Abstract
Background
Knowledge of changes in the outcome in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma from the molecular-targeted therapy era to the immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) era remains limited in the real-world setting.
Objectives
We aimed to clarify outcome changes from the previous molecular-targeted therapy era to the current ICI era in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma using multi-institution real-world data.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated 415 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received first-line systemic therapy at five Japanese institutions between January 2008 and August 2021. We divided the patients into two groups based on the treatment era: molecular-targeted therapy era (January 2008–August 2018) and ICI era (September 2018–August 2021). According to the era, progression-free survival, overall survival, and objective response rate from first-line systemic therapy were compared.
Results
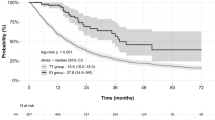
Overall, 304 (73.3%) and 111 (26.7%) patients were categorized into the molecular-targeted therapy and ICI eras, respectively. The proportion of patients without prior nephrectomy (p = 0.0030) or those with low Karnofsky Performance Status scores [≤ 70] (p = 0.0258) were significantly higher in the ICI era group. The patients in the ICI era group had significantly longer overall survival (median: not reached vs 23.2 months, p = 0.0001) and a higher objective response rate (47.8% vs 24.7%, p < 0.0001) than those in the molecular-targeted therapy era group, and progression-free survival tended to be longer in the ICI era group (median: 13.3 vs 8.75 months, p = 0.0579). Multivariate analysis further showed that the treatment era (ICI vs molecular-targeted therapy) was an independent factor for overall survival and objective response (both, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
The present multi-institution real-world data showed the improved outcome of previously untreated patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the ICI era group compared with that in the molecular-targeted therapy era group. These findings strongly encourage the use of ICI-based treatment for patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the real-world setting. Further studies with extended follow-up periods are needed to confirm our findings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, Aren Frontera O, Melichar B, Choueiri TK, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(14):1277–90. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1712126.
Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V, Gafanov R, Hawkins R, Nosov D, et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(12):1116–27. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1816714.
Motzer RJ, Penkov K, Haanen J, Rini B, Albiges L, Campbell MT, et al. Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(12):1103–15. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1816047.
Choueiri TK, Powles T, Burotto M, Escudier B, Bourlon MT, Zurawski B, et al. Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):829–41. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2026982.
Motzer R, Alekseev B, Rha SY, Porta C, Eto M, Powles T, et al. Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab or everolimus for advanced renal cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(14):1289–300. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2035716.
Massari F, Rizzo A, Mollica V, Rosellini M, Marchetti A, Ardizzoni A, et al. Immune-based combinations for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Eur J Cancer. 2021;154:120–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2021.06.015.
Bedke J, Albiges L, Capitanio U, Giles RH, Hora M, Lam TB, et al. Updated European Association of Urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: nivolumab plus cabozantinib joins immune checkpoint inhibition combination therapies for treatment-naïve metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2021;79(3):339–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2020.12.005.
Bedke J, Albiges L, Capitanio U, Giles RH, Hora M, Lam TB, et al. The 2021 updated European Association of Urology guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: immune checkpoint inhibitor-based combination therapies for treatment-naive metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma are standard of care. Eur Urol. 2021;80(4):393–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2021.04.042.
Mol L, Koopman M, van Gils CW, Ottevanger PB, Punt CJ. Comparison of treatment outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients included in a clinical trial versus daily practice in The Netherlands. Acta Oncol. 2013;52(5):950–5. https://doi.org/10.3109/0284186x.2013.777158.
Knauf W, Aldaoud A, Hutzschenreuter U, Klausmann M, Dille S, Wetzel N, et al. Survival of non-transplant patients with multiple myeloma in routine care differs from that in clinical trials-data from the prospective German Tumour Registry Lymphatic Neoplasms. Ann Hematol. 2018;97(12):2437–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-018-3449-8.
Xu C, Zhang Y, Chen L, Li WF, Tang SQ, Tang LL, et al. Association between outcome disparities and pragmatic features related to clinical trial and real-world settings in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a population-based retrospective cohort study, 2006–2016. Radiother Oncol. 2020;151:306–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2020.08.019.
Heng DY, Choueiri TK, Rini BI, Lee J, Yuasa T, Pal SK, et al. Outcomes of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma that do not meet eligibility criteria for clinical trials. Ann Oncol. 2014;25(1):149–54. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt492.
