Abstract
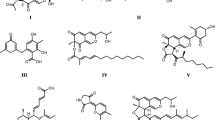
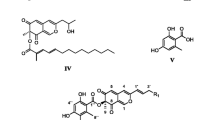
A novel azaphilone named hypomiltin was isolated by preparative reversed phase HPLC from the stromatal extract of the xylariaceous ascomycete Hypoxylon hypomiltum. Its chemical structure was determined by mass spectrometry and 2D nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Analytical HPLC profiling of stromatal crude extracts, using UV/visual (diode array) and mass spectrometric detection based on electrospray ionisation, revealed the presence of hypomiltin also in Hypoxylon intermedium, H. perforatum, H. trugodes, and Pulveria porrecta. In contrast, this compound was found neither in type material of H. hypomiltum var. lavandulocinereum nor in several further Hypoxylon species. Despite being chemically related to mitorubrin, hypomiltin never co-occurred with the latter compound and its derivatives. Characteristic secondary metabolite profiles of several further Hypoxylon species are correlated with the colours of their taxonomically significant KOH-extractable pigments. These species are divided into chemotypes, based on analytical HPLC data. The results point toward an extraordinary diversity of secondary metabolites in Hypoxylon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bills GF, Polishook JD, Goetz MA, Sullivan RF, White Jr. JF (2002) Chaunopycnis pustulata sp. nov., a new claviciptalean anamorph producing metabolites that modulate potassium ion channels. — Mycological Progress 1: 3–17.
Casser I (1983) Isolierung und Strukturaufklärung von Farbstoffen aus holzbewohnenden Pilzen. Doctoral thesis. University of Bonn, Germany.
Gill M, Steglich W (1987) Pigments of fungi (Macromycetes). In Herz W, Grisebach H, Kirby GW, Tamm C (eds) Progress in the chemistry of organic natural products, vol. 51, Springer Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
Granmo A (1999) Morphotaxonomy and chorology of the genus Hypoxylon (Xylariaceae) in Norway. — Sommerfeltia 26: 1–81.
Greenhalgh GN, Chesters CGC (1968) Conidiophore morphology in some British members of the Xylariaceae. — Transactions of the British Mycological Society 51: 57–82.
Greenhalgh, GN, Whalley AJS (1970) Stromal pigments of some species of Hypoxylon. — Transactions of the British Mycological Society 55: 89–96.
Hashimoto T, Tahara S, Takaoka S, Tori M, Asakawa Y (1994) Structures of Daldinins A-C, three novel azaphilone derivatives from ascomycetous fungus Daldinia concentrica. — Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 42: 2397–2399.
Hashimoto T, Asakawa Y (1998) Biologically active substances of Japanese inedible mushrooms. — Heterocycles 47: 1067–1110.
Johannesson H (2001) Ecology of Daldinia spp. with special emphasis on Daldinia loculata. PhD Thesis. Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala, Sweden.
Jong SC, Rogers JD (1972) Illustrations and descriptions of conidial states of some Hypoxylon species. Washington State Agricultural Experimental Station Bulletin, No. 71.
Ju YM, Rogers JD (1996) A revision of the genus Hypoxylon. Mycologia Memoir no. 20. APS Press, St. Paul, MN., USA.
Ju Y-M, Rogers JD (2002) The genus Nemania (Xylariaceae). — Nova Hedwigia 74: 75–120.
Ju YM, Rogers JD, San Martín F (1997) A revision of the genus Daldinia. — Mycotaxon 61: 243–293.
Ju Y-M, Rogers JD, San Martín F, Granmo A (1998) The genus Biscogniauxia. — Mycotaxon 66: 1–98.
Ju Y-M, Rogers JD & Hsieh HM (2004) New Hypoxylon species and notes on some names associated with or related to Hypoxylon. — Mycologia 96: 154–161.
Laessøe T, Rogers JD, Whalley AJS (1989) Camillea, Jongiella and light-spored species of Hypoxylon. — Mycological Research 93: 121–155.
Malloch D, Rogerson CT (1977) Pulveria, a new genus of Xylariaceae (Ascomycetes). — Canadian Journal of Botany 55: 1505–1509.
Martin P (1968) Studies in the Xylariaceae: IV. Hypoxylon, sections Papillata and Annulata. — South African Journal of Botany 34: 303–330.
