Abstract
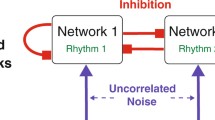
We show that chaos and oscillations in a higher-order binary neural network can be tuned effectively using interactions between neural networks. Our results suggest that network interactions may be useful as a means of adjusting the level of dynamic activities in systems that employ chaos and oscillations for information processing, or as a means of suppressing oscillatory behaviors in systems that require stability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babloyantz A, Lourenco C (1994) Computation with chaos: a paradigm for cortical activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9027–9031
Bruce Teter, J. Wesson Ashford (2002) Neuroplasticity in Alzheimers disease. J Neurosci Res 70:402–437
Chen L, Aihara K (1995). Chaotic simulated annealing by a neural network model with transient chaos. Neural Networks 8(6):915–930
Churchland PS, Sejnowski TJ (1989) The Computational Brain. MIT Press, Cambridge MA
Dan Qiao, Frederic J. Seidler, Charlotte A. Tate, Mandy M. Cousins, Theodore A. Slotkin (2003) Fetal chlorpyrifos exposure: Adverse effects on brain cell development and cholinergic biomarkers emerge postnatally and continue into adolescence and adulthood. Environ Health Persp 111(4):536–544
Derrida B, Gardner E, Zippelius A (1987) An exactly solvable asymmetric neural network model. Europhys Lett 4(2):167–173
Haixiang Shi, Lipo Wang (2005) Broadcast scheduling in wireless multihop networks using a neural-network-based hybrid algorithm. Neural Networks 18:765–771
Hopfield JJ (1982) Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:2554–2558
Joshua T. Trachtenberg, Wesley J. Thompson (1997) Nerve terminal withdrawal from rat neuromuscular junctions induced by neuregulin and schwann cells. J Neurosci 17(16):6243–6255
Lipo Wang and Haixiang Shi, “A gradual noisy chaotic neural network for solving the broadcast scheduling problem in packet radio networks,” IEEE Trans Neural Networ, accepted, 2006
Nozawa H (1992) A neural network model as a globally coupled map and applications based on chaos. Chaos 2(3):377–86
Russell Blaylock (2003) Interaction of cytokines, excitotoxins, and reactive nitrogen and oxygen species in autism spectrum disorders. J Am Nutraceutical Assoc 6(4):21–35
Tsai J, Grutzendler J, Duff K, Gan WB (2004) Fibrillar amyloid deposition leads to local synaptic abnormalities and breakage of neuronal branches. Nat Neurosci 7:1181–1183
Wang LP (1996) Oscillatory and chaotic dynamics in neural networks under varying operating conditions. IEEE Trans Neural Networ 7(6):1382–1388
Wang LP (1996) Suppressing chaos with hysteresis in a higher order neural network. IEEE Trans Circuit and Syst-II 43(12):845–846
Wang LP, Kate Smith (1998) On chaotic simulated annealing. IEEE Trans Neural Networ 9(4):716–718
Wang LP, Pichler EE, Ross J (1990) Oscillations and chaos in neural networks: an exactly solvable model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9467–9471
Wang LP, Ross J (1990) Interactions of neural networks: models for distraction and concentration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:7110–7114
Wang LP, Sa Li, Fuyu Tian, Fu XJ (2004) A noisy chaotic neural network for solving combinatorial optimization problems: Stochastic chaotic simulated annealing. IEEE Trans System, Man, Cybern, Part B - Cybernetics 34(5):2119–2125
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful for the helpful review comments that have helped to improve the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
URL: http:// www.ntu.edu.sg/home/elpwang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L. Interactions between neural networks: a mechanism for tuning chaos and oscillations. Cogn Neurodyn 1, 185–188 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-006-9004-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-006-9004-7