Abstract
Purpose
Existing methods for sorting, labeling, registering, and across-subject localization of electrodes in intracranial encephalography (iEEG) may involve laborious work requiring manual inspection of radiological images.
Methods
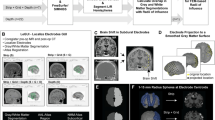
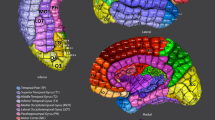
We describe a new open-source software package, the interactive electrode localization utility which presents a full pipeline for the registration, localization, and labeling of iEEG electrodes from CT and MR images. In addition, we describe a method to automatically sort and label electrodes from subdural grids of known geometry.
Results
We validated our software against manual inspection methods in twelve subjects undergoing iEEG for medically intractable epilepsy. Our algorithm for sorting and labeling performed correct identification on 96% of the electrodes.
Conclusions
The sorting and labeling methods we describe offer nearly perfect performance and the software package we have distributed may simplify the process of registering, sorting, labeling, and localizing subdural iEEG grid electrodes by manual inspection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Penfield W, Jasper HH (1954) Epilepsy and the functional anatomy of the human brain. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Engel AK, Moll CK, Fried I, Ojemann G (2005) Invasive recordings from the human brain: clinical insights and beyond. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:35–47
Tao JX, Ray A, Hawes-Ebersole S, Ebersole JS (2005) Intracranial EEG substrates of scalp EEG interictal spikes. Epilepsia 46:669–676
Crone NE, Boatman D, Gordon B, Hao L (2001) Induced electrocorticographic gamma activity during auditory perception. Clin Neurophysiol 112:565–582
Meltzer JA, Zaveri HP, Goncharova II, Distasio MM, Papademetris X, Spencer SS, Constable RT (2008) Effects of working memory load on oscillatory power in human intracranial EEG. Cereb Cortex 18:1843–1855
Lachaux JP, Fonlupt P, Kahane P, Minotti L, Hoffman D, Bertrand O, Baclu M (2007) Relationship between task-related gamma oscillations and BOLD signal: new insights from combined fMRI and intracranial EEG. Hum Brain Mapp 28:1368–1375
Jerbi K, Ossandon T, Hamame CM, Senova S, Dalal SS, Jung J, Minotti L, Bertrand O, Berthaz A, Kahane P, Lachaux JP (2009) Task-related gamma-band dynamics from an intracerebral perspective: review and implications for surface EEG and MEG. Hum Brain Mapp 30:1758–1771
Cash SS, Halgren E, Dehghani N, Rossetti AO, Thesen T, Wang C, Devinsky O, Kuzniecky R, Doyle W, Madsen JR, Bromfield E (2009) The human K-complex represents an isolated cortical down-state. Science 324:1084–1087
Hermes D, Miller KJ, Noordmans HJ, Vansteensel MJ, Ramsey NF (2010) Automated electrocorticographic electrode localization on individually rendered brain surfaces. J Neurosci Methods 185:293–298
Dalal SS, Edwards E, Kirsch HE, Barbaro NM, Knight RT, Nagarajan SS (2008) Localization of neurosurgically implanted electrodes via photograph-MRI-radiograph coregistration. J Neurosci Methods 174:106–115
Yang AI, Wang X, Doyle WK, Halgren E, Carlson C, Belcher TL, Cash SS, Devinsky O, Thesen T (2012) Localization of dense intracranial electrode arrays using magnetic resonance imaging. NeuroImage 63:157–165
Schulze-Bonhage AH, Huppertz HJ, Comeau RM, Honegger JB, Spreer JM, Zentner JK (2002) Visualization of subdural strip and grid electrodes using curvilinear reformatting of 3D MR imaging data sets. Am J Neuroradiol 23:400–403
Kovalev D, Spreer JM, Honegger JB, Zentner JK, Schulze-Bonhage AH, Huppertz H-J (2005) Rapid and fully automated visualization of subdural electrodes in the presurgical evaluation of epilepsy patients. Am J Neuroradiol 26:1078–1083
Kamida T, Anan M, Shimotaka K, Abe T, Fujiki M, Kobayashi H (2010) Visualization of subdural electrodes with fusion CT scan/MRI during neuronavigation-guided epilepsy surgery. J Clin Neurosci 17:511–513
Reuter M, Rosas HD, Fischl B (2010) Highly accurate inverse consistent registration: a robust approach. NeuroImage 53:1181–1196
Dykstra AR, Chan AM, Quinn BT, Zepeda R, Keller CJ, Cormier J, Madsen JR, Eskandar EN, Cash SS (2012) Individualized localization and cortical surface-based registration of intracranial electrodes. NeuroImage 59:3563–3570
Taimouri V, Akhonda-Asi A, Tomas-Fernandez T, Peters JM, Prabhu SP, Poduri A, Takeoka M, Loddenkemper T, Bergin AMR, Harini C, Madsen JR, Warfield SK (2014) Electrode localization for planning surgical resection of the epileptogenic zone in pediatric epilepsy. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 9:91–105
Princich JP, Wassermann D, Latini F, Oddo S, Blenkmann AO, Seifer G, Kochen S (2013) Rapid and efficient localization of depth electrodes and cortical labeling using free and open source medical software in epilepsy surgery candidates. Front Neurosci 7:260
Hill DL, Maurer CR, Maciunas RJ, Barwise JA, Fitzpatrick MJ, Wang MY (1998) Measurement of intraoperative brain surface deformation under a craniotomy. Neurosurgery 43:514–526
Van Laarhoven PJ, Aarts EH (1987) Simulated annealing: theory and applications. Springer, Berlin
Ramachandran P, Varoquaux G (2011) Mayavi: 3D visualization of scientific data. Comput Sci Eng 13:40–51
Hunter JD (2007) Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. IEEE Comput Sci Eng 9:90–95
Gramfort A, Luessi M, Larson E, Engemann DA, Strohmeier D, Brodbeck C, Goj R, Jas M, Brooks T, Parkkonen L, Hämäläinen M (2013) MEG and EEG data analysis with MNE-python. Front Neurosci 7:267
Fischl B (2012) FreeSurfer. NeuroImage 62:774–781
Acknowledgements
We thank Giovanni Piantoni for his assistance with hardware and technical support. We thank Kristen K. Ellard, Samuel Zorowitz, Tatiana Sitnikova, Afsana Afzal, Anna L. Gilmour, Amanda R. Arulpragasam, and Thilo Deckersbach for their assistance with data collection. This work was made possible by grants NCRR S10RR014978, NIH S10RR031599, R01-NS069696, 5RO1-NS060918, U01MH093765, 1S10RR023043, 1S10RR023401, P41-EB015896. This work was sponsored by the U.S. Army Research Office and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency under Cooperative Agreement Number W911NF-14-2-0045. The aforementioned sponsor played no role in collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, and played no role in preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Statement of human rights
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Statement on the welfare of animals
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LaPlante, R.A., Tang, W., Peled, N. et al. The interactive electrode localization utility: software for automatic sorting and labeling of intracranial subdural electrodes. Int J CARS 12, 1829–1837 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1504-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1504-2