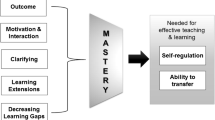
Abstract
In academic settings where digital badges are taking over conventional task formats, educators are faced with the challenge of how to deliver and assess content and skills within badges. Imposing a mastery learning approach, where feedback is key, to a digital badge system may be a potential solution to using digital badges within higher education. As a way to support student learning, Guskey, Journal of Advanced Academics, 19(1), 8–31 (2007) emphasizes the importance of not only frequent feedback but specific feedback. In order to examine how students are using feedback to inform their coursework within a digital badge context, an online survey was designed consisting of open-ended questions about the nature and value of instructional feedback within a digital badge system. Results from the questionnaire indicated three major thematic groups illustrating feedback from the students’ perspective: Importance and Nature of Feedback, Authority over Knowledge and Learning, and Learning for Mastery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovich, S., Schunn, C., & Higashi, R. M. (2013). Are badges useful in education?: It depends upon the type of badge and expertise of learner. Educational Technology Research and Development, 61, 217–232.
Author (2016a). Exploring the role of feedback and its impact within a digital badge system from multiple perspectives: A case study of preservice teachers (doctoral dissertation, Purdue University).
Author (2016b). Passport to Designing, Developing and Issuing Digital Instructional Badges. In Foundation of digital badges and Micro-Credentials (pp. 179–201). Springer International Publishing.
Balzer, W. K., Doherty, M. E., & O'Connor, R. (1989). Effects of cognitive feedback on performance. Psychological Bulletin, 106(3), 410.
Bangert, A. W. (2004). The seven principles of good practice: A framework for evaluating on-line teaching. The Internet and Higher Education, 7(3), 217–232.
Baxter, P., & Jack, S. (2008). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report, 13(4), 544–559.
Bloom, B. S. (1968). Learning for mastery. Instruction and curriculum. Regional education Laboratory for the Carolinas and Virginia, topical papers and reprints, number 1. Evaluation Comment, 1(2), n2.
Bloom, B. S. (1976). Human characteristics and school learning. New York. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Boud, D., & Feletti, G. (1998). The challenge of problem-based learning. Psychology Press.
Bowen, K., & Thomas, A. (2014). Badges: A common currency for learning. Change, 46(1), 21–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/00091383.2014.867206.
Brigham Young University: Instructional Psychology, t. (n.d.). How we use badges. Retrieved November 27, 2014, 2014, from http://iptedtec.org/what-are-badges/.
Buell, C. (2013, 2013/08/30). Using Badges to Quantify Learning Outcomes at UC Davis. Retrieved December 10, 2014, 2014, from http://edcetera.rafter.com/using-badges-to-quantify-learning-outcomes-at-uc-davis/.
Butler, D. L., & Winne, P. H. (1995). Feedback and self-regulated learning: A theoretical synthesis. Review of Educational Research, 65(3), 245–281.
Chickering, A. W., & Gamson, Z. F. (1987). Seven principles for good practice in undergraduate education. AAHE Bulletin, 3, 7.
Chickering, A. W., & Gamson, Z. F. (1989). Seven principles for good practice in undergraduate education. Biochemical Education, 17(3), 140–141.
Creswell, J. W. (2014). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Washington, D.C.: SAGE Publications.
Creswell, J. W., & Clark, V. L. P. (2007). Designing and conducting mixed methods research. Washington, D.C.: SAGE Publications.
CS2N. (n.d.). CS2N Badges. Retrieved January 29, 2015, 2015, from https://www.cs2n.org/teachers/badges
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2011). The SAGE handbook of qualitative research (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications.
Ertmer, P. A., & Koehler, A. A. (2014). Online case-based discussions: Examining coverage of the afforded problem space. Educational Technology Research and Development, 62(5), 617–636.
Fain, P. (2014, 2014/01/03). Badging From Within. Retrieved January 27, 2015, 2015, from https://www.insidehighered.com/news/2014/01/03/uc-daviss-groundbreaking-digital-badge-system-newsustainable-agriculture-program.
Falchikov, N., & Goldfinch, J. (2000). Student peer assessment in higher education: A meta-analysis comparing peer and teacher marks. Review of Educational Research, 70(3), 287–322.
Garrison, C., & Ehringhaus, M. (2007). Formative and summative assessments in the classroom.
Gibson, D. (2013). Assessing Deeper Learning in Open Online Learning Communities. Paper presented at the Society for Information Technology & teacher education international conference 2013, New Orleans, Louisiana, United States. http://www.editlib.org/p/48146 .
Glover, I., & Latif, F. (2013). Investigating perceptions and potential of open badges in formal higher education. Paper presented at the world conference on educational multimedia, hypermedia and telecommunications.
Grant, S. (2014). Badges: Show what you know. Young Adult Library Services, 12(2), 28–32.
Guskey, T. R. (2007). Closing achievement gaps: Revisiting Benjamin S. Bloom's “learning for mastery”. Journal of Advanced Academics, 19(1), 8–31.
Hepplestone, S., & Chikwa, G. (2014). Understanding how students process and use feedback to support their learning. Practitioner Research in Higher Education, 8(1), 41–53.
Higgins, R., Hartley, P., & Skelton, A. (2002). The conscientious consumer: Reconsidering the role of assessment feedback in student learning. Studies in Higher Education, 27(1), 53–64.
Hmelo-Silver, C. E., & Barrows, H. S. (2006). Goals and strategies of a problem-based learning facilitator. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-based Learning, 1(1), 4.