Martin P (1969) Studies in the Xylariaceae: V. Euhypoxylon. — South African Journal of Botany 35: 149–206.
Miller JH (1961) A monograph of the world species of Hypoxylon. Univ. Georgia Press, Athens, Georgia, USA.
Mühlbauer A, Triebel D, Persoh D, Wollweber H, Seip S, Stadler M (2002) Macrocarpones, novel metabolites from stromata of Hypoxylon macrocarpum and new evidence on the chemotaxonomy of Hypoxylon. — Mycological Progress 1: 235–248.
Nielsen KF, Smedsgaard J (2003) Fungal metabolite screening: database of 474 mycotoxins and fungal metabolites for dereplication by standardised liquid chromatography—UV-mass spectrometry methodology. — Journal of Chromatography 1002A: 111–136.
Ogasawara N, Kawai K (1998) Hydrogenated azaphilones from Emericella falconensis and E. fruticulosa. — Phytochemistry 47: 1131–1135.
Parenicova L, Skouboe P, Frisvad JC, Samson RA, Rossen L, ten Hoor-Suykerbuyk M, Visser J (2001) Combined molecular and biochemical approach identifies Aspergillus japonicus and Aspergillus aculeatus as two species. — Applied and Environmental Microbiology 67: 521–527
Petch T (1924) Xylariaceae Zeylanicae. — Annuals of the Royal Botanical Garden (Peradeniya) 8: 119–166.
Petrini, LE, Müller E (1986) Haupt-und Nebenfruchtformen europäischer Hypoxylon-Arten (Xylariaceae, Sphaeriales) und verwandter Pilze. — Mycologia Helvetica 1: 501–627.
Polishook JD, Ondeyka JB, Dombrowski AW, Peláez F, Platas G, Teran AM (2001). Biogeography and relatedness of Nodulisporium strains producing nodulisporic acid. — Mycologia 93: 1125–1137.
Pouzar Z (1972) Hypoxylon fraxinophilum spec. nov. and H. moravicum spec. nov., two interesting species found on Fraxinus angustifolia. — Ceská Mykologia 26: 129–137.
Quang DN, Hashimoto T, Tanaka M, Baumgartner M, Stadler M, Asakawa Y (2002) Chemical constituents of the ascomycete Daldinia concentrica. — Journal of Natural Products 65: 1869–1874.
Quang DN, Hashimoto T, Tanaka M, Stadler M, Asakawa Y (2004a) Cyclic azaphilones daldinins E and F from the ascomycete fungus Hypoxylon fuscum. — Phytochemistry 65: 469–473.
Quang DN, Hashimoto T, Stadler M, Asakawa Y (2004b) Chemical constituents of the inedible mushroom Hypoxylon rubignosum. — Journal of Natural Products 67: 1152–1155.
Rayner RW (1970) A mycological colour chart. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew and British Mycological Society.
Rogers JD (1982) Entonaema liquescens: description of the anamorph and thoughts on its systematic position. — Mycotaxon 15: 500–506.
Rogers JD (2000) Thoughts and musings about tropical Xylariaceae. — Mycological Research 104: 1412–1420.
Rogers JD, Ju Y-M (1998) The genus Kretzschmaria. — Mycotaxon 68: 345–393.
Sánchez-Ballesteros J, González V, Salazar O, Acero J, Portal MA, Julián M, Rubio V, Bills GF, Polishook JD, Platas G, Mochales S, Peláez F (2000) Phylogenetic study of Hypoxylon and related genera based on ribosomal ITS sequences. — Mycologia 92: 964–977.
Stadler M, Anke H, Dekermendijan K, Reiss R, Sterner O, Witt M.R. (1995) New azaphilones from fruit-bodies and mycelial cultures of the ascomycete Bulgaria inquinans. — Natural Product Letter 7: 7–14.
Stadler M, Baumgartner M, Grothe T, Mühlbauer A, Seip S, Wollweber H (2001c) Concentricol, a taxonomically significant triterpenoid from Daldinia concentrica. — Phytochemistry 56: 787–793.
Stadler M, Baumgartner M, Wollweber H. (2001d) Three new Daldinia species with yellow stromatal pigments. — Mycotaxon 80: 179–196.