Marschner N, Staehler M, Müller L, Nusch A, Harde J, Koska M, et al. Survival of patients with advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma in routine practice differs from that in clinical trials: analyses from the German Clinical RCC Registry. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017;15(2):e209–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2016.08.022.
Ishihara H, Tachibana H, Fukuda H, Yoshida K, Kobayashi H, Takagi T, et al. Prognostic impact of trial-eligibility criteria in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Urol Int. 2021;106(4):368–75. https://doi.org/10.1159/000518162.
Tomita Y, Kondo T, Kimura G, Inoue T, Wakumoto Y, Yao M, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in previously untreated advanced renal-cell carcinoma: analysis of Japanese patients in CheckMate 214 with extended follow-up. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020;50(1):12–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyz132.
Tamada S, Kondoh C, Matsubara N, Mizuno R, Kimura G, Anai S, et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: outcomes of Japanese patients enrolled in the randomized, phase III, open-label KEYNOTE-426 study. Int J Clin Oncol. 2022;27(1):154–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-021-02014-7.
Uemura M, Tomita Y, Miyake H, Hatakeyama S, Kanayama HO, Numakura K, et al. Avelumab plus axitinib vs sunitinib for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Japanese subgroup analysis from JAVELIN Renal 101. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(3):907–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14294.
Ishihara H, Kondo T, Yoshida K, Omae K, Takagi T, Iizuka J, et al. Time to progression after first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor predicts survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving second-line molecular-targeted therapy. Urol Oncol. 2017;35(9):542.e1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.05.014.
Ishihara H, Takagi T, Kondo T, Tachibana H, Yoshida K, Omae K, et al. Efficacy and safety of third-line molecular-targeted therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma resistant to first-line vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor and second-line therapy. Int J Clin Oncol. 2018;23(3):559–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-018-1241-3.
Kondo T, Takagi T, Kobayashi H, Iizuka J, Nozaki T, Hashimoto Y, et al. Superior tolerability of altered dosing schedule of sunitinib with 2-weeks-on and 1-week-off in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: comparison to standard dosing schedule of 4-weeks-on and 2-weeks-off. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014;44(3):270–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyt232.
Tachibana H, Kondo T, Ishihara H, Fukuda H, Yoshida K, Takagi T, et al. Modest efficacy of nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with papillary renal cell carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2021;51(4):646–53. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyaa229.
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 11). Eur J Cancer. 2009;45(2):228–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026.
Mejean A, Ravaud A, Thezenas S, Colas S, Beauval JB, Bensalah K, et al. Sunitinib alone or after nephrectomy in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(5):417–27. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1803675.
Bex A, Mulders P, Jewett M, Wagstaff J, van Thienen JV, Blank CU, et al. Comparison of immediate vs deferred cytoreductive nephrectomy in patients with synchronous metastatic renal cell carcinoma receiving sunitinib: the SURTIME randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5(2):164–70. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.5543.
Naito S, Kato T, Numakura K, Hatakeyama S, Koguchi T, Kandori S, et al. Prognosis of Japanese metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients in the targeted therapy era. Int J Clin Oncol. 2021;26(10):1947–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-021-01979-9.
Ishihara H, Takagi T, Kondo T, Fukuda H, Tachibana H, Yoshida K, et al. Assessing improvements in metastatic renal cell carcinoma systemic treatments from the pre-cytokine to the immune checkpoint inhibitor eras: a retrospective analysis of real-world data. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2021;51(5):793–801. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyaa232.
Ishihara H, Takagi T, Kondo T, Fukuda H, Tachibana H, Yoshida K, et al. Prognostic impact of systemic therapy change in metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with cytoreductive nephrectomy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2021;51(2):296–304. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyaa171.
Ishihara H, Takagi T, Kondo T, Fukuda H, Tachibana H, Yoshida K, et al. Prognostic impact of metastasectomy in renal cell carcinoma in the postcytokine therapy era. Urol Oncol. 2021;39(1):77.e17-77.e25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2020.08.011.
Ciccarese C, Iacovelli R, Porta C, Procopio G, Bria E, Astore S, et al. Efficacy of VEGFR-TKIs plus immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients with favorable IMDC prognosis. Cancer Treat Rev. 2021;100: 102295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102295.
Kroeger N, Xie W, Lee JL, Bjarnason GA, Knox JJ, Mackenzie MJ, et al. Metastatic non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma