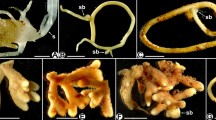
Abstract
Aproximately 5,000–6,000 fungal species form ectomyorrhizae (ECM), the symbiotic organs with roots of predominantly trees. The contributing fungi are not evenly distributed over the system of fungi. Within Basidiomycota exclusively Hymenomycetes and within Ascomycota exclusively Ascomycetes contribute to the symbiosis. Hymenomycetes play a big part, Ascomycetes a minor role; Zygomycetes only form exceptionally ECM. Responsible for ascomycetous ECM are mostly Pezizales with their hypogeous derivatives, whereas Boletales, Gomphales, Thelephorales, Amanitaceae, Cantharellaceae, Cortinariaceae, Russulaceae, and Tricholomataceae are the most important ectomycorrhizal relationships within Hymenomycetes. ECM, as transmitting organs between soil and roots, are transporting carbohydrates for growth of mycelium and fruitbodies from roots and have to satisfy the tree’s demand for water and nutrients. The latter task particularly influences the structure of ECM as nutrients are patchily distributed in the soil and saprotrophic as well as ectomycorrhizal fungi can act as strong competitors for nutrients. In focusing these requirements, ECM developed variously structured hyphal sheaths around the roots, the so-called mantles, and differently organized mycelium that emanates from the mantle, the so-called extramatrical mycelium. The mantles can be plectenchymatous consisting of loosely woven, differently arranged hyphae or they are densely packed, forming a pseudoparenchyma similar to the epidermis of leaves. The extramatrical mycelium grows either as simple scattered hyphae from the mantle into the soil or it can be united to undifferentiated rhizomorphs with a small reach or to highly organized root-like organs with vessel-like hyphae for efficient water and nutrient transport from distances of decimeters. Cystidia, sterile and variously shaped hyphal ends, possibly appropriate for preventing animal attack, in addition, can cover mantles and rhizomorphs. Although only a limited number of species could be considered, some general conclusions are possible.
The genus Tuber forms needle-shaped cystidia and lacks rhizomorphs and clamps. Gomphales ECM are identified by rhizomorphs with ampullate inflations at septa of some hyphae and by oleoacanthocystidia or/and oleoacanthohyphae. Thelephoraceae reveal a great diversity of mantle structures and of extramatrical mycelium, with some additional optional characters, i.e., dark brown color, cystidia, blue granules, amyloid hyphae, or amyloid septa. Bankeraceae are mostly characterized by plectenchymatous mantles with star-like pattern and chlamydospores. Russulaceae possess smooth and hydrophilic ECM. Russula forms plectenchymatous mantles with knob-bearing cystidia, so-called russuloid cystidia, or pseudoparenchymatous mantles without cystidia. Lactarius lacks cystidia and shows laticifers within plectenchymatous or within pseudoparenchymatous mantles. The Boletales families Boletaceae, Gyroporaceae, Melanogastraceae, Paxillaceae, Rhizopogonaceae, Sclerodermataceae, and Suillaceae have the most advanced rhizomorph type, the so-called boletoid rhizomorphs, and reveal generally plectenchymatous mantles, frequently with ring-like patterns. Gomphidiaceae and Albatrellaceae provide cystidia, plectenchymatous mantles, and amyloidy; Gomphidiaceae are generally growing in ECM of Suillaceae and Rhizopogonaceae. Cortinariaceae reveal plectenchymatous mantles and undifferentiated or differentiated rhizomorphs or lack rhizomorphs at all. Cortinarius and Dermocybe are distinct by irregularly shaped, bent to tortuous ECM with many rhizomorphs, some growing over the mycorrhizal tip into the soil. Inocybe lacks rhizomorphs and its emanating hyphae are furnished by many secondary septa and prominent clamps with a hole. Rozites lacks rhizomorphs, too, and reveals a distinctly amyloid gelatinous mantle matrix. Descolea and Descomyces are covered by bolbitioid cystidia. Lastly, the genus Tricholoma forms plectenchymatous mantles and a high diversity of rhizomorphs.
Some of the ectomycorrhizal features are used to hypothesize relationships at different taxonomic levels. These conclusions are compared with recently developed molecular hypotheses. Correspondence between the two types of hypotheses are evident, while some conflicts wait for a settlement.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agerer R (1986a) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. II. Introducing remarks on characterization and identification. Mycotaxon 26:473–492
Agerer R (1986b) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. III. Mycorrhizae formed by four fungi in the genera Lactarius and Russula on spruce. Mycotaxon 27:1–59
Agerer R (1987a) Russula ochroleuca. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 1. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1987b) Russula xerampelina. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 2. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1987c) Lactarius deterrimus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 3. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1987d) Lactarius picinus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour Atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 4. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1987e) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. X. Mycorrhizae formed by Cortinarius obtusus and Cortinarius venetus on spruce. Mycologia 79:524–539
Agerer R (1987f) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. V. Mycorrhizae formed by Dermocybe cinnamomea and D. sanguinea on spruce. Nova Hedwig 44:69–89
Agerer R (1987g) Dermocybe sanguinea. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 8. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1987h) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. IX. Mycorrhizae formed by Tricholoma sulfureum and Tricholoma vaccinum on spruce. Mycotaxon 28(2):327–360
Agerer R (1987i) Tricholoma sulphureum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 9. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1987k) Tricholoma vaccinum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 10. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1987–2006) Colour atlas of ectomycorrhizae: 1st–13th delivery. Einhorn-Verlag, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1988a) Studies on ectomycorrhizae XVII. The ontogeny of the ectomycorrhizal rhizomorphs of Paxillus involutus and Thelephora terrestris. Nova Hedwig 47:311–334
Agerer R (1988b) Studies on ectomycorrhizae XIV. Mycorrhizae formed by Cortinarius hercynicus and C. variecolor on Picea abies. Can J Bot 66:2068–2078
Agerer R (1988c) Cortinarius venetus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 13. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1989) Cortinarius variecolor. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 24. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1990a) Studies on ectomycorrhizae XXIV. Ectomycorrhizae of Chroogomphus helveticus and C. rutilus (Gomphidiaceae, Basidiomycetes) and their relationship to those of Suillus and Rhizopogon. Nova Hedwig 50:1–63
Agerer R (1990b) Chroogomphus helveticus ssp. tatrensis. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 37. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1990c) Cortinarius hercynicus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 38. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1991a) Characterization of ectomycorrhiza. In: Norris JR, Read DA, Varma AK (eds) Techniques for the study of mycorrhiza. Methods Microbiol 23:25–73
Agerer R (1991b) Ectomycorrhizae of Sarcodon imbricatus on Norway spruce and their chlamydospores. Mycorrhiza 1:21–30
Agerer R (1991c) Sarcodon imbricatus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 66. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1991d) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. XXXIV. Mycorrhizae of Gomphidius glutinosus and of G. roseus with some remarks on Gomphidiacee (Basidiomycetes). Nova Hedwig 53:127–170
Agerer R (1991e) Gomphidius glutinosus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 58. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1991f) Comparison of the ontogeny of hyphal and rhizoid strands of Pisolithus tinctorius and Polytrichum juniperinum. Cryptogam Bot 2/3:85–92
Agerer R (1992a) Ectomycorrhizae of Phellodon niger on Norway spruce and their chlamydospores. Mycorrhiza 2:47–52
Agerer R (1992b) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. XLIV. Ectomycorrhizae of Boletopsis leucomelaena (Thelephoraceae, Basidiomycetes) and their relationship to an unidentified ectomycorrhiza. Nova Hedwig 55:501–518
Agerer R (1992c) Gomphidius roseus. In Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 71. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1993a) Phellodon niger. In Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhiza, plate 78, Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1993b) Ectomycorrhizae of Hydnellum peckii on Norway spruce and their chlamydospores. Mycologia 85:74–83
Agerer R (1993c) Hydnellum peckii. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 77. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1993d) Boletopsis leucomeaena. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 75. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1994a) Pseudotomentella tristis (Thelephoraceae). Eine Analyse von Fruchtkörper und Ektomykorrhizen. Z Mykol 60:143–158
Agerer R (1994b) Pseudotomentella tristis. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 84. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1995) Anatomical characteristics of identified ectomycorrhizas: an attempt towards a natural classification. In: Varma K, Hock B (eds) Mycorrhiza: structure, function, molecular biology and biotechnology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 685–734
