Abstract
Rational and objectives
To compare thin-section computed tomography (CT) features of pulmonary cryptococcosis (PC) in immunocompetent and non-AIDS immunocompromised patients.
Materials and methods
We retrospectively reviewed CT findings of 18 immunocompetent and 24 non-AIDS immunocompromised patients with clinically proven PC. Different patterns of pulmonary abnormalities between the two groups of patients were compared by Fisher’s exact test.
Results
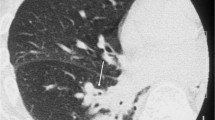
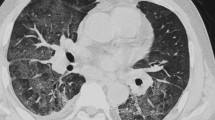
Pulmonary nodules were present in 37 of the 42 patients. Masses were detected in 16 patients and consolidation in 9. There were 12 patients with a solitary nodule or mass. Masses were associated with nodules in 12 patients. Consolidation was associated with nodules/masses in nine patients. The nodules/masses were associated with cavitations in 13 patients. Margination of nodules/masses was well defined in nine patients and ill-defined in 33. The abnormalities were predominantly distributed in the peripheral region of the lung (n = 29, 69.0%). The presence of cavitations in nodules/masses was significantly more frequent in non-AIDS immunocompromised than in immunocompetent patients (P = 0.001).
Conclusions
The most common thin-section CT feature of PC was pulmonary nodules/masses, which were ill-defined and located peripherally. Cavitations within nodules/masses were more commonly found in non-AIDS immunocompromised patients. PC should be considered in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary nodules/masses.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perfect JR, Dismukes WE, Dromer F, Goldman DL, Graybill JR, Hamill RJ, Harrison TS, Larsen RA, Lortholary O, Nguyen MH, Pappas PG, Powderly WG, Singh N, Sobel JD, Sorrell TC (2010) Clinical practice guidelines for the management of cryptococcal disease: 2010 update by the infectious diseases society of America. Clin Infect Dis 50(3):291–322. https://doi.org/10.1086/649858
Chang WC, Tzao C, Hsu HH, Lee SC, Huang KL, Tung HJ, Chen CY (2006) Pulmonary cryptococcosis: comparison of clinical and radiographic characteristics in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. Chest 129(2):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.129.2.333
Xie L, Chen Y, Liu S, Shi Y (2015) Pulmonary cryptococcosis: comparison of CT findings in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. Acta Radiol 56(4):447–453. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185114529105
Kishi K, Homma S, Kurosaki A, Kohno T, Motoi N, Yoshimura K (2006) Clinical features and high-resolution CT findings of pulmonary cryptococcosis in non-AIDS patients. Respir Med 100(5):807–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2005.09.017
Lacomis JM, Costello P, Vilchez R, Kusne S (2001) The radiology of pulmonary cryptococcosis in a tertiary medical center. J Thorac Imaging 16(3):139–148
Hu Z, Chen J, Wang J, Xiong Q, Zhong Y, Yang Y, Xu C, Wei H (2017) Radiological characteristics of pulmonary cryptococcosis in HIV-infected patients. PLoS ONE 12(3):e0173858. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173858
Fox DL, Müller NL (2005) Pulmonary cryptococcosis in immunocompetent patients: CT findings in 12 patients. Am J Roentgenol 185(3):622–626. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.185.3.01850622
Lindell RM, Hartman TE, Nadrous HF, Ryu JH (2005) Pulmonary cryptococcosis: CT findings in immunocompetent patients. Radiology 236(1):326–331. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2361040460
Nadrous HF, Antonios VS, Terrell CL, Ryu JH (2003) Pulmonary cryptococcosis in nonimmunocompromised patients. Chest 124(6):2143–2147
He Q, Ding Y, Zhou W, Li H, Zhang M, Shi Y, Su X (2017) Clinical features of pulmonary cryptococcosis among patients with different levels of peripheral blood CD4(+) T lymphocyte counts. BMC Infect Dis 17:768. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-017-2865-z
Song KD, Lee KS, Chung MP, Kwon OJ, Kim TS, Yi CA, Chung MJ (2010) Pulmonary cryptococcosis: imaging findings in 23 non-AIDS patients. Korean J Radiol 11(4):407–416. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2010.11.4.407
Qu Y, Liu G, Ghimire P, Liao M, Shi H, Yang G, Xu L, Wang G (2012) Primary pulmonary cryptococcosis: evaluation of CT characteristics in 26 immunocompetent Chinese patients. Acta Radiol 53(6):668–674. https://doi.org/10.1258/ar.2012.110612
Connor DH, Chandler F, Schwartz DA et al (eds) (1997) Pathology of infectious diseases. Appleton & Lange, Baltimore
Park CM, Goo JM, Lee HJ, Lee CH, Chun EJ, Im JG (2007) Nodular ground-glass opacity at thin-section CT: histologic correlation and evaluation of change at follow-up. Radiographics 27(2):391–408. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.272065061
Guimaraes MD, Marchiori E, Meirelles GS, Hochhegger B, Santana PR, Gross JL, Bitencourt AG, Boonsirikamchai P, Godoy MC (2013) Fungal infection mimicking pulmonary malignancy: clinical and radiological characteristics. Lung 191(6):655–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-013-9506-0
Igai H, Gotoh M, Yokomise H (2006) Computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography with [18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose (FDG-PET) images of pulmonary cryptococcosis mimicking lung cancer. Eur J Cardio-thorac Surg 30(6):837–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcts.2006.09.022
Sudhakaran S, Bashoura L, Stewart J, Balachandran DD, Faiz SA (2017) Pulmonary cryptococcus presenting as a solitary pulmonary nodule. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 196(9):1217–1218. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201703-0601IM
Wang SY, Chen G, Luo DL, Shao D, Liu ET, Sun T, Wang SX (2017) (18)F-FDG PET/CT and contrast-enhanced CT findings of pulmonary cryptococcosis. Eur J Radiol 89:140–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.02.008
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors Xin Sui, Yao Huang, Wei Song, Fuling Zheng, Xiao Wang, Xiaoli Xu, Zixing Wang, Jinmei Jiang and Zhengyu Jin declare that they have no conflict of interest.
IRB statement
The Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Peking Union Medical College Hospital (Approval No. S-598).
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sui, X., Huang, Y., Song, W. et al. Clinical features of pulmonary cryptococcosis in thin-section CT in immunocompetent and non-AIDS immunocompromised patients. Radiol med 125, 31–38 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-019-01088-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-019-01088-8