Abstract
Background
We aimed to establish risk factors for radiological lung damage associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and determine whether clinical findings and pulmonary function test were correlated with Warrick score calculated on the basis of high-resolution computed tomography or not.
Methods
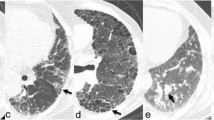
One hundred thirty RA patients who were followed at rheumatology outpatient clinic were included through retrospective screening. To evaluate radiological involvement, the semi-quantitative evaluation proposed by Warrick was used to assign a score for each lesion based on the severity and extent of the pulmonary damage. In addition to the total score, indices for alveolitis and fibrosis were created. The correlations between each score and clinical and functional parameters were tested for all patients.
Results
We showed that age was an independent explanatory variable of radiological lung damage. Percentage of predicted lung diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (DLco) below 75 % and presence of respiratory symptoms were found to contribute more to radiological lung damage. Warrick score was positively correlated with age at study onset (r = 0.43, p < 0.001). In addition, a negative correlation was found between Warrick score and DLco % predicted (r = −0.357, p = 0.001). Alveolitis index was negatively correlated with DLco % predicted (r = −0.321, p = 0.003).
Conclusions
It is considered that this semi-quantitative method may have added value in early diagnosis, appropriate treatment decisions and follow-up when taken into account together with risk factors associated with pulmonary damage in RA.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turesson C, O’Fallon WM, Crowson CS, Gabriel SE, Matteson EL (2002) Occurrence of extra-articular disease manifestations is associated with excess mortality in a community based cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 29:62–67
Gabriel SE, Crowson CS, Kremers HM et al (2003) Survival in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based analysis of trends over 40 years. Arthritis Rheum 48:54–58
Turesson C, O’Fallon WM, Crowson CS, Gabriel SE, Matteson EL (2003) Extra-articular disease manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis: incidence trends and risk factors over 46 years. Ann Rheum Dis 62:722–727
Bongartz T, Nannini C, Medina-Velasquez YF et al (2010) Incidence and mortality of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 62:1583–1591
Anaya JM, Diethelm L, Ortiz LA et al (1995) Pulmonary involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 24:242–254
Nannini C, Ryu JH, Matteson EL (2008) Lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Cur Opin Rheum 20:340–346
Wallaert B, Hatron PY, Grosbois JM, Tonnel AB, Devulder B, Voisin C (1986) Subclinical pulmonary involvement in collagen-vascular diseases assessed by bronchoalveolar lavage. Relationship between alveolitis and subsequent changes in lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis 133:574–580
Bellia M, Cannizzaro F, Scichilone N et al (2009) HRCT and scleroderma: semi-quantitative evaluation of lung damage and functional abnormalities. Radiol Med 114:190–203
Murata K, Khan A, Herman PG (1989) Pulmonary parenchymal disease: evaluation with high-resolution CT. Radiology 170:629–635
Warrick JH, Bhalla M, Schabel SI, Silver RM (1991) High-resolution computed tomography in early scleroderma lung disease. J Rheumatol 18:1520–1528
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
van der Heijde DM, van’t Hof MA, van Riel PL, van Leeuwen MA, van Rijswijk MH, van de Putte LB (1992) Validity of single variables and composite indices for measuring disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 51:177–181
Quanjer PH, Tammeling GJ, Cotes JE, Pedersen OF, Peslin R, Yernault JC (1993) Lung volumes and forced ventilatory flows. Report Working Party Standardization of Lung Function Tests, European Community for Steel and Coal. Official Statement of the European Respiratory Society. Eur Respir J Suppl 16:5–40
Cotes JE, Chinn DJ, Quanjer PH, Roca J, Yernault JC (1994) Standardization of the measurement of transfer factor (diffusing capacity). Work Group on Standardization of Respiratory Function Tests. European Community for Coal and Steel. Official position of the European Respiratory Society. Rev Mal Respir 11:41–52
Akira M, Sakatani M, Hara H (1999) Thin-Section CT findings in rheumatoid arthritis associated lung disease: CT patterns and their courses. J Comput Assist Tomogr 23:941–948
Jin Seon L, Jung-Gi I, Joong MA, Yang MK, Man CH (1992) Fibrosing alveolitis: prognostic implication of ground glass attenuation at high resolution CT. Radiology 184:451–454
Dawson JK, Fewins HE, Desmond J, Lynch MP, Graham DR (2001) Fibrosing alveolitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis as assessed by high resolution computed tomography, chest radiography, and pulmonary function tests. Thorax 56:622–627