Agerer R (1996a) Ramaria aurea (Schaeff.: Fr.) Quél. + Fagus sylvatica L. Descr Ectomyc 1:107–112
Agerer R (1996b) Ramaria largentii Marr & D. E. Stuntz + Picea abies (L.) H. Karst. Descr Ectomyc 1:113–118
Agerer R (1996c) Ramaria largentii. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 103. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1996d) Ramaria spinulosa (Fr.) Quel. + Fagus sylvatica. Descr Ectomyc 1:119–124
Agerer R (1996e) Ramaria subbotrytis (Coker) Corner + Quercus robur L. Descr Ectomyc 1:125–130
Agerer R (1996f) Ectomycorrhizae of Tomentella albomarginata (Thelephoraceae) on Scots pine. Mycorrhiza 6:1–7
Agerer R (1996g) Tomentella albomarginata. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 111. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1996h) Albatrellus ovinus (Schaeff.: Fr.) Kotl. & Pouz. + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 1:23–28
Agerer R (1996i) Albatrellus ovinus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 91. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1996k) Russula acrifolia. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhiazae, plate 105. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1996l) Ectomycorrhizae in the fungal community: with special emphasis on interactions between ectomycorrhizal fungi. In: Azcon-Aguilar C, Barea JM (eds) Mycorrhizas in integrated systems from genes to plant development. European Commission, Science Research and Development, Brussels, pp 52–57
Agerer R (1996m) Rhizopogon subcaerulescens. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 104. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1997) Entoloma sinuatum (Bull.: Fr.) Kummer + Salix spec. Descr Ectomyc 2:13–18
Agerer R (1998a) Ramaria subbotrytis. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 134. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1998b) Geastrum fimbriatum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 119. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1998c) Tomentellopsis submollis. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 138. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1998d) Entoloma sinuatum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 117. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1998e) Lyophyllum decastes. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 124. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (1999a) Never change a functionally successful principle: the evolution of Boletales s. l. (Hymenomycetes, Basidiomycota) as seen from below-ground features. Sendtnera 6:5–91
Agerer R (1999b) Elaphomyces aculeatus Tul. + Quercus robur L. Descr Ectomyc 4:37–41
Agerer R (1999c) Gyroporus cyanescens (Bull.: Fr.) Quél. + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 4:43–47
Agerer R (1999d) Rozites caperatus (Pers.: Fr.) Karst. + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 4:109–113
Agerer R (2001) Exploration types of ectomycorrhizae. A proposal to classify ectomycorrhizal mycelial systems according to their patterns of differentiation and putative ecological importance. Mycorrhiza 11:107–114
Agerer R (2002a) Elaphomyces aculeatus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 158, Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (2002b) Gomphus clavatus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 155. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (2002c) Die besonderen Beziehungen von Gomphidius roseus und seiner Verwandten, oder wie intim können Mykorrhizapilze sein. Der Tintling 7:12–20
Agerer R (2002d) Gyroporus cyanescens. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizze, plate 156. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (2002e) Rozites caperatus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 157. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R (2002f) The ectomycorrhiza Piceirhiza internicrassihyphis: a weak competitor of Cortinarius obtusus? Mycol Progress 1:291–299
Agerer R (2002g) Rhizomorph structures confirm the relationship between Lycoperdales and Agaricaceae (Hymenomycetes, Basidiomycota). Nova Hedwig 75:367–385
Agerer R (2003) Classification of fungi in modern view. Mycoses 46(Suppl 1):2–14
Agerer R, Ammirati (1998) Polyporoletus sublividus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 130. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R, Beenken L (1998a) Geastrum fimbriatum Fr. + Fagus sylvatica L. Descr Ectomyc 3:13–18
Agerer R, Beenken L (1998b) Lyophyllum decastes (Fr.) Sing. + Quercus robur L. Descr Ectomyc 3:43–47
Agerer R, Bougher NL (2001a) Tomentella brunneorufa M. J. Larsen + Eucalyptus spec. Descr Ectomyc 5:205–212
Agerer R, Bougher NL (2001b) Tomentella subamyloidea sp. nov., and T. radiosa (Thelephoraceae, Hymenomycetes, Basidiomycota) from Australia. Australian Syst Bot 14:607–614
Agerer R, Gronbach E (1987) Dermocybe cinnamomea. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 7. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R, Gronbach E (1989) Paxillus involutus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 27. Einhorn, Schwäbich Gmünd
Agerer R, Gronbach E (1990a) Boletus edulis. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 36. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R, Gronbach E (1990b) Xerocomus badius. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 49. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R, Iosifidou P (2004) Rhizomorph structure of Hymenomycetes: a possibility to test DNA-based phylogenetic hypotheses? In: Agerer R, Piepenbring M, Blanz P (eds) Frontiers in basidiomycote mycology. IHW-Verlag, Eching, pp 249–302
Agerer R, Otto P (1997) Bankera fuligineo-alba (J. C. Schmidt.: Fr.) Pouzar + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 2:1–6
Agerer R, Otto P (1998) Bankera fuligineo-alba. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 115. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R, Raidl S (2004) Distance-related semi-quantitative estimation of the extramatrical ectomycorrhizal mycelia of Cortinarius obtusus and Tylospora asterophora. Mycol Progress 3:57–64
Agerer R, Rambold G (1998) DEEMY—a delta-based system characterization and DEtermination of EctoMYcorrhizae. CD-ROM, version 1.1. Institute for Systematic Botany, Section Mycology, University of München
Agerer R, Rambold G (2004–2005 [first posted on 2004-06-01; most recent update: 2005-10-25]) DEEMY—an information system for characterization and DEtermination of EctoMYcorrhizae. www.deemy.de-München, Germany
Agerer R, Treu R (1993) Gyrodon lividus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 76. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R, Uhl M (1989) Dermocybe semisanguinea. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 25. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R, Waller K (1993a) Mycorrhizae of Entoloma saepium: parasitism or symbiosis? Mycorrhiza 3:145–154
Agerer R, Waller K (1993b) Tricholoma acerbum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 82. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R, Weiss M (1989) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. XX. Mycorrhizae formed by Thelephora terrestris on Norway spruce. Mycologia 81:444–453
Agerer R, Weiss M (1990) Thelephora terrestris. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 48. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Agerer R, Waller K, Treu R (1993) Die Ektomykorrhizen und Sklerotien von Gyrodon lividus. Z Mycol 59:131–140
Agerer R, Franz F, Acker G (1994) The ectomycorrhizae of Russula acrifolia: an anatomical and ultrastructural treatise. Mycol Helv 6:23–48
Agerer R, Klostermeyer D, Steglich W (1995) Piceirhiza nigra, an ectomycorrhiza on Picea abies formed by a species of Thelephoraceae. New Phytol 131:377–380
Agerer R, Klostermeyer D, Steglich W, Franz F, Acker G (1996a) Ectomycorrhizae of Albatrellus ovinus (Scutigeraceae) on Norway spruce with some remarks on the systematic position of the family. Mycotaxon 59:289–307
Agerer R, Kraigher H, Javornik B (1996b) Identification of ectomycorrhizae of Hydnum rufescens on Norway spruce and the variability of the ITS region of H. rufescens and H. repandum (Basidiomycetes). Nova Hedwig 63:183–194
Agerer R, Müller WR, Bahnweg G (1996c) Ectomycorrhizae of Rhizopogon subcaerulescens on Tsuga heterophylla. Nova Hedwig 63:397–415
Agerer R, Beenken L, Christan J (1998a) Gomphus clavatus (Pers.: Fr.) S. F. Gray + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 3:25–29
Agerer R, Beenken L, Ammirati J (1998b) Polyporoletus sublividus Snell + Abies amabilis Forb. Descr Ectomyc 3:85–91
Agerer R, Schloter M, Hahn C (2000) Fungal enzymatic activity in fruitbodies. Nova Hedwig 71:315–336
Agerer R, Beenken L, Bougher NL (2001) Descomyces albus (Klotzsch) Bougher & Castellano + Eucalyptus spec. Descr Ectomyc 5:41–47
Agerer R, Grote R, Raidl S (2002) The new method ‘micromapping’, a means to study species-specific associations and exclusions of ectomycorrhizae. Mycol Progress 1:155–166
Amiet R, Egli S (1991) Die Ektomykorrhizen des Grubigen Milchlings (Lactarius scrobiculatus (Scop.: Fr.) Fr.) an Fichte (Picea abies Karst.) Schweiz Z Forstwes 142:53–60
Andruszewska A, Dominik T (1971) Mikoryza Prunus cerasus L. x Rhodophyllus clypeatus (Bull. ex Fr.) Quél. Zeszyty Naukowe Wyzszej Szkoly Rolniczej W Szczecini 37:3–14
Arnold N, Besl H, Bresinsky A, Kemmer H (1987) Notizen zur Chemotaxonomie der Gattung Dermocybe (Agaricales) und zu ihrem Vorkommen in Bayern. Z Mykol 53:187–194
