cybern 90:302–309
Maye M (2003) Correlated neural activity can represent multiple bonding solutions. Neurocomputing 52–54:73–77
Maye A, Werning M (2004) Temporal binding of non-uniform objects. Neurocomputing 58–60:941–948
Mechelli A, Price CJ, Friston KJ, Ishai A (2004) Where Bottom-up Meets Top-down: neuronal interactions during Perception and Imagery. Cereb Cortex 14:1256–1265
Mesulam MM (1998) From sensation to cognition. Brain 121:1013–1052
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Zieman U, Hajak G, Cohen L, Berman KF (2002) Transitions between dynamical states of differing stability in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:10948–10953
Michel CM, Henggeler B, Lehmann D (1992) 42-channel potential map series to visual contrast and stereo stimuli: perceptual and cognitive event related segments. Int J Psychophysiol 12:133–145
Mikhailov AAS, Calenbuur V (2006) From cells to societies. Springer, New York
Milo R, Shen-Orr S, Itzkovitz S, Kashtan N, Chlovskii D, Alon U (2002) Network motifs: simple building blocks of complex networks. Science 298:824–827
Mirollo RE, Strogatz SH (1990) Synchronization of pulse coupled oscillators. SIAM J Appl Math 50:1645–1662
Moore C, Newman MEJ (2000) Epidemics and percolation in small world networks. Phys Rev E 61:5678–5682
Newman MEJ (2000) Models of the small world. arXiv:cond-mat/0001118v2
Newman MEJ (2003) The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Rev 45:167–256
Newman MEJ, Watts DJ (1999) Scaling and percolation in small-world networks. Phys Rev E 60:7332–7342
Newman MEJ, Jensen J, Ziff RM (2002) Percolation and epidemics in a two-dimensional small-world. Phys Rev E 65:21904-1
Odor G (2004) Universality classes in nonequilibrium lattice systems. Rev Mod Phys 76:663–724
Pascual-Leone A., Wals V (2001) Fast backprojections from the motion to the primary visual area necessary for visual awareness. Science 292:510–512
Percha B, Dzakpasu R, Zochowski M, Parent J (2005) Transition from local to global phase synchrony in small world neural networks and its possible implication for epilepsy. Phys Rev E 72:031909
Pikovsky A, Rosenblum M, Kurths J (2001) Synchronization. Cambridge University Press
Plenz D, Thiagarajan TC (2007) The organizing principle of neuronal avalanches: cell assemblies in the cortex. Trends Neurosci 30:101–110
Port RF, van Gelder T (1995) Mind as motion: explorations in the dynamics of cognition. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Primas H (1998) Emergence in exact natural sciences. http://philsci-archive.pitt.edu/archive/00000953.pdf
Rodriguez E, George N, Lachaux J-P, Martineri J, Renaults B, Varela FJ (1999) Perception’s shoadow: long-distance synchronization of human brain activity. Nature 397:430–433
Rolf J, Bohr T, Jensen MH (1998) Directed percolation universality in asynchronous evolution of spontaneous intermittency. Phys Rev E 57:R2503-57
Rudrauf D, Damasio A (2006) The biological basis of subjectivity: a hypothesis. In: Kriegel U, Williford K (eds) Self-representational approaches to consciousness. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 423–464
Saalman YB, Pigarev IN, Vidyasagar TR (2007) Neural mechanisms of visual attention: how top-down feedback highlights relevant locations. Science 316:1612–1615
Salinas E, Sejnowski TJ (2001) Correlated neural activity and the flow of neural Information. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:539–550
Salvador R, Suckling J, Coleman MR, Pickard JD, Menon D, Bullmore E (2005a) Neurophysiological architecture of functional magnetic resonance images of human brain. Cereb Cortex 15:1332–1342
Salvador R, Suckling J, Schwarzbauer C, Bullmore E (2005b) Undirected graphs of frequency-dependent functional connectivity in whole brain networks. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 360:937–946
Schnitzler A, Gross J (2005) Normal and pathological oscillatory communication in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:285–296
Schreiber T (2000) Measuring information transfer. Phys Rev Lett 85:461–464
Schulman LS, Gaveau B (2001) Coarse grains: the emergence of space and order. Found Phys 31:713–731
Searl JR (2000) Consciousness. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:557–578
Sergent C, Dehaene S (2004) Is consciousness a graded phenomenon? Psychol Sci 15:720–728
Seth AK, Edelman GM (2004) Environment and behavior influence the complexity of evolved neural networks. Adapt Behav 12:5–20
Seth AK, Izhikevich E, Reeke GN, Edelman GM (2006) Theories and measures on consciousness: an extended framework. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:10799–10804
Sokal A, Bricmont J (2004) Defense of a modest scientific realism. In: Carrier M, Roggenhofer J, Kueppers G, Banchard Ph (eds) Knowledge and the world: beyond the science wars. Springer, New York
Sporns O (2006) Small-world connectivity, motif composition and complexity of fractal neural connections. BioSystems 85:55–64