Johnson, B., & Christensen, L. (2012). Educational research: Quantitative and qualitative approaches (4th ed.). Los Angeles: SAGE Publications.
Kluger, A. N., & DeNisi, A. (1996). The effects of feedback interventions on performance: A historical review, a meta-analysis, and a preliminary feedback intervention theory. Psychological Bulletin, 119(2), 254.
Kulhavy, R. W. (1977). Feedback in written instruction. Review of Educational Research, 211–232.
Light, D., & Pierson, E. (2014). Increasing student engagement in math: The use of khan academy in Chilean classrooms. International Journal of Education and Development using ICT, 10(2), 103–119.
Lin, C.-H., Liu, E. Z.-F., Chen, Y.-L., Liou, P.-Y., Chang, M., Wu, C.-H., & Yuan, S.-M. (2013). Game-based remedial instruction in mastery learning for upper-primary school students. Educational Technology & Society, 16(2), 271–281.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1986). But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation. New directions for program evaluation, 1986(30), 73–84.
Lynch, R., McNamara, P. M., & Seery, N. (2012). Promoting deep learning in a teacher education programme through self- and peer-assessment and feedback. European Journal of Teacher Education, 35(2), 179–197. https://doi.org/10.1080/02619768.2011.643396.
MacArthur Foundation. (n.d.). DePaul University. Retrieved January 27, 2015, 2015 from http://www.macfound.org/grantees/252/.
MacArthur Foundation, M. (2014). Digital badges. Retrieved December 6, 2014, from http://www.macfound.org/programs/digital-badges/.
Mastery Transcript Consortium. (n.d.). Mastery Transcript Consortium. Retrieved September 30, 2018, from http://mastery.org/
Mayer, R. E. (2008). Learning and instruction (2nd ed.. Ed.). Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Upper Saddle River, N.J.: Pearson Merrill Prentice Hall.
Mehta, N. B., Hull, A. L., Young, J. B., & Stoller, J. K. (2013). Just imagine: New paradigms for medical education. Academic Medicine, 88(10), 1418–1423.
Mettler, E., Massey, C., & Kellman, P. J. (2011). Improving adaptive learning technology through the use of response times. In Paper presented at the proceedings of the 33 rd annual conference of the cognitive science society. Boston, MA: Cognitive Science Society.
Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., & Saldaña, J. (2014). Qualitative data analysis: A methods sourcebook. Washington, D.C.: SAGE Publications.
Mozilla. (n.d.). Mozilla Open Badges. Retrieved June 12, 2014, from http://openbadges.org/about/.
Nicol, D. J., & Macfarlane-Dick, D. (2006). Formative assessment and self-regulated learning: A model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Studies in Higher Education, 31(2), 199–218.
Ostashewski, N., & Reid, D. (2015). A history and frameworks of digital badges in education Gamification in Education and Business (pp. 187–200). Springer International Publishing.
Pokorny, H., & Pickford, P. (2010). Complexity, cues, and relationships: Student perceptions of feedback. Active Learning in Higher Education, 11(1), 21–30.
Ramaprasad, A. (1983). On the definition of feedback. Behavioral Science, 28(1), 4–13.
Randall, D. L., Harrison, J. B., & West, R. E. (2013). Giving credit where credit is due: Designing open badges for a technology integration course. Tech Trends, 57(6), 88–95.
Reigeluth, C. M., & Karnopp, J. R. (2013). Reinventing schools: It’s time to break the mold. New York: Rowman & Littlefield Education.
Schunk, D. H. (1983). Developing children's self-efficacy and skills: The roles of social comparative information and goal setting. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 8(1), 76–86.
Seton Hall University's Teaching, L., & Technology, C. (n.d.). Stillman Passport. Retrieved December 10, 2014, 2014 from https://tltc.shu.edu/badges/stillmanPassport.php.
Slavin, R. E., & Karweit, N. L. (1984). Mastery learning and student teams: A factorial experiment in urban general mathematics classes. American Educational Research Journal, 21(4), 725–736.
Tally, S. (2012, 2012/12/11). Digital badges show students' skills along with degree. Retrieved January 27, 2015, 2015, from http://www.purdue.edu/newsroom/releases/2012/Q3/digital-badges-show-students-skills-along-with-degree.html
Tucker, S. A. (1993). Evaluation as feedback in instructional technology: The role of feedback in program evaluation. Interactive Instruction and Feedback (pp. 301–342). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Educational Technology Publications.
Wonder-McDowell, C., Reutzel, D. R., & Smith, J. A. (2011). Does instructional alignment matter? The Elementary School Journal, 112(2), 259–279.
Wright, C. V., & O'Shea, K. (2014). digital badges and Outcomes-Based Learning. from http://www.educause.edu/events/educause-connect-baltimore/2014/digital-badges-and-outcomes-based-learning
Yang, M., & Carless, D. (2013). The feedback triangle and the enhancement of dialogic feedback processes. Teaching in Higher Education, 18(3), 285–297.
Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research: Design and methods (applied social research methods) (4th ed.). Washington, D.C.: SAGE Publications, Inc.
Yin, R. K. (2014). Case study research: Design and methods (5th ed.). Los Angeles: SAGE Publications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Erin D. Besser declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Author Timothy J. Newby declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 579 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Besser, E.D., Newby, T.J. Exploring the Role of Feedback and its Impact within a Digital Badge System from Student Perspectives. TechTrends 63, 485–495 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-019-00386-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-019-00386-2