Azul M, Freitas H (2006a) Quercirhiza ateracusrugosa. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 175. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Azul M, Freitas H (2006b) Quercirhiza auraterocystidiata. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 176. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Azul M, Freitas H (2006c) Quercirhiza tomentellocystidiata. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 187. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Azul M, Freitas H (2006d) Quercirhiza tomentelloflexuosa. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 188. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Azul M, Freitas H (2006e) Quercirhiza tomentellofuniculosa. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 189. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Azul AM, Agerer R, Freitas H (1999) “Quercirhiza nodulosomorpha” + Quercus suber L. Descr Ectomyc 4:103–108
Azul AM, Agerer R, Freitas H (2001) “Quercirhiza sclerotiigera” + Quercus suber L. Descr Ectomyc 5:99–105
Azul AM, Agerer R, Freitas H (2006) Quercirhiza dendrohyphidiomorpha + Quercus suber L. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Becerra A, Daniele G, Domínguez L, Nouhra E, Horton T (2002) Ectomycorrhizae between Alnus acuminata H.B.K. and Naucoria escharoides (Fr.: Fr.) Kummer from Argentina. Mycorrhiza 12:61–66
Becerra A, Nouhra E, Daniele G, Domínguez L, McKay D (2005) Ectomycorrhizas of Cortinarius helodes and Gyrodon monticola with Alnus acuminata from Argentina. Mycorrhiza 15:7–15
Beenken L (2001a) Russula aeruginea Lindbl. ex Fr. + Betula pendula Roth. Descr Ectomyc 5:107–113
Beenken L (2001b) Russula alnetorum Romagn + Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 5:115–123
Beenken L (2001c) Russula atroglauca Einhellinger + Betula pubescens Ehrh. Descr Ectomyc 5:125–130
Beenken L (2001d) Russula cyanoxantha (Schaeff.) Fr. + Fagus sylvatica. Descr Ectomyc 5:131–137
Beenken L (2001e) Russula delica Fr. + Tilia sp. Descr Ectomyc 5:139–145
Beenken L (2001f) Russula densifolia Secr. ex Gill. + Fagus sylvatica L. Descr Ectomyc 5:147–155
Beenken L (2001g) Russula densifolia Secr. ex Gill. + Picea abies (L.) H. Karst. Descr Ectomyc 5:157–161
Beenken L (2001h) Russula foetens (Pers.: Fr.) Fr. + Fagus sylvatica L. Descr Ectomyc 5:163–168
Beenken L (2001i) Russula medullata Romagn. + Populus tremula L. Descr Ectomyc 5:169–174
Beenken L (2001k) Russula nothofaginea Sing. + Nothofagus dombeyi (Mirbel) Oersted. Descr Ectomyc 5:175–179
Beenken L (2001l) Russula versicolor J. Schäff. + Betula pubescens Ehrh. Descr Ectomyc 5:181–185
Beenken L (2001m) Russula vesca Fr. + Quercus robur L. Descr Ectomyc 5:187–192
Beenken L (2001n) Russula vinosa Lindbl. + Picea abies (L.) H. Karst. Descr Ectomyc 5:193–198
Beenken L (2001o) Russula virescens (Schaeff.) Fr. + Quercus robur L. Descr Ectomyc 5:199–203
Beenken L (2004a) Die Gattung Russula. Untersuchungen zu ihrer Systematik anhand von Ektomykorrhizen. Dissertation, University of München. http://edoc.ub.uni-muenchen.de/archive/00003175/
Beenken L (2004b) Les ectomycorhizes du genre Russula. Bull Soc Mycol Fr 120:293–333
Beenken L, Agerer R, Bahnweg G (1996a) Inocybe terrigena (Fr.) Kuyper + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 1:53–58
Beenken L, Agerer R, Bahnweg G (1996b) Inocybe obscurobadia (J. Favre) Grund & D. E. Stuntz + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 1:47–52
Beenken L, Agerer R, Bahnweg G (1996c) Inocybe fuscomarginata Kühn. + Salix spec. / Populus nigra L. Descr Ectomyc 1:41–46
Beenken L, Agerer R, Bahnweg G (1996d) Inocybe appendiculata Kühn. + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 1:35–40
Begerow D, Bauer R, Oberwinkler F (1997) Phylogenetic studies on nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences of smut fungi and related taxa. Can J Bot 2045–2056
Berg B (1986) Untersuchungen zur Ektomykorrhiza der Gattung Cenococcum Fries. Diploma work, University of München
Berg B (1989) Charakterisierung und Vergleich von Ektomykorrhizen gekalkter Fichtenbestände. Dissertation, University of München
Berg B, Gronbach E (1989) Piceirhiza gelatinosa. In: Agerer (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 30. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Binder M, Bresinsky A (2002) Derivation of a polymorphic lineage of Gasteromycetes from boletoid ancestors. Mycologia 94:85–98
Binder M, Hibbett DS, Larsson K-H, Larsson E, Langer E, Langer G (2005) The phylogenetic distribution of resupinate forms across the major clades of mushroom-forming fungi (Homobasidiomycetes). Syst Biodivers 3(2):113–157
Blaschke H (1987) Vorkommen und Charakterisierung der Ektomykorrhizaassoziation Tuber puberulum mit Picea abies. Z Mykol 53:283–288
Blaschke H (1988) Tuber puberulum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 22, Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Bon M (1988) Clé monographique des Russules d’Europe. Doc Mycol 71–72:1–125
Bonfante-Fasolo P, Scannerini S (1977) Cytological observations on the mycorrhiza “Endogone flammicorona”–“Pinus strobus”. Allionia 22:23–24
Bougher NL, Malajczuk N (1985) A new species of Descolea (Agaricales) from Western Australia, and aspects of its mycorrhizal status. Aust J Bot 33:619–627
Bougher NL, Fuhrer BA, Horak E (1994) Taxonomy and biogeography of Australian Rozites species mycorrhizal with Nothofagus and Myrtaceae. Aust Syst Bot 7:353–375
Brand F (1987a) Lactarius subdulcis. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 5. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1987b) Lactarius vellereus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 6. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1988a) Fagirhiza tubulosa. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 17. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1988b) Fagirhiza granulosa.In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 16. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1988c) Laccaria amethystina. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 18. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1989a) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. XXI. Beech ectomycorrhizae and rhizomorphs of Xerocomus chrysenteron (Boletales). Nova Hedwig 48:469–483
Brand F (1989b) Xerocomus chrysenteron. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 34. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1991a) Ektomykorrhizen an Fagus sylvatica. Charakterisierung und Identifizierung, ökologische Kennzeichnung und unsterile Kultivierung. Libri Botanici vol 2. IHW, Eching
Brand F (1991b) Elaphomyces muricatus. In Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 53. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1991c) Genea hispidula. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 57. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1991d) Russula illota. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 64. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1991e) Russula mairei. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 65. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1991f) Lactarius pallidus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 59. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1991g) Lactarius rubrocinctus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 60. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1991h) Byssocorticium atrovirens. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 51. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1991i) Piloderma croceum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 62. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1992a) Lactarius acris. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 72. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1992b) Cortinarius bolaris. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 67. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1992c) Cortinarius cinnabarinus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 68. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F (1992d) Tricholoma sciodes. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 74. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Brand F, Agerer R (1986) Studien an Ektomykorrhizen VIII. Die Mykorrhizen von Lactarius subdulcis, Lactarius vellereus und Laccaria amethystina an Buche. Z Mykol 52:287–320
Brand F, Agerer R (1988) Studien an Ektomykorrhizen XIII. Drei häufige Ektomykorrhizen an der Buche (Fagus sylvatica L.). Charakterisierung und unsterile Kultivierung von Buchenmykorrhizen. Sydowia Ann Mycol 40:1–37
Brand F, Gronbach E, Taylor AFS (1992) Picerihiza bicolorata. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 73. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Breitenbach J, Kränzlin F (1986) Pilze der Schweiz 2. Nichtblätterpilze. Mycologia, Luzern
Bresinsky A, Rennschmid A (1971) Pigmentmerkmale, Organisationsstufen und systematische Gruppen bei Höheren Pilzen. Ber Dtsch Bot Ges 84:313–329
Bresinsky A, Jarosch M, Fischer M, Schönberger I, Wittmann-Bresinsky B (1999) Phylogenteic relationships within Paxillus s. l. (Basidiomycetes, Boletales): separation of a southern hemisphere genus. Plant Biol 1:1–7
Brownlee C, Duddridge JA, Malbari A, Read DJ (1983) The structure and function of mycelial systems of ectomycorrhizal roots with special reference to their role in forming interplant connections and providing pathways for assimilate and water transport. Plant Soil 71:433–443
Brunner I, Amiet R, Schneider B (1991) Characterization of naturally grown and in vitro synthesized ectomycorrhizae of Hebeloma crustuliniforme and Picea abies. Mycol Res 95:1407–1413
Bruns TD, Szaro TM, Gardes M, Cullings KW, Pan JJ, Taylor DL, Horton TR, Kretzer A, Garbelotto M, Li Y (1998) A sequences database for the identification of ectomycorrhizal badidiomycetes by phylogenetic analysis. Mol Ecol 7:257–272
Cairney JWG, Jennings DH, Agerer R (1991) The nomenclature of fungal multi-hyphal linear aggregates. Cryptogam Bot 2/3:246–251
Chilvers GA (1968) Some distinctive types of eucalypt mycorrhiza. Aust J Bot 16:49–70
Christan J, Hahn C (2005) The systematics of the genus Ramaria (Basidiomycota, Gomphales). Z Mykol 71:7–42
Chu-Chou M, Grace LJ (1979) Endogone flammicorona as a mycorrhizal associate of Douglas fir in New Zealand. NZ J For Sci 9:344–347
