Abstract
Purpose
The Italian National Centre for Oncological Hadrontherapy (Centro Nazionale di Adroterapia Oncologica, CNAO), equipped with a proton and ion synchrotron, started clinical activity in September 2011. The clinical and technical characteristics of the first ten proton beam radiotherapy treatments are reported.
Materials and methods
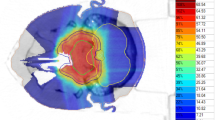
Ten patients, six males and four females (age range 27–73 years, median 55.5), were treated with proton beam radiotherapy. After one to two surgical procedures, seven patients received a histological diagnosis of chordoma (of the skull base in three cases, the cervical spine in one case and the sacrum in three cases) and three of low-grade chondrosarcoma (skull base). Prescribed doses were 74 GyE for chordoma and 70 GyE for chondrosarcoma at 2 GyE/fraction delivered 5 days per week.
Results
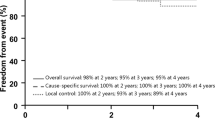
Treatment was well tolerated without toxicity-related interruptions. The maximal acute toxicity was grade 2, with oropharyngeal mucositis, nausea and vomiting for the skull base tumours, and grade 2 dermatitis for the sacral tumours. After 6–12 months of follow-up, no patient developed tumour progression.
Conclusions
The analysis of the first ten patients treated with proton therapy at CNAO showed that this treatment was feasible and safe. Currently, patient accrual into these as well as other approved protocols is continuing, and a longer follow-up period is needed to assess tumour control and late toxicity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fattori G, Riboldi M, Desplanques M et al (2012) Automated fiducial localization in CT images based on surface processing and geometrical prior knowledge for radiotherapy applications. IEEE Trans Biomed 59:2191–2199
Hug EB, Loredo LN, Slater JD et al (1999) Proton radiation therapy for chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base. J Neurosurg 91:432–439
Munzenrider JE, Liebsch NJ (1999) Proton therapy for tumors of the skull base. Strahlenther Onkol 175(Suppl 2):57–63
Vujovic S, Henderson S, Presneau N et al (2006) Brachyury, a crucial regulator of notochordal development, is a novel biomarker for chordomas. J Pathol 209:157–165
Schulz-Ertner D, Nikoghosyan A, Thilmann C et al (2004) Results of carbon ion radiotherapy in 152 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:631–640
Weber DC, Rutz HP, Pedroni ES et al (2005) Results of spot scanning proton radiation therapy for chordoma and chondrosarcoma of the skull base: the Paul Scherrer Institut experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:401–409
Ares C, Hug EB, Lomax AJ et al (2009) Effectiveness and safety of spot scanning proton radiation therapy for chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base: first long-term report. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75:1111–1118
Saxton JP (1981) Chordoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 7:913–915
Rich TA, Schiller A, Suit HD, Mankin HJ (1981) Clinical and pathological review of 48 cases of chordomas. Cancer 56:182–187
Catton C, O’Sullivan B, Bell R et al (1996) Chordoma: long term follow-up after radical photon irradiation. Radiother Oncol 41:67–72
Zorlu F, Gurkaynak M, Yildiz F et al (2000) Conventional external radiotherapy in the management of clivus chordomas with overt residual disease. Neurol Sci 21:203–207
Debus J, Schulz-Ertner D, Schad L et al (2000) Stereotactic fractionated radiotherapy for chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:591–596
Terahara A, Niemierko A, Goitein M (1999) Analysis of the relationship between tumor dose inhomogeneity and local control in patients with skull base chordoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 45:351–358
Noël G, Feuvret L, Ferrand R et al (2004) Radiotherapeutic factors in the management of cervical-basal chordomas and chondrosarcomas. Neurosurgery 55:1252–1260
Park L, DeLaney TF, Liebsch NJ et al (2006) Sacral chordomas: impact of high-dose proton/photon-beam radiation therapy combined with or without surgery for primary versus recurrent tumor. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65:1514–1521
Orecchia R, Zurlo A, Loasses A et al (1998) Particle beam therapy (hadrontherapy): basis for interest and clinical experience. Eur J Cancer 34:459–468
Jereczek-Fossa BA, Krengli M, Orecchia R (2006) Particle beam radiotherapy for head and neck tumors: radiobiological basis and clinical experience. Head Neck 28:750–760
Goitein M (2010) Trials and tribulations in charged particle radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 95:23–31
Lomax AJ, Bortfeld T, Goitein G et al (1999) A treatment planning inter-comparison of protons and intensity-modulated photon therapy. Radiother Oncol 51:257–271
Jakel O (2009) Medical physics aspects of particle therapy. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 137:156–166
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the President, the Technical and Scientific Committee, the Advisory Board, the General Secretary, the Office of Communications, the Department of Safety Prevention and Environment Service, the Department of Legal Affairs and Human Resources, the Department of Radioprotection, the Office of Quality, the Accelerator Department, the Department of Infrastructure, the Department of Administration and Finance, the Radiation Technologist Unit and the nursing staff for their contribution towards making it possible to initiate clinical activity at CNAO.
Conflict of interest
Roberto Orecchia, V. Vitolo, M.R. Fiore, P. Fossati, A. Iannalfi, B. Vischioni, A. Srivastava, J. Tuan, M. Ciocca, S. Molinelli, A. Mirandola, G. Vilches, A. Mairani, B. Tagaste, M. Riboldi, G. Fontana, G. Baroni, S. Rossi and M. Krengli declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orecchia, R., Vitolo, V., Fiore, M.R. et al. Proton beam radiotherapy: report of the first ten patients treated at the “Centro Nazionale di Adroterapia Oncologica (CNAO)” for skull base and spine tumours. Radiol med 119, 277–282 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-013-0345-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-013-0345-0