Abstract
Purpose
This study sought to evaluate acute toxicity and local control in patients who underwent extracranial stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for paracardiac and cardiac metastatic lesions, defined as such when located at a maximum distance of 1 cm from the heart or inside its parenchyma.
Materials and methods
Between January 2009 and May 2011, 16 patients with paracardiac and cardiac lesions were treated with SBRT. For dose specification, in 15 of 16 patients, the prescription dosage was 36 Gy in three fractions (70% isodose). In one patient, the target lesion was inside the heart, and the prescription dosage was 30 Gy in three fractions (70% isodose).
Results
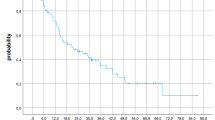
Regarding response to stereotactic radiotherapy, we recorded one (6%) complete response (CR), six (37%) partial responses (PR), five (32%) stable disease (SD) and four (25%) local failures. Median interval to local failure was 5.2 (range, 3–12) months. The cause of death was distant progression of disease in all four patients. Compliance to treatment was excellent; no patient developed cardiological symptoms or electrocardiographic abnormalities, even months after SBRT.
Conclusions
Results of our retrospective study indicate that SBRT represents a safe and effective treatment option for patients with cardiac and paracardiac metastases.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
Scopo di questo lavoro è valutare la tossicità acuta e il controllo locale nel trattamento di pazienti sottoposti a radioterapia stereotassica extracranica (SBRT) per lesioni metastatiche paracardiache e cardiache, definite come tali se localizzate entro 1 cm dal cuore o nel contesto del suo parenchima
Materiali e metodi
Fra gennaio 2009 e maggio 2011, 16 pazienti con lesioni paracardiache e cardiache sono stati sottoposti a SBRT. In 15/16 pazienti la dose prescritta è stata di 36 Gy in 3 frazioni (all’isodose del 70%). In un paziente la lesione target era intracardiaca, e la dose di prescrizione è stata di 30 Gy in 3 frazioni (all’isodose del 70%).
Risultati
Per quanto concerne la risposta alla radioterapia stereotassica, è stata registrata 1 (6%) risposta completa (CR), 6 (37%) risposte parziali (PR), 5 (32%) stabilità di malattia (SD) e 4 (25%) progressioni locali. L’intervallo mediano alla progressione locale è stato di 5,2 mesi (range 3–12 mesi). La tolleranza al trattamento è stata ottimale; nella serie di pazienti trattati nessuno ha sviluppato segni o sintomi di natura cardiologica in conseguenza della SBRT.
Conclusioni
I risultati della nostra analisi retrospettiva indicano che la SBRT rappresenta una opzione terapeutica sicura ed efficace per metastasi cardiache e paracardiache.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
Pastorino U, Buyse M, Freidel G et al (1997) Long-term results of lung metastectomy: prognostic analyses based on 5206 cases. The International Registry of Lung Metastases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 113:37–49
Salgia R, Hensing T, Campbell N et al (2011) Personalized treatment of lung cancer. Semin Oncol 38:274–83
Timmerman RD, Bizekis CS, Pass HI et al (2009) Local surgical, ablative, and radiation treatment of metastases. Ca cancer J Clin 59:145–170
Rusthoven KE, Kavanagh BD, Burri SH et al (2009) Multi-institutional phase I/II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung metastases. J Clin Oncol 27:1579–1584
Si YS, Wonsik C, Seong SS et al (2009) Fractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable stage I lung cancer adjacent to central large bronchus. Lung Cancer 66:89–93
Timmerman R, McGarry R, Yiannoutsos C et al (2006) Excessive toxicity when treating central tumors in a phase II study of stereotactic body radiation therapy for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:4833–4839
Masi L, Casamassima F, Menichelli C et al (2008) On-line image guidance for frameless stereotactic radiotherapy of lung malignancies by cone beam CT: comparison between target localization and alignment on bony anatomy. Acta Oncol 47:1422–1431
International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (1999) Prescribing, recording and reporting photon beam therapy (Supplement to ICRU Report 50). ICRU Report, Bethesda
Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) and Common Toxicity Criteria (CTC) v. 4. U.S.Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health National Cancer Institute (2009). Available at http://evs.nci.nih.gov/ftp1/CTCAE/About.html. Last access August 2012
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J et al (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA 303:1070–1076
Onishi H, Araki T, Shirato H et al (2004) Stereotactic hypofractionated high-dose irradiation for stage I non small cell lung carcinoma. Clinical Outcomes in 245 subjects in a Japanese multiinstitutional study. Cancer 101:1623–1631
Onishi H, Shirato H, Nagata Y et al (2011) Stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) for operable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer: can SBRT be comparable to surgery? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:1352–1358
Soltys SG, Kalani MY, Cheshier SH et al (2008) Stereotactic radiosurgery for a cardiac sarcoma: a case report. Technol Cancer Res Treat 7:363–368
Gagliardi G, Lax I, Ottolenghi A et al (1996) Long-term cardiac mortality after radiotherapy of breast cancer — application of the relative seriality model. Br J Radiol 69:839–846
Andratschke N, Maurer J, Molls M et al (2011) Late radiation-induced heart disease after radiotherapy. Clinical importance, radiobiological mechanisms and strategies of prevention. Radiother Oncol 100:160–166
Wei X, Liu HH, Tucker SL (2008) Risk factors for pericardial effusion in inoperable esophageal cancer patients treated with definitive chemoradiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:707–714
Huang EX, Hope AJ, Lindsay PE et al (2011) Heart irradiation as a risk factor for radiation pneumonitis. Acta Oncol 50:51–60
Gagliardi G, Constine LS, Moiseenko V et al (2010) Radiation dose-volume effect in the heart. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(3 Suppl):S77–S85
Nieder C, Schill S, Kneschaurek P et al (2007) Influence of different treatment techniques on radiation dose to the LAD coronary artery. Radiother Oncol 5:2–20
Milano MT, Chen Y, Katz AW et al (2009) Central thoracic lesions treated with hypofractionated stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 91:301–306
Ricardi U, Filippi AR, Guarneri A et al (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer: results of a prospective trial. Lung Cancer 68:72–77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonomo, P., Livi, L., Rampini, A. et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for cardiac and paracardiac metastases: University of Florence experience. Radiol med 118, 1055–1065 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-013-0932-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-013-0932-0