Stadler M, Ju YM, Rogers JD (2004a) Chemotaxonomy of Entonaema, Rhopalostroma and other Xylariaceae. — Mycological Research 108: 239–256.
Stadler M, Tichy HV, Katsiou E, Hellwig V (2003) Chemotaxonomy of Pochonia and other conidial fungi with Verticillium-like anamorphs. — Mycological Progress 2: 95–122.
Stadler M, Wollweber H, Baumgartner M, Ju YM, Rogers JD (2001e) Daldinia decipiens sp. nov. and notes on further Daldinia spp. inhabiting Betulaceae in Europe. — Mycotaxon 80: 167–176.
Stadler M, Wollweber H, Fournier J (2004b) A host-specific species of Hypoxylon from France, and notes on the chemotaxonomy of the ‘Hypoxylon rubiginosum complex’. — Mycotaxon 90: 187–211.
Stadler M, Wollweber H, Mühlbauer A, Asakawa Y, Hashimoto T, Rogers JD, Ju YM, Wetzstein HG, Tichy HV (2001b) Molecular chemotaxonomy of Daldinia and other Xylariaceae. — Mycological Research 105: 1191–1205.
Stadler M, Wollweber H, Mühlbauer A, Henkel T, Wollweber H, Asakawa Y, Hashimoto T, Rogers JD, Ju YM, Wetzstein HG, Tichy HV (2001a) Secondary metabolite profiles, genetic fingerprints and taxonomy of Daldinia and allies. — Mycotaxon 77: 379–429.
Steglich W, Klaar M, Furtner W (1974) (−)-Mitorubrin derivatives from Hypoxylon fragiforme. — Phytochemistry 13: 2874–2875.
Suzuki S, Hosoe T, Nozawa K, Yaguchi T, Udagawa S, Kawai K (1999) Mitorubrin derivatives on ascomata of some Talaromyces species of ascomyceteous fungi. — Journal of Natural Products 62: 1329–1329.
Thines E, Anke H, Sterner O (1998) Trichoflectin, a bioactive azaphilone from the ascomycete Trichopezizella nidulus. — Journal of Natural Products 61: 306–308.
Triebel D, Persoh D, Wollweber, H & Stadler M (2005) Phylogenetic relationships among Daldinia, Entonaema, and Hypoxylon as inferred from ITS nrDNA analyses of Xylariales. — Nova Hedwigia 80: 25–43.
Tuthill DE, Frisvad JC, Christensen M (2001) Systematics of Penicillium simplicissimum based on rDNA sequences, morphology and secondary metabolites. — Mycologia 93: 298–308.
Whalley AJS, Edwards RL (1995) Secondary metabolites and systematic arrangement within the Xylariaceae. — Canadian Journal of Botany 73Suppl.1: S802–S810.
Whalley AJS, Edwards RL (1998) The Xylariaceae: A study in biological and chemical diversity. — Pure and Applied Chemistry 70: 2123, and concurrent pdf download available from the Internet: http://www.iupac.org/symposia/proceedings/phuket97/whalley.pdf
Whalley AJS, Greenhalgh GN (1971) Chemical races of Hypoxylon rubiginosum. — Transactions of the British Mycological Society 57: 161–164.
Whalley AJS, Whalley MA (1977) Stromal pigments and taxonomy of Hypoxylon. — Mycopathologia 61: 99–103.
Wollweber H, Stadler M (2001) Zur Kenntnis der Gattung Daldinia in Deutschland und Europa. — Zeitschrift für Mykologie 67: 3–51.
Yasukawa K, Takahashi M, Natori S, Kawai K, Yamazaki M, Takeuchi M, Takido M (1994) Azaphilones inhibit tumor promotion by 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate in two-stage carcinogenesis in mice. — Oncology 51: 108–112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to Timm Anke, Kaiserslautern, on the occasion of his 60th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hellwig, V., Ju, YM., Rogers, J.D. et al. Hypomiltin, a novel azaphilone from Hypoxylon hypomiltum, and chemotypes in Hypoxylon sect. Hypoxylon as inferred from analytical HPLC profiling. Mycol Progress 4, 39–54 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-006-0108-6
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-006-0108-6