Sporns O, Koetter R (2004) Motifs in brain networks. PLoS Biol 2:3369
Sporns O, Zwi JD (2004) The small world of the cerebral cortex. Neuroinformatics 2:145–162
Sporns O, Gally JA, Reeke GN, Edelman GM (1989) Reentrant signaling among simulated neuronal groups leads to coherency in their oscillatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7265–7269
Sporns O, Tononi G, Edelman GM (2000) Theoretical neuroanatomy: relating anatomical and functional connectivity in graphs and cortical connection matrices. Cereb Cortex 10:127–140
Sporns O, Chialvo DR, Kaiser M, Hilgetag CC (2004) Organization, development and function of complex brain networks. Trends Cogn Sci 8:418–425
Stam CJ (2004) Functional connectivity patterns of human magnetoencephalographic recordings: a ‘small-world’ network? Neurosci Lett 355:25–28
Stam CJ, de Bruin EA (2004) Scale-free dynamics of global functional connectivity in the human brain. Hum Brain Mapp 22:97–109
Stanley HE (1987) Introduction to phase transitions and critical phenomena. Oxford University Press, UK
Stanley HE (1999) Scaling, universality and renormalization: the three pillars of modern critical phenomena. Rev Mod Phys 71:S358–S366
Stauffer D, Aharony A (1991/1994) Introduction to percolation theory. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Strogatz SH (2001) Exploring complex networks. Nature 410:268–276
Super H, Spekreijse H, Lamme VAF (2001) Two distinct modes of sensory processing observed in monkey primary visual cortex (V1). Nat Neurosci 4:304–310
Tass P, Haken H (1996) Synchronization in networks of limit cycle oscillators. Z Phys B 100:303–320
Thompson E (2007) Mind in life. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Thompson E, Varela FJ (2001) Radical embodiment: neural dynamics and consciousness. Trends Cogn Sci 5:418–425
Tononi G, Edelman GM (1998) Consciousness and complexity. Science 282:1846–1851
Tononi G, Sporns O, Edelman GM (1994) A measure for brain complexity: relating functional segregation and integration in the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5033–5037
Van Gelder T (1998) The dynamical hypothesis in cogitive science. Behav Brain Sci 21:615–628
Varela FJ (1995) Resonant cell assemblies: a new approach to cognitive functions and neuronal synchrony. Biol Res 28:81–95
Varela FJ, Lachaux JP, Rodriguez E, Martineri J (2001) The Brainweb: phase synchronization and large-scale integration. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:229–239
Von der Malsburg C (1981/82, 1994) The correlation theory of brain function. In: Domany E (ed) Models of the nervous systems, vol. 2
Von der Malsburg C (1999) The what and the why of binding: the modeler’s perspective. Neuron 24:95–104
Wackermann J (1999) Towards a quantitative characterization of functional states of the brain: from non-linear methodology to the global linear description. Int J Psychophysiol 34:65–80
Wang XF, Chen G (2002) Synchronization in small-world dynamical networks. Int J Bifurcat Chaos 12:187–192
Wallenstein GV, Kelso JAS, Bressler l (1995) Phase transitions in spatiotemporal patterns of brain activity and behavior. Physica D 84:626–634
Watts DJ (1999) Small worlds. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ
Watts DJ, Strogatz SH (1998) Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 393:440–442
Weiskrantz L (1986) Blindsight: case study and implications. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Werner G (2007a) Brain dynamics across levels of organization. J Physiol Paris 101:273–279
Werner G (2007b) Perspectives of the neuroscience of cognition and consciousness. BioSystems 87:82–95
Werning M, Maye M (2006) Frames, coherency chains and hierarchical binding: the cortical implementation of concepts. http://www.psych.unito.it/csc/cogsci05/frame/poster/3/f794-werning.pdf
Wilson KG (1979) Problems in physics with many scales of length. Sci Am 241:140–157
Womelsdorf T, Schoffelen J-M, Oostenveld R, Singer W, Desimone R, Engel AK, Fries P (2007) Modulation of neuronal interactions through neuronal synchronization. Science 316:1609–1612
Yeomans JM (1992/2002) Statistical mechanics of phase transitions. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Zemanova L, Zhou C, Kurths J (2006) Structural and functional clusters of complex brain networks. Physica D 224:202–212
Zhou C, Zemanova L, Zamora G, Hilgetag CC, Kurths J (2006) Hierarchical organization unveiled by functional connectivity in complex brain networks. Phys Rev Lett 97:238103
Zhou C, Zemanova L, Zamora-Lopez G, Hilgetag CC, Kurths J (2007) Structure-function relationship in complex brain networks expressed by hierarchical synchronization. New J Phys 9:178–199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Werner, G. Consciousness related neural events viewed as brain state space transitions. Cogn Neurodyn 3, 83–95 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-008-9040-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-008-9040-6