Youssef AA, Machaly SA, El-Dosoky ME, El-Maghraby NM (2012) Respiratory symptoms in rheumatoid arthritis: relation to pulmonary abnormalities detected by high-resolution CT and pulmonary functional testing. Rheumatol Int 32:1985–1995
Karazincir S, Akoglu S, Guler H, Balci A, Babayigit C, Egilmez E (2009) The evaluation of early pulmonary involvement with high-resolution computerized tomography in asymptomatic and non-smoker patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Tuberk Toraks 57:14–21
Kanat F, Levendoglu F, Teke T (2007) Radiological and functional assessment of pulmonary involvement in the rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatol Int 27:459–466
Bilgici A, Ulusoy H, Kuru O, Celenk C, Unsal M, Danaci M (2005) Pulmonary involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 25:429–435
Zrour SH, Touzi M, Bejia I et al (2005) Correlations between high-resolution computed tomography of the chest and clinical function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Prospective study in 75 patients. Joint Bone Spine 72:41–47
Koduri G, Norton S, Young A et al (2010) Interstitial lung disease has a poor prognosis in rheumatoid arthritis: results from an inception cohort. Rheumatology 49:1483–1489
Aubart F, Crestani B, Nicaise-Roland P et al (2011) High levels of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide autoantibodies are associated with co-occurrence of pulmonary diseases with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 38:979–982
Bongartz T, Nannini C, Medina-Velasquez YF et al (2010) Incidence and mortality of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 62:1583–1591
Shidara K, Hoshi D, Inoue E et al (2010) Incidence of and risk factors for interstitial pneumonia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a large Japanese observational cohort, IORRA. Mod Rheumatol 20:280–286
Doyle TJ, Dellaripa PF, Batra K et al (2014) Functional impact of a spectrum of interstitial lung abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis. Chest 146:41–50
Perez T, Remy-Jardin M, Cortet B (1998) Airways involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical, functional, and HRCT findings. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157:1658–1665
Lee HK, Kim DS, Yoo B et al (2005) Histopathologic pattern and clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis associated interstitial lung disease. Chest 127:2019–2027
Hamblin MJ, Horton MR (2011) Rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: diagnostic dilemma. Pulm Med. doi:10.1155/2011/872120
Leonel D, Lucia C, Muniz A, Martha-Alicia H, Blanca M (2012) Pulmonary function test: its correlation with pulmonary high-resolution computed tomography in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 32:2111–2116
Pappas DA, Giles JT, Connors G, Lechtzin N, Bathon JM, Danoff SK (2010) Respiratory symptoms and disease characteristics as predictors of pulmonary function abnormalities in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: an observational cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R104. doi:10.1186/ar3037
Dawson JK, Graham DR, Desmond J, Fewins HE, Lynch MP (2002) Investigation of the chronic pulmonary effects of low-dose oral methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study incorporating HRCT scanning and pulmonary function tests. Rheumatology (Oxford) 41:262–267
Khadadah ME, Jayakrishnan B, Al-Gorair S et al (2002) Effect of methotrexate on pulmonary function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis—a prospective study. Rheumatol Int 22:204–207
Conway R, Low C, Coughlan RJ, O’Donnell MJ, Carey JJ (2014) Methotrexate and lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheum 66:803–812
Saag KG, Kolluri S, Koehnke RK et al (1996) Rheumatoid arthritis lung disease. Determinants of radiographic and physiologic abnormalities. Arthritis Rheum 39:1711–1719
Remy-Jardin M, Giraud F, Remy J, Copin MC, Gosselin B, Duhamel A (1993) Importance of ground-glass attenuation in chronic diffuse infiltrative lung diseases: pathologic- CT correlations. Radiology 189:693–698
Gochuico BR, Avila NA, Chow CK et al (2008) Progressive preclinical interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Intern Med 168:159–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding support
There was no funding support in this study.
Conflict of interest
Baris Yilmazer declares that he has no conflict of interest. Sevtap Gümüştaş declares that she has no conflict of interest. Fulya Coşan declares that she has no conflict of interest. Nagihan İnan declares that she has no conflict of interest. Fatih Ensaroğlu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Gökhan Erbağ declares that he has no conflict of interest. Füsun Yıldız declares that she has no conflict of interest. Ayşe Cefle declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yilmazer, B., Gümüştaş, S., Coşan, F. et al. High-resolution computed tomography and rheumatoid arthritis: semi-quantitative evaluation of lung damage and its correlation with clinical and functional abnormalities. Radiol med 121, 181–189 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-015-0590-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-015-0590-5