Chu-Chou M, Grace LJ (1983) Characterization and identification of mycorrhizas of Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii). Eur J For Pathol 23(4):251–260
Chu-Chou M, Grace LJ (1984) Endogone flammicorona and Tuber sp. as mycorrhizal fungi or Pinus radiata in New Zealand. NZ J Bot 22:525–531
Clémencçn H (2004) Die basidiomalen rhizomorphen einiger Cortinarien. Journal des J.E.C. 7:7–18
Clémençon H (2005) Rhizomorph anatomy of Ossicaulis lignatilis (Tricholomatales), with special attention to its haustoria-like intrahyphal hyphae. Mycol Progress 4:176–173
Comandini O, Pacioni G (1997) Mycorrhizae of Asian black truffles, Tuber himalayense and T. indicum. Mycotaxon 63:77–86
Comandini O, Haug I, Rinaldi AC, Kuyper TW (2004) Uniting Tricholoma sulphureum and T. bufonium. Mycol Res 108:1162–1171
Corner EJH (1966) A monograph of cantharelloid fungi. Oxford University Press
Countess RE, Goodman DM (2000) Cantharellus formosus Corner + Tsuga heterophylla (Raf.) Sarg. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement, Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE21.1–CDE21.4
Cripps CL (1997a) Inocybe lacera (Fr.: Fr.) Kumm. + Populus tremuloides Michx. Descr Ectomyc 2:19–23
Cripps CL (1997b) Tricholoma scalpturatum (Fr.) Quel. + Populus tremuloides Michx. Descr Ectomyc 2:73–78
Cuvelier J-J (1990) Characterisation des ectomycorhizes de Betula pendula (I): Cortinarius armillatus, Dermocybe phoenicea et Amanita muscaria. Belg J Bot 123:73–91
Cuvelier J-J (1991) Characterization of birch ectomycorrhiza (II): Laccaria amethystea and Russula ochroleuca. Belg J Bot 124:195–203
Cuvelier J-J, Agerer R (1991) Cortinarius armillatus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 52. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Dahlman M, Danell E, Spatafora JW (2000) Molecular systematics of Craterellus: cladistic analysis of nuclear LSU rDNA sequence data. Mycol Res 104(4):388–394
Danielson RM (1984a) Ectomycorrhizal associations in Jack pine stands in northeastern Alberta (Canada). Can J Bot 62:932–939
Danielson RM (1984b) Ectomycorrhiza formation by the operculate Discomycete Sphaerosporella brunnea. Mycologia 76:454–461
de Román M, Agerer R, de Miguel A (2002) “Quercirhiza cumulosa” + Quercus ilex L. subsp. ballota (Desf.) Samp. Descr Ectomyc 6:13–18
de Roman M, Claveria V, de Miguel AM (2005) A revision of the descriptions of ectomycorrhizas published since 1961. Mycol Res 109:1063–1104
Dominik T (1956) Projekt nowego podzialu mikoryz ektotroficznych oparty na cechach morfologiczno-anatomicznych. Rocz Nauk Lesn 14:223–246
Dominik T (1969) Key to ectotrophic mycorrhizae. Folia For Pol Ser A 15:309–328
Donk MA (1962) The generic names proposed for Hymenomcetes-XII: Deuteromycetes. Taxon 11:75–104
Dunabeitia MK, Hormilla S, Salcedo I, Pena JI (1996) Ectomycorrhizae synthesized between Pinus radiata and eight fungi associated with Pinus spp. Mycologia 88:897–908
Eberhardt U (2000) Molekulare Analysen zur Verwandtschaft der agaricoiden Russulaceen im Vergleich mit Mykorrhiza- und Fruchtkörpermerkmalen. Dissertation, University of Tübingen
Eberhardt U (2002) Molecular kinship analyses of the agaricoid Russulaceae: correspondence with mycorrhizal anatomy and sporocarp features in the genus Russula. Mycol Progress 1:201–223
Eberhardt U, Walter L, Kottke I (1999) Molecular and morphological discrimination between Tylospora fibrillosa and Tylospora asterophora mycorrhizae. Can J Bot 77:11–21
Eberhardt U, Oberwinkler F, Verbeken A, Rinaldi AC, Pacioni G, Comandini O (2000) Lactarius ectomycorrhizae on Abies alba: morphological description, molecular characterization, and taxonomic remarks. Mycologia 92:860–873
Eberhart J, Luoma D (1996) Truncocolumella citrina Zeller + Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement. Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE9.1–CDE9.4
Eberhart J, Luoma D (1997) Lactarius rubrilacteus Hesler &Smith + Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement, Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE15.1–CDE15.4
Eberhart J, Luoma D (2000) Russula densifolia (Secr.) Gillet + Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement, Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE22.1–CDE22.4
Edwards HH, Gessner R (1984) Light and transmission electron microscopy of English oak ectomycorrhizal roots. Can J Bot 62:1327–1335
Egli S (1992) Der Anisklumpfuß, Cortinarius odorifer Britz.: Ökologie, Biologie und Ektomykorrhiza. Mitt Eidgenoss Forschanst Wald Schnee Landsch 67:317–412
Egli S, Ayer F, Peter M, Schneider B (2001) Arcangeliella borziana Cavara + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 5:9–14
Einhellinger A (1985) Die Gattung Russula in Bayern. Hoppea volume 43. Regensburg
Falck R (1912) Die Meruliusfäule des Bauholzes.-Neue Untersuchungen über Unterscheidung, Verbreitung, Entstehung und Bekämpfung des echten Hausschwammes. Hausschwammforschung, vol 6. Fischer, Jena
Farmer DJ, Sylvia DM (1998) Variation in the ribosomal DNA internal transeibed spacer of a diverse collection of ectomycorrhizal fungi. Mycol Res 102:859–865
Fassi B (1965) Micorrize ectotrofiche di Pinus strobus L. prodotte da un’ endogone (Endogone lactiflua Berk.). Allionia 11:7–15
Fassi B, de Vecchi E (1962) Ricerche suslle micorrize ectotrofiche del Pino strobo in vivaio. I. Descrizione di alacune fomre piu diffuse in Piemonte. Allionia 8:133–151
Fassi B, Palenzona M (1969) Mycorrhizal synthesis between Pinus strobus, Pseudotsuga menziesii and Endogone lactiflua. Allionia 15:105–114
Fassi B, Fontana A, Trappe JM (1969) Ectomycorrhizae formed by Endogone lactiflua with species of Pinus and Pseudotsuga. Mycologia 61:412–414
Feibelman TP, Doudrick RL, Cibula WG, Bennett JW (1997) Phylogenetic relationships within the Cantharellaceae inferred from sequence analysis of the nuclear large subunit rDNA. Mycol Res 101:1423–1430
Fischer C, Agerer R (1996) “Quercirhiza argenteobrunneola” + Quercus ilex L. Descr Ectomyc 1:101–105
Fischer C, Suz LM, Martin MP (2004) Tuber brumale Vitt. + Quercus ilex L. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:135–141
Fontana A, Bonfante-Fasolo P (1971) Sintesi micorrizica di Tuber brumale Vitt. con Pinus nigra Arnold. Allionia 17:15–18
Frank AB (1885) Über die auf Wurzelsymbiose beruhende Ernährung gewisser Bäume durch unterirdische Pilze. Ber Dtsch Bot Ges 3:128–145
Fransson PMA (2004a) Craterellus tubaeformis (Fr.) Quél. (syn. Cantharellus tubaeformis Fr.: Fr.) + Quercus robur L. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:37–43
Fransson PMA (2004b) Russula decolorans Fr. + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:109–115
Franz F, Acker G (1995) Rhizomorphs of Picea abies ectomycorrhizae: ultrastructural aspects and elemental analysis (EELS and ESI) on hyphal inclusions. Nova Hedwig 60:253–267
Fries E (1874) Hymenomycetes Europaei. Uppsala
Froidevaux L (1973) The ectomycorrhizal association, Alnus rubra + Lactarius obscuratus. Can J For Res 3:601–603
Gaie W, Heinemann P (1980) Synthese et morphologie des l’ectomycorhize Betula pendula/Astraeus hygrometricus. Bull Soc R Bot Belg 113:161–165
Gibelli G (1883) Nuovi studii sulla malattia del Castagno detta dell’ inchiostro. Mem R Accad Sci Ist Bologna 4:287–314
Gill M, Steglich W (1987) Pigments of fungi (Macromycetes). In: Herz W, Grisebach H, Kirby GW, Tamm C (eds) Progress in the chemistry of organic natural products, vol 51. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Giomaro G, Zambonelli A, Sisti D, Cecchini M, Evangelista V, Stocchi V (2000) Anatomical and morphological characterization of mycorrhizas of five strains of Tuber borchii Vittad. Mycorrhiza 10:107–114
Giovannetti G, Fontana A (1981) Simbiosi micorrizica di Tuber macrosporum Vitt. con alcune Fagales. Allionia 24(13):13–17
Giraud M (1979) Etude comparative des mycorhizes d’arbres producteurs de truffe ou non en zone truffiere. Mem de fin d’etudes, Diplome d’Agronomie Approfondie, E.N.S.A. Rennes, INRA, Clermont-Fd., 56 pp
Giraud M (1990) Mycorhizes: prelevement et analyse. In: Verlhac A, Geraud M, Leteinturnier J (eds) La truffe guide pratique. Ctfl FPGV, Reims, pp 77–88
Godbout C, Fortin JA (1985) Synthesized ectomycorrhizae of aspen: fungal genus level of structural characterization. Can J Bot 63:252–262
Golldack J, Münzenberger B, Hüttl RF (1998a) “Pinirhiza cyaneoviridis” + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 3:49–54
Golldack J, Münzenberger B, Hüttl RF (1998b) “Pinirhiza discolor” + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 3:55–60
Golldack J, Münzenberger B, Hüttl RF (1999) “Pinirhiza dimorpha” + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 4:73–78
Goodman DM (1996a) Tomentella-like + Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement. Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE2.1–CDE2.4
Goodman DM (1996b) Rhizopogon vinicolor-like + Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement. Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE7.1–CDE7.4
Goodman DM, Trofymow JA (1996) Piloderma fallax (Libert) Stalpers + Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement. Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE1.1–CDE1.4
Granetti B (1995) Caratteristiche morfologiche biometriche e strutturali delle micorrize di Tuber di interesse economico. Micol Ital 24(2):101–117
Gronbach E (1988) Charakterisierung und Identifizierung von Ektomykorrhizen in einem Fichtenbestand mit Untersuchungen zur Merkmalsvariabilität in sauer beregneten Flächen. Bibliotheca mycologica, vol 125. Cramer, Berlin Stuttgart
Gronbach E (1989a) Piceirhiza glutinosa. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 31. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Gronbach E (1989b) Piceirhiza guttata. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 32. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Gronbach E, Agerer R (1986) Charakterisierung und Inventur der Fichten-Mykorrhizen im Höglwald und deren Reaktion auf saure Beregnung. Forstwiss Centbl 105:329–335
