Abstract
Purpose
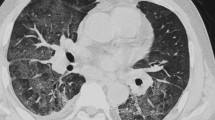
This paper describes chest X-ray (CXR) and computed tomography (CT) findings of diffuse alveolar haemorrhage (DAH).
Materials and methods
We retrospectively reviewed 23 episodes of DAH in 20 patients, 17 of known aetiology and three of unknown aetiology. All cases were studied by CXR and 15 also by CT. Parenchymal consolidations and ground-glass opacities were evaluated after dividing each lung into three regions (upper, middle, lower) for a total of six zones.
Results
Consolidations or ground-glass opacities were identified on CXR in 16/20 patients, mainly in the middle fields (73%). In 4/20 patients, all with Wegener’s granulomatosis, CXR was negative or demonstrated only nodular opacities; in two of these cases, CT revealed ground-glass opacities. A complete follow-up was available for ten patients: initially, they showed consolidation opacities in 36/60 zones, which persisted in 16/60 after 7 days and in 11/60 after 15 days. Conversely, ground-glass opacities increased after 7 days owing to the partial regression of consolidation opacities, and they markedly diminished after 15 days.
Conclusions
DAH is radiologically characterised by a nonspecific alveolar-filling pattern. Diagnosis or suspicion of DAH needs to be supported by the evidence of haemoptysis and/or rapid-onset anaemia. CT is superior in detecting ground-glass opacities and is required in cases of suspected DAH with normal CXR findings.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
Descrivere i reperti Rx e TC della emorragia alveolare diffusa (EAD).
Materiali e metodi
Studio retrospettivo di 23 episodi di EAD in 20 pazienti, 17 con eziologia identificata, 3 senza causa specifica, studiati tutti con Rx torace e 15 con TC. È stata valutata la presenza di opacità consolidative e ground glass dividendo arbitrariamente in sei zone (superiore, media ed inferiore) sia il polmone destro, sia il polmone sinistro.
Risultati
Opacità consolidative o ground glass erano dimostrate all’Rx, prevalentemente nei campi medi (73%), in 16/20 pazienti. In 4/20, tutti con Wegener, il radiogramma risultava negativo o dimostrava solo lesioni nodulari mentre la TC in 2/4 evidenziava opacità ground glass. Dieci pazienti di cui era disponibile follow-up completo esordivano con opacità consolidative in 36/60 zone, persistenti in 16/60 dopo 7 giorni e in 11/60 dopo 15. Le opacità ground glass aumentavano dopo 7 giorni per l’attenuazione delle consolidazioni, riducendosi nettamente 15 giorni.
Conclusioni
L’EAD presenta aspetti radiologici aspecifici di occupazione alveolare. Per la diagnosi o il semplice sospetto di EAD è indispensabile la correlazione con i dati clinico-anamnestici di emottisi o di anemia insorta rapidamente. La TC, più sensibile dell’Rx nel riconoscere opacità ground-glass, è indispensabile in pazienti con possibile EAD e quadro Rx negativo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
Lee AS, Specks U (2004) Pulmonary capillaritis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 25:547–555
Green R, Ruoss R, Kraft SA et al (1996) Pulmonary capillaritis and alveolar hemorrhage. Update on diagnosis and management. Chest 110:1305–1316
Primack Sl, Miller RR, Muller NL (1995) Diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage: clinical, pathologic and imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol 164:295–300
Travis WD (2004) Pathology of pulmonary vasculitis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 25:475–482
Jennings CA, King TE, Tuder R et al (1997) Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage with underlying isolated pauciimmune pulmonary capillaritis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 155:1101–1109
Sharma OP (1998) The problem of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage syndromes. Curr Opin Pulm Med 4:247–250
Rossi SE, Erasmus JJ, Volpacchio M et al (2003) “Crazy-Paving“ pattern at thin-section CT of the lungs: radiologic-pathologic overview. Radiographics 23:1509–1515
Johkoh T, Itoh H, Muller NL et al (1999) Crazy paving appearance at thin section CT: spectrum of disease and pathologic findings. Radiology 211:155–160
Collard HR, Schwarz MI (2004) Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Clin Chest Med 25:583–592
Specks U (2001) Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage syndromes. Curr Opin Rheumatol 13:12–17
Serisier DJ, Wong RC, Armstrong JG (2006) Alveolar hemorrhage in antiglomerular basement membrane disease without detectable antibodies by conventional assays. Thorax 61:636–639
Tanaka N, Newell JD, Brown KK et al (2004) Collagen vascular diseaserelated lung disease: high-resolution computed tomography findings based on the pathologic classification. J Comput Assist Tomogr 28:351–360
Pesci A, Pavone L, Buzio C et al (2005) Respiratory system involvement in ANCA-associated systemic vasculitides. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 22Suppl 1:S40–S48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cortese, G., Nicali, R., Placido, R. et al. Radiological aspects of diffuse alveolar haemorrhage. Radiol med 113, 16–28 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-008-0229-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-008-0229-x