Gronbach E, Agerer R (1988) Cortinarius obtusus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 12. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Grubisha LC, Trappe JM, Molina R, Spatafora JW (2001) Biology of the ectomycorrhizal genus Rhizopogon. V. Phylogenetic relationships in the Boletales inferred from LSU rDNA sequences. Mycologia 93:82–89
Hahn C (2001) Boletus rhodoxanthus Kallenb. + Cistus cf. ladanifer L. Descr Ectomyc 5:15–22
Hahn C, Raidl S (2006) Boletus subappendiculatus Dermek, Lazebn. & J. Veselský + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Hahn C, Agerer R, Wanner G (2000) Anatomische und ultrastrukturelle Analyse von Ramaricium alboochraceum, einer seltenen Art der Gomphales und seine verwandtschaftliche Beziehung zu Geastrum und Gautieria. Hoppea 61:115–125
Halász K, Bratek Z, Stegö D, Rudnóy S, Rácz I, Lásztity D, Trappe JM (2005) Tests of species concepts of the small, white, European group of Tuber spp. based on morphology and rDNA ITS sequences with special refrence to Tuber rapaeodorum. Mycol Progress 4(4):281–290
Harniman SMK, Durall DM (1996a) Cenococcum geophilum Fr. + Picea engelmannii (Parry) Engelm. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement, Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE10.1–CDE10.4
Harniman SMK, Durall DM (1996b) Amphinema byssoides-like + Picea engelmannii (Parry) Engelm. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement. Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE6.1–CDE6.4
Harrington TJ, Mitchell DT (2002) Characterization of Dryas octopetala ectomycorrhizas from limestone karst vegetation, western Ireland. Can J Bot 80:970–982
Hatch AB (1934) A jet-black mycelium forming ectotrophic mycorrhizae. Sven Bot Tidskr 28:369–383
Haug I (2002a) Identification of Picea-ectomycorrhizae by comparing DNA-sequences. Mycol Progress 2:167–178
Haug I (2002b) Hebeloma velutipes. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 150. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Haug I, Oberwinkler F (1987) Some distinctive types of spruce mycorrhizae. Trees 1:172–188
Haug I, Pritsch K (1992) Ectomycorrhizal types of spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) in the Black Forest. A microscopical atlas. Kernforschungszentrum Karlsruhe, PEF-Ber, pp 1–89
Haug I, Weiß M, Homeier J, Oberwinkler F, Kottke I (2005) Russulaceae and Thelephoraceae form ectomycorrhizas with members of the Nyctaginaceae (Caryophyllales) in the tropical mountain rain forest of southern Ecuador. New Phytol 165:923–936
Hawksworth DL, Kirk PM, Sutton BC, Pegler DN (1995) Ainsworth & Bisby’s dictionary of the fungi, 8th edn. CABInternational, Wallingford
Hawksworth DL, Kirk PM, Sutton BC, Pegler DN (2001) Ainsworth & Bisby’s dictionary of the fungi, 9th edn. CABInternational, Wallingford
Heilmann-Clausen J, Verbeken A, Vesterholt J (1998) The genus Lactarius. Fungi of Northern Europe, vol 2. Oddense
Hibbett DS, Binder M (2002) Evolution of complex fruiting-body morphologies in homobasidiomycetes. Proc R Soc Lond B 269:1963–1969
Hibbett DS, Thorn RG (2001) Basidiomycota: Homobasidiomycetees. In: McLaughlin DJ, McLaughlin EG, Lemke PA (eds) The Mycota VII, part B. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg new York, pp 121–168
Hibbett DS, Pine EM, Langer E, Langer G, Donoghue MJ (1997a) Evolution of gilled mushrooms and puffballs inferred from ribosomal DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:12002–12006
Hibbett DC, Grimaldi D, Donoghue J (1997b) Fossil mushrooms from Miocene and Cretaceous ambers and the evolution of Homobasidiomycetes. Am J Bot 84:981–991
Hibbett DS, Gilbert L-B, Donoghue MJ (2000) Evolutionary instability of ectomycorrhizal symbiosis in basidiomycetes. Nature 407:506–508
Hoch M, Goodman DM, Chyplyk C, Kurucz M (1998) Suillus caerulescens A. H. Smith & Thiers + Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement. Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE19.1–CDE19.4
Høiland K (1983) Cortinarius subg. Dermocybe. Opera Botanica 71:5–113
Høiland K, Holst-Hensen A (2000) Cortinarius phylogeny and possible taxonomic implications of ITS rDNA sequences. Mycologia 92:694–710
Horak E (1968) Synopsis generum Agaricalium (Die Gattungen der Agaricales). Beiträge zur Krypotgamenflora der Scheiz XIII, Büchler, Wabern-Bern
Humpert AJ, Muench EL, Giachini AJ, Castellano MA, Spatafora JW (2001) Molecular phylogenetics of Ramaria and related genera: evidence from nuclear large subunit and mitochondrial small subunit rDNA sequences. Mycologia 93:465–477
Index Fungorum (2005) http://www.indexfungorum.org/Names/Names.asp
Ingleby K (1999a) Scleroderma sinnamarense Mont. + Gnetum africanum Welw. Descr Ectomyc 4:127–133
Ingleby K (1999b) Inocybe avellana Horak + Shorea leprosula Miq. Descr Ectomyc 4:55–60
Ingleby K, Mason PA (1996) Ectomycorrhizas of Thelephora terrestris formed with Eucalyptus globulus. Mycologia 88:548–553
Ingleby K, Mason PA, Last FT, Fleming LV (1990) Identification of ectomycorrhizas. ITE research publication 5. HMSO, London, pp 112
Iosifidou P, Raidl S (2006) Clavariadelphus pistillaris (Fr.) Donk + Fagus sylvatica L. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Jakucs E (1999) Russula amoenolens Romagn. + Populus alba. Descr Ectomyc 4:115–119
Jakucs E (2002a) Tomentella pilosa. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 141. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Jakucs E (2002b) Tomentella subtestacea. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 147. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Jakucs R (2002c) Russula amoenolens. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 142. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Jakucs E (2002d) Lactarius controversus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 143. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Jakucs E (2002e) Scleroderma bovista. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 144. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Jakucs E (2002f) Xerocomus lanatus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 149. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Jakucs E (2002g) Hebeloma ammophilum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 145. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Jakucs E, Agerer R (1999a) Tomentella pilosa (Burt) Bourdot & Galzin + Populus alba L. Descr Ectomyc 4:135–140
Jakucs E, Agerer R (1999b) Scleroderma bovista Fr. + Populus alba L. Descr Ectomyc 4:121–126
Jakucs E, Agerer R (2001) Tomentella subtestacea Bourdot & Galzin + Populus alba L. Descr Ectomyc 5:213–219
Jakucs E, Beenken L (2001) Xerocomus lanatus (Rosk.) Sing. + Quercus cerris L. Descr Ectomyc 5:221–225
Jakucs E, Bratek Z (1998a) Genea verrucosa. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 120. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Jakucs E, Bratek Z (1998b) Rhizopogon vulgaris var. intermedius. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 136. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Jakucs E, Agerer R, Bratek Z (1997) “Quercirhiza fibulocystidiata” + Quercus spec. Descr Ectomyc 2:67–71
Jakucs E, Agerer R, Bratek Z (1998a) Quercirhiza fibulocystidiata. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 132. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Jakucs E, Bratek Z, Agerer R (1998b) Genea verrucosa Vitt. + Quercus spec. Descr Ectomyc 3:19–23
Jakucs E, Bratek Z, Beenken L, Agerer R (1998c) Rhizopogon vulgaris (Vitt.) M. Lange var. intermedius Svrcek + Pinus nigra Arn. Descr Ectomyc 3:111–116
Jakucs E, Magyar L, Beenken L (1999) Hebeloma ammophilum Bohus + Fumana procumbens (Dun.) Gr. Godr. Descr Ectomyc 4:49–54
Jakucs E, Majoros E, Beenken L (2001) Lactarius controversus Pers. + Populus alba L. Descr Ectomyc 5:55–59
Jakucs E, Kovacs GM, Agerer R, Romsics C, Erös-Honti Z (2005) Morphological–anatomical characterization and molecular identification of Tomentella stuposa ectomycorrhizae and related anatomotypes. Mycorrhiza 15:247–258
Jany J-L, Garbaye J, Martin F (2002) Cenococcum geophilum populations show a high degree of genetic diversity in beech forests. New Phytol 154:651–659
Kammerbauer H, Agerer R, Sandermann H (1989) Studies on ectomycorrhiza. XXII. Mycorrhizal rhizomorphs of Thelephora terrestris and Pisolithus tinctorius in association with Norway spruce (Picea abies): formation in vitro and translocation of phosphate. Trees 3:78–84
Kernaghan G (2001) Ectomycorrhizal fungi at tree line in the Canadian Rockies. II. Identification of ectomycorrhizae by anatomy and PCR. Mycorrhiza 10:217–229
Kernaghan G, Berch SM (1997) Lactarius scrobiculatus (Fr.) Fr. + Tsuga heterophylla (Raf.) Sarg. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement. Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE11.1–CDE11.4
Köljalg U (1996) Tomentella (Basidiomycota) and related genera in temperate Eurasia. Fungiflora, Oslo
Köljalg U, Dahlberg A, Taylor AFS, Larsson E, Hallenberg N, Stenlid J, Larsson K-H, Fransson PM, Karén O, Jonsson L (2000) Diversity and abundance of resupinate thelephoroid fungi as ectomycorrhizal symbionts in Swedish boreal forests. Mol Ecol 9:1985–1996
Köljalg U, Jakucs E, Boka K, Agerer R (2001) Three ectomycorrhiza with cystidia formed by different Tomentella species as revealed by rDNA ITS sequences and anatomical characteristics. Folia Cryptog Estonia Facs 38:27–39
Köljalg U, Tammi H, Timonen S, Agerer R, Sen R (2002) ITA rDNA sequence-based phylogenetic analysis of Tomentellopsis species from boreal and temperate forests, and the identification of pink-type ectomycorrhizas. Mycol Progress 1:81–92
Kost G (1981) Vergleichende morphologische, anatomische und feinstrukturelle Merkmalsstudien an Arten der Gattung Tricholoma (Fr.) Staude, Sektion Genuina (Fr.) Sacc. Dissertation, Tübingen
Kottke I (1997) Fungal adhesion pad formation and penetration of root cuticle in early stage mycorrhizas of Picea abies and Laccaria amethystea. Protoplasma 196:55–64
Kovacs GM (2002) Study of mycorrhizae on the Great Hungarian Plain. Ph.D. thesis, University of Szeged. http://www.vmri.hu/~gkovacs/engthes.doc
Kovács G, Jakucs E, Diéz J, Manjón JL, Esteve-Raventós F (2002) Cortinarius hinnuleus Fr. + Betula celtilibera Rothm. & Vasc. Descr Ectomyc 6:7–11
Kraigher H, Agerer R, Javornik B (1995) Ectomycorrhizae of Lactarius lignyotus on Norway spruce, characterized by anatomical and molecular tools. Mycorrhiza 5:175–180
Kretzer A, Li Y, Szaro T, Bruns TD (1996) Internal transcribed spacer sequences from 38 recognized species of Suillus sensu lato: phylogenetic and taxonomic implications. Mycologia 88:776–785
Kuss P, Raidl S, Beenken L (2004) Cortinarius huronensis Ammirati & Smith var. huronensis + Pinus rotundata Link. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:21–27
Landvik S, Egger KN, Schumacher T (1997) Towards a subordinal classification of the Pezizales (Ascomycota): phylogenetic analyses of SU rDNA sequences. Nord J Bot 17(4):403–418
Larsson E, Larsson K-H (2003) Phylogenetic relationships of russuloid basidiomycetes with emphasis on aphyllophoralean taxa. Mycologia 95:1037–1065
Larsson K-H, Larsson E, Köljalg U (2004) High phylogenetic diversity among corticioid honobasidiomycetes. Mycol Res 108:983–1002
Le Disquet I, Pargney J-C (1996) Ultrastructural and cytophysiological studies on the spinules of Tuber ectomycorrhizas. In: Azcon-Aguilar C, Barea JM (eds) Mycorrhizas in integrated systems from genes to plant development. European Commission, Brussels, Luxembourg, pp 314–317
LePage BA, Currah RS, Stockey RA, Rothwell GW (1997) Fossil ectomycorrhizae from the Middle Eocene. Am J Bot 83:410–412
Lefevre CK, Müller WR (1998) Tricholoma magnivelare (Peck) Redhead + Pinus contorta Dougl var. latifolia Engelm. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement, Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE18.1–CDE18.4
Lihnell D (1942) Cenococcum graniforme als Mykorrhizabildner von Waldbäumen. Symb Bot Ups 5:1–18
LoBuglio KF, Berbee ML, Taylor JW (1996) Phylogenetic origins of the asexual mycorrhizal symbiont Cenococcum geophilum Fr. and other mycorrhizal fungi among ascomycetes. Mol Phylogenet Evol 6(2):287–294
Luppi AM, Gautero C (1967) Ricerche sulle micorrize di Quercus robur, Q. petraea e Q. pubescens in Piemonte. Allionia 13:129–148
Maas Geesteranus RA (1975) Die terrestrischen Stachelpilze Europas. North-Holland, Amsterdam London
Magyar L, Beenken L, Jakucs E (1999) Inocybe heimii Bon + Fumana procumbens (Dun.) Gr. Godr. Descr Ectomyc 4:61–65
Maia LC, Yano AM, Kimbrough JW (1996) Species of Asomycota forming ectomycorrhizae. Mycotaxon 57:371–390
Marx DH, Davey CB (1969) The influence of ectotrophic mycorrhizal fungi on the resistance of pine roots to pathogenic infections. III. Resistance of aseptically formed mycorrhizae to infection by Phytophthora cinnamomi. Phytopathology 59:549–558
Massicotte HB, Peterson RL, Ackerley CA, Piche Y (1986) Structure and ontogeny of Alnus crispa–Alpova diplophloeus ectomycorrhizae. Can J Bot 64:177–192
Meotto F, Carraturo P (1988) Ectomicorrizica di Sphaerosporella brunnea (A. & S.) Svrcek & Kubicka in piantine tartufigene. Allionia 28:109–116
Miller OK Jr (1964) Monograph of Chroogomphus (Gomphidiaceae). Mycologia 56:526–549
Miller OK Jr (2003) The Gomphidiaceae revisited: a worldwide perspective. Mycologia 95:176–183
Miller SL, Koo CD, Molina R (1988) An oxidative blue-bruising reaction in Alpova diplophloeus (Basidiomycetes, Rhizopogonaceae) + Alnus rubra ectomycorrhizae. Mycologia 80:576–581
Miller SL, McClean TM, Walker JF, Buyck B (2001) A molecular phylogeny of the Russulales including agaricoid, gasteroid and pleurotoid taxa. Mycologia 93:344–354
Mleczko P (1997a) Paxillus involutus (Batsch) Fr. + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 2:25–30
Mleczko P (1987b) “Populirhiza pustulosa” + Populus tremula L. Descr Ectomyc 2:61–66
Mleczko P (1998a) “Pinirhiza gomphidioidea” + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 3:67–72
Mleczko P (1998b) Pinirhiza gomphidioidea. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 128. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Mleczko P (1998c) “Pinirhiza globulifera” + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 3:61–66
Mleczko P (2002a) Russula nigricans. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 167. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Mleczko P (2002b) Russula sardonia. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 168. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Mleczko P (2002c) Amanita citrina. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 159. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Mleczko P (2002d) Rhodocollybia butyracea. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour Atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 166. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Mleczko P (2004a) Craterellus tubaeformis (Bull.) Quél. + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:29–36
Mleczko P (2004b) “Pinirhiza amyloidea” + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:59–68
Mleczko P (2004c) “Pinirhiza ligulata” + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:79–86
Mleczko P (2004d) Russula nigricans Fr. + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:117–125
Mleczko P (2004e) Russula sardonia Fr. + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:127–134
Mleczko P (2004f) Amanita citrina (Schaeff.) S. F. Gray + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:1–10
Mleczko P (2004g) Rhodocollybia butyracea (Bull. Fr.) Lennox (forma butyracea) + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:101–108
Mohan V, Natarajan K, Ingleby K (1993) Anatomical studies on ectomycorrhizas. I. The ectomycorrhizas produced by Thelephora terrestris on Pinus patula. Mycorrhiza 3:39–42
Molina R, Massicotte H, Trappe JM (1992) Specificity phenomena in mycorrhizal symbioses: community-ecological consequences and practical implications. In: Allen MF (ed) Mycorrhizal functioning, an integrative plant–fungal process. New York, pp 357–423
Moncalvo J-M, Vilgalys R, Redhead SA, Johnson JE, James TY, Aime MC, Hofstetter V, Verduin SJW, Larsson E, Baroni TJ, Thorn RG, Jacobsson S, Clémençon H, Miller OK (2002) One hundred and seventeen clades of euagarics. Mol Phylogenet Evol 23:357–400
Montecchio L, Agerer R (1997) “Piceirhiza cornuta” + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 2:31–35
Montecchio L, Rossi S (2006) Amphinema byssoides. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 169. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Montecchio L, Rossi S, Grendene A, Causin R (2001) Cortinarius ionochlorus R. Maire + Quercus ilex L. Descr Ectomyc 5:35–40
Montecchio L, Rossi S, Grendene A, Causin R (2002) Amphinema byssoides (Pers.: Fr.) J. Erikss. + Quercus ilex. Descr Ectomyc 6:1–6
Montecchio L, Rossi S, Courty P-E, Garbaye J (2006) Entoloma nitidum Quél. + Carpinus betulus L. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Moser M (1983) Basidiomyceten II. Röhrlinge und Blätterpilze (Agaricales). Kleine Kryptogamenflora. II/b2. 5. Auflage. Fischer, Stuttgart
Müller W, Agerer R (1990) Studien an Ektomykorrhizen XXIX. Drei Mykorrhzen aus der Leccinum-scabrum-Gruppe. Nova Hedwig 51:381–410
Müller W, Agerer R (1991) Leccinum scabrum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 61. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Müller WR, Agerer R (1996a) Hysterangium crassirhachis Zeller &Dodge + Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Fanco. Descr Ectomyc 1:29–34
Müller WR, Agerer R (1996b) Hysterangium crassirhachis. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 93. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Müller WR, Rauscher T, Agerer R, Chevalier G (1996) Tuber aestivum Vitt. + Corylus avellana L. Descr Ectomyc 1:167–172
Münzenberger B, Metzler B, Kottke I, Oberwinkler F (1986) Morphologische und anatomische Charakterisierung der Mykorrhiza Lactarius deterrimus–Picea abies in vitro. Z Mykol 52:407–422
Nebel M, Kreier H-P, Peussing M, Weiß M, Kottke I (2004) Symbiotic fungal associations of liverworts are the possible ancestors of mycorrhizae. In: Agerer R, Piepenbring M, Blanz P (eds) Frontiers in basidiomycote mycology. IHW-Verlag, Eching, pp 339–360
Nouhra ER, Horton TR, Cazares E, Castellano M (2005) Morphological and molecular characterization of selected Ramaria mycorrhizae. Mycorrhiza 15:55–59
Nuytinck J, Verbeken A, Rinaldi AC, Leonardi M, Pacioni G, Comandini O (2004) Characterization of Lactarius tesquorum ectomycorrhizae on Cistus sp. and molecular phylogeny of related European Lactarius taxa. Mycologia 96:272–282
O’Donnell K, Cigelnik E, Weber NS, Trappe JM (1997) Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetous truffles and the true and false morels inferred from 18S and 28S ribosomal DNA sequence analysis. Mycologia 89:48–65
Oberwinkler F (1977) Das neue System der Basidiomyceten. In: Frey W, Hurka H, Oberwinkler F (eds) Beiträge zur Biologie der niederen Pflanzen. Fischer, Stuttgart, pp 59–105
Olsson PA, Münzenberger B, Mahmood S, Erland S (2000) Molecular and anatomical evidence for a three-way association between Pinus sylvestris and the ectomycorrhizal fungi Suillus bovinus and Gomphidius roseus. Mycol Res 104:1372–1378
Palenzona M, Chevalier G, Fontana A (1972) Sintesi micorrizica tra i miceli in coltura di Tuber brumale, T. melanosporum, T. rufum e semenzali di conifere e latifoglie. Allionia 18:41–52
Palfner G (1996a) Thaxterogaster albocanus Horak & Moser + Nothofagus pumilio (Poepp. et Endl.) Krasser. Descr Ectomyc 1:155–160
Palfner G (1996b) Thaxterogaster albocanus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 110. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Palfner G (1997) Descolea antarctica Singer + Nothofagus alpina (Poepp. et Endl.) Oerst. Descr Ectomyc 2:7–12
Palfner G (1998a) Balsamia alba. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 114. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Palfner G (1998b) Leucangium carthusianum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 123. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Palfner G (1998c) Lactarius chrysorrheus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 121. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Palfner G (1998d) Descolea antarctica. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 116. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Palfner G (2001) Taxonomische Studien an Ektomykorrhizen aus den Nothofagus-Wäldern Mittelsüdchiles. Bibliotheca mycologica vol. 190. Cramer, Berlin Stuttgart
Palfner G (2002a) Austropaxillus boletinoides. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 151. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Palfner G (2002b) Cortinarius austrosalor. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 152. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Palfner G (2002c) Cortinarius magellanicus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 153. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Palfner G, Agerer R (1995) Sind die Ektomykorrhizen von Xerocomus subtomentosus und X. armeniacus anatomisch unterscheidbar? Z Mykol 61:45–58
Palfner G, Agerer R (1996) Die Ektomykorrhizen von Lactarius chrysorrheus und L. serifluus an Quercus robur. Sendtnera 3:119–136
Palfner G, Agerer R (1998a) Balsamia alba Harkness + Pinus jeffreyi Grev. &Balf. Descr Ectomyc 3:1–6
Palfner G, Agerer R (1998b) Leucangium carthusianum (Tul.) Paol. (=Picoa carthusiana Tul. &Tul.) + Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco. Descr Ectomyc 3:37–42
Palfner G, Godoy R (1996a) Russula fuegiana. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 106. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Palfner G, Godoy R (1996b) Russula fuegiana Singer + Nothofagus pumilio (Poepp. et Endl.) Krasser. Descr Ectomyc 1:131–136
Pelegrini S, Patrignani G (1994) Septal pore apparatus in some clavarioid fungi: taxonomic and phylogenetic implications. Caryologia 47:131–139
Peintner U, Horak E, Moser MM, Vilgalys R (2002a) Phylogeny of Rozites, Cuphocybe and Rapacea inferred from ITS and LSU rDNA sequences. Mycologia 94:620–629
Peintner U, Horak E, Moser M, Vilgalys R (2002b) Rozites, Cuphocybe and Rapacea are taxonomic synonyms of Cortinarius: new combinations and new names. Mycotaxon 83:447–445
Peintner U, Moncalvo J-M, Vilgalys R (2004) Toward a better understanding of the infrageneric relationships in Cortinarius (Agaricales, Basidiomycota). Mycologia 96:1042–1058
Petersen RH (1989) Contributions toward a monograph of Ramaria-VIII. Some taxa sheltered under the name Ramaria flava. Persoonia 14:23–42
Pillukat A (1991) Vergleichende Untersuchung der Ektomykorrhizen von Russula ochroleuca und Paxillus involutus an verschiedeneen Baumarten. Thesis, University of München
Pillukat A (1996) Lactarius salmonicolor R. Heim &Leclair + Abies alba Mill. Descr Ectomyc 2:59–64
Pillukat A (1998) Lactarius salmonicolor. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 122. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Pillukat A, Agerer R (1992) Studien an Ektomykorrhizen XL. Vergleichende Untersuchungen zur baumbezogenen Variabilität der Ektomykorrhizen von Russula ochroleuca. Z Mykol 58:211–242
Pine EM, Hibbett DS, Donoghue MJ (1999) Phylogenetic relationships of cantharelloid and clavarioid Homobasidiomycetes based on mitochondrial and nuclear rDNA sequences. Mycologia 91:944–963
Powell CL (1976) Development of mycorrhizal infections from Endogone spores and infected root segments. Trans Br Mycol Soc 66:439–445
Prevost A, Pargney JC (1995) Comparison of natural ectomycorrhizas between beech (Fagus sylvatica) and 2 fungi (Lactarius blennius var. viridis and Lactarius subdulcis) I. Morphological and cytological characteristics. Ann Sci For (Paris) 52:131–146
Pritsch K (1996) Untersuchungen zur Diversität und Ökologie von Mykorrhizen der Schwarzerle (Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn.). Dissertation, University of Tübingen
Pritsch K, Munch JC, Buscot F (1997) Morpholgical and anatomical characterizaton of black alder Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn. Ectomycorrhizas. Mycorrhiza 7:201–216
Pritsch K, Raidl S, Marksteiner E, Blaschke H, Agerer R, Schloter M, Hartmann A (2004) A rapid and highly sensitive method for measuring enzyme activities in single mycorrhizal tips using 4-methylumbelliferone-labelled fluorogenic substrates in a microplate system. J Microbiol Methods 58:233–241
Raidl S (1997) Studien zur Ontogenie an Rhizomorphen von Ektomykorrhizen. Bibliotheca mycologica, vol 169. Cramer, Berlin Stuttgart
Raidl S (1998a) Tomentella ferruginea. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 137. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Raidl S (1998b) Rhizopogon melanogastroides. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 135. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Raidl S (1999) Chamonixia caespitosa Rolland + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 4:1–6
Raidl S, Agerer R (1992) Studien an Ektomykorrhizen XLII. Ontogenie der Rhizomorphen von Laccaria amethystina, Hydnum rufescens und Sarcodon imbricatus. Nova Hedwig 55:279–307
Raidl S, Agerer R (1998a) Hysterangium stoloniferum Tul. &Tul. + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 3:31–35
Raidl S, Agerer R (1998b) Rhizopogon roseolus (Corda) Th. M. Fr. + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 3:105–110
Raidl S, Hahn C (2006) Porphyrellus porphyrosporus (Fr. &Hök) E.-J. Gilbert + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Raidl S, Müller WR (1996) Tomentella ferruginea (Pers.) Pat. + Fagus sylvatica L. Descr Ectomyc 1:161–166
Raidl S, Scattolin L (2006) Ramaria formosa (Pers.) Quél. + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Raidl S, Verma R (2006) Amanita strobiliformis (Paulet ex Vittad.) Bertill.+ Betula pendula Roth. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Raidl S, Beenken L, Agerer R (1998) Rhizopogon melanogastroides M. Lange + Pinus mugo Turra. Descr Ectomyc 3:99–104
Raidl S, Scattolin L, Agerer R (2006a) Gyroporus castaneus (Bull.) Quél. + Quercus robur L. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Raidl S, Scattolin L, Agerer R (2006b) Cortinarius buillardii (Pers.) Fr.+ Quercus pubescens Willd. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Rauscher T, Chevalier G (1995a) Tuber melanosporum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 87. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Rauscher T, Chevalier G (1995b) Tuber mesentericum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 88. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Rauscher T, Chevalier G (1995c) Tuber rufum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 89. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Rauscher T, Agerer R, Chevalier G (1995) Ektomykorrhizen von Tuber melanosporum, Tuber mesentericum und Tuber rufum (Tuberales) an Corylus avellana. Nova Hedwig 61:281–322
Rauscher T, Müller WR, Chevalier G, Agerer R (1996a) Tuber aestivum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 112. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Rauscher T, Müller WR, Agerer R, Chevalier G (1996b) Tuber borchii Vitt. + Corylus avellana L. Descr Ectomyc 1:173–178
Rauscher T, Müller WR, Chevalier G, Agerer R (1996c) Tuber borchii. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 113. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Richter DL, Bruhn JN (1989) Pinus resinosa ectomycorrhizae: seven host–fungus combinations synthesized in pure culture. Symbiosis 7:211–228
Romagnesi H (1967) Les Russules d’Europa et d’Afrique du Nord. Bordas, Paris
Romagnesi H (1985) Les Russules d’Europe et d’Afrique du Nord (Reprint with supplement). Cramer, Vaduz
Romagnesi H (1987) Status et Noms nouveaux pour les taxa infrageneriques dans le Genre Russula. Doc Mycol Tome XVIII, Fascucule 69. Novitates 3:39–40
Rose RW, Van Dyke CG, Davey CB (1981) Scanning electron microscopy of three types of ectomycorrhizae formed on Eucalyptus novaanglica in the souteastern United States. Can J Bot 59:683–688
Sarnari M (1998) Monografia illustrata del genre Russula in Europa. Tomo Primo, Associazione Micologica Bresadola, Trento
Scattolin L, Raidl S (2006) Ramaria flavigelatinosa Marr &D. E. Stuntz + Fagus sylvatica L. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Scattolin L, Raidl S, Agerer R (2006) Byssoporia terrestris (DC.) Larsen &Zak + Picea abies (L.) Karst. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Schramm JR (1966) Plant colonization studies on black wastes from anthracite mining in Pennsylvania. Trans Am Philos Soc 56:5–189
Schweiger PF, Rouhier H, Söderström B (2002) Visualisation of ectomycorrhizal rhizomorph structure using laser scanning confocal microscopy. Mycol Res 106:349–354
Singer R (1986) The Agaricales in modern taxonomy, 4th edn. Koeltz, Koenigstein
Stadler M, Sterner O (1998) Production of bioactive secondary metablites in the fruit bodies of macrofungi as a response to injury. Phytochemistry 49:1013–1019
Stalpers JA (1974) Spiniger, a new genus for imperfect states of Basidiomycetes. Proc K Ned Akad Wet Ser C 77:402–407
Taylor AFS, Alexander IJ (1990) Ectomycorrhizal synthesis with Tylospora fibrillosa, a member of the Corticiaceae. Mycol Res 95:381–384
Trappe JM (1964) Mycorrhizal hosts and distribution of Cenococcum graniforme. Lloydia 27:100–106
Trappe M, Eberhart J, Luoma D (2000) Craterellus tubaeformis (Fr.) Quél. + Tsuga heterophylla (Raf.) Sarg. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement. Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE23.1–CDE23.4
Treu R (1990a) Charakterisierung und Identifizierung von Ektomykorrhizen aus dem Nationalpark Berchtesgaden. Bibliotheca mycologica vol 134. Cramer, Berlin Stuttgart
Treu R (1990b) Russula firmula.In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 43. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Treu R (1990c) Russula laricina. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 44. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Treu R (1990d) Lactarius alpinus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 40. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Treu R (1990e) Lactarius badiosanguineus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 41. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Treu R (1990f) Lactarius porninsiss. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 42. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Treu R (1990g) Boletinus cavipes. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 35. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Treu R (1990h) Suillus flavus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 45. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Treu R (1990i) Suillus plorans. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 46. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Treu R (1990k) Suillus sibiricus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 47. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Treu R (199l) Hebeloma edurum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 39. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Treu R (1993) Suillus laricinus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 81. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Uhl M (1988a) Identifizierung und Charakterisierung von Ektomykorrhizen an Pinus silvestris und von Ektomykorrhizen aus der Gattung Tricholoma. Dissertation, University of München
Uhl M (1988b) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. XV. Mycorrhizae formed by Rhizopogon luteolus on Pinus silvestris. Persoonia 13:449–458
Uhl M (1988c) Rhizopogon luteolus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 21. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Uhl M (1988d) Studies on ectomycorrhizae XVI. Ectomycorrhizae formed by Tricholoma flavobrunneum and Betula pendula and Tricholoma auratum and Pinus silvestris. Mycotaxon 33:1–21
Uhl M (1989) Tylopilus felleus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 33. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Uhl M, Agerer R (1987) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. XI. Mycorrhizae formed by Dermocybe crocea on Pinus silvestris and Dermocybe palustris on Pinus mugo. Nova Hedwig 45:509–527
Uhl M, Agerer R (1988) Dermocybe crocea. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 14. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Urban A (2003) Identifikation und Charakterisierung von Ektomykorrhizen an Eichen. Ph.D. thesis, University of Wien
Urban A, Weiß M, Bauer R (2003) Ectomycorrhizas involving sebacinoid mycobionts. Mycol Res 107:3–14
Urban A, Meuner-Plattner I, Krisai-Greilhuber I, Haselwandter K (2004) Molecular studies on terricolous microfungi reveal novel anamorphs of two Tuber species. Mycol Res 108:749–758
Verma R, Raidl S (2006) Lactarius lilacinus (Lasch) Fr.+ Alnus viridis (Caix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 9/10 (in press)
Vralstad T, Fossheim T, Schumacher T (2000) Piceirhiza bicolorata—the ectomycorrhizal expression of the Hymenoscyphus ericae aggregate? New Phytol 145:549–563
Waller K, Agerer R (1993a) Scleroderma citrinum. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 80. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Waller K, Agerer R (1993b) Ektomykorrhizen von Dermocybe cinnamomeolutea (Cortinariaceae) und Tricholoma acerbum (Tricholomataceae). Sendtnera 1:23–38
Waller K, Raidl S, Agerer R (1993) Die Ektomykorrhizen von Scleroderma citrinum. Z Mykol 59:141–153
Watling R, Taylor A, Lee Su See, Sims K, Alexander I (1995a) A rainforest Pisolithus, its taxonomy and ecology. Nova Hedwig 61:417–429
Watling R, Taylor AFS, Lee Su See, Sims K, Alexander I (1995b) Pisolithus aurantioscabrosus. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 85. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Weiß M, Oberwinkler F (2001) Phylogenetic relationships in Auriculariales and related groups—hypotheses derived from nuclear ribosomal sequences. Mycol Res 105:403–415
Weiss M (1989) Amphinema byssoides. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 23. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Weiss M (1990) Studien an Ektomykorrhizen. XXV. Untersuchungen zur Ontogenie von Ektomykorrhizen an Picea abies. Nova Hedwig 50:361–393
Weiss M (1991a) Studies on ectomycorrhizae. XXXIII. Description of three mycorrhizae synthesized on Picea abies. Mycotaxon 40:53–77
Weiss M (1991b) Pisolithus tinctorius. In: Agerer R (ed) Colour atlas of Ectomycorrhizae, plate 85. Einhorn, Schwäbisch Gmünd
Weiss M (1992) Mycorrhizae formed by Pisolithus tinctorius (Basidiomycetes) on Norway spruce. Cryptogam Bot 2:337–344
Weiss M, Bauer R, Begerow D (2004a) Spotlights on heterobasidiomycetes. In: Agerer R, Piepenbring M, Blanz P (eds) Frontiers in basidiomycote mycology. IHW-Verlag, Eching, pp 7–48
Weiss M, Selosse M-A, Rexer K-H, Urban A, Oberwínkler F (2004b) Sebacinales: a hitherto overlooked cosm of heterobasidiomycetes with a broad mycorrhizal potential. Mycol Res 108:1003–1010
Wiedmer E, Senn-Irlet B (1999a) Cortinarius alnobetulae Kühn. + Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 4:7–12
Wiedmer E, Senn-Irlet B (1999b) Cortinarius atropusillus Favre + Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 4:13–18
Wiedmer E, Senn-Irlet B (1999c) Cortinarius badiovestitus Mos.+ Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 4:29–23
Wiedmer E, Senn-Irlet B (1999d) Cortinarius kühneri Mos.+ Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 4:25–29
Wiedmer E, Senn-Irlet B (1999e) Cortinarius pluvius (Fr.) Fr. + Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 3:31–36
Wiedmer E, Senn-Irlet B (2001a) Cortinarius bibulus Quél.(= C. pulchellus Lge. = C. americanus Smith)+ Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 5:23–27
Wiedmer E, Senn-Irlet B (2001b) Cortinarius helvelloides (Fr.) Fr.+ Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 5:29–34
Wiedmer E, Senn-Irlet B (2004) Lactarius lepidotus Smith & Hesler + Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:45–48
Wiedmer E, Senn-Irlet B, Agerer R (2001) Alpova diplophloeus (Zeller &Dodge) Trappe &A. H. Smith + Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 5:1–8
Wiedmer E, Senn-Irlet B, Hahn C, Agerer R (2004) Melanogaster broomeianus Berk. ex Tul. + Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. Descr Ectomyc 7/8:49–57
Wöllecke J, Münzenberger B, Hüttl RF (1999) “Pinirhiza hyphocystidia” + Pinus sylvestris L. Descr Ectomyc 4:85–90
Wu C-G, Lin S-J (1997) Endogonales in Taiwan: a new genus with unizygosporic sporocarps and a hyphal mantle. Mycotaxon 64:179–188
Yamada A (1998a) Russula delica Fr. + Betula platyphylla Sukatchev var. japonica Hora. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement, Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE16.1–CDE16.4
Yamada A (1998b) Russula nigricans (Bull.: Fr.) Fr. + Betula platyphylla Sukatchev var. japonica Hora. In: Goodman DM, Durall DM, Trofymow JA, Berch SM (eds) Concise descriptions of North American Ectomycorrhizae. Mycologue Publications and Canada-B. C. Forest Resource Development Agreement, Canadian Forest Service, Victoria, B. C., pp CDE17.1–CDE17.4
Yamada A, Katsuya K (1996) Morphological classification of ectomycorrhizas of Pinus densiflora. Mycoscience 37:145–155
Yamada A, Kanekawa S, Ohmasa M (1999) Ectomycorrhiza formation of Tricholoma matsutake on Pinus densiflora. Mycoscience 40:193–198
Zak B (1969) Chracterization and classification of mycorrhizae of Douglas fir. I. Pseudotsuga menziesii + Poria terrestris (blue- and orange-staining strains). Can J Bot 47:1833–1840
Zak B (1971) Characterization and classification of mycorrhizas of Douglas fir. II. Pseudotsuga menziesii + Rhizopogon vinicolor. Can J Bot 49:1079–1084
Zak B, Larsen JM (1978) Characterization and classification of mycorrhizae of Douglas-fir. III. Pseudotsuga menziesii + Byssoporia (Poria) terrestris vars. lilacinorosea, parksii, and sublutea. Can J Bot 56:1616–1424
Zambonelli A, Branzanti MB (1984) Prove do micorrizazione del nocciolo con Tuber aestivum e Tuber albidum. Micol Ital 13(1):47–52
Zambonelli A, Salomoni S, Pisi A (1993) Caratterizzazione anatomo-morfologica delle micorrize di Tuber spp. su Quercus pubescens Willd. Micol Ital 3:73–90
Zambonelli A, Salomoni S, Pisi A (1995) Caratterizzazione anatomo-morfologica delle micorrize di Tuber borchii, Tuber aestivum, Tuber mesentericum, Tuber brumale, Tuber melanosporum su Pinus pinea. Micol Ital 1995(2):119–137
Zambonelli A, Tibiletti E, Pisi A (1997) Caratterizzazione anatomo-morfologica delle micorrize di Tuber indicum Cooke &Massee su Pinus pinea L. e Quercus cerris L. Micol Ital 28:29–36
Zambonelli A, Jotti M, Amicucci A, Pisi A (1999) Caratterizzazione anatomo-morfologica delle micorrize di Tuber maculatum Vittad. su Ostrya carpinifolia Scop. Micol Ital 28:29–35
Acknowledgements
I am very much obliged to Ludwig Beenken, Philomena Bodensteiner, Ingeborg Haug, and Stefan Raidl for reading and critically commenting on some parts of the manuscript and to Rita Verma for technical help. The financial support of our ectomycorrhizal studies during several projects by DFG (German Research Council) for more than 20 years is very much appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agerer, R. Fungal relationships and structural identity of their ectomycorrhizae. Mycol Progress 5, 67–107 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-006-0505-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-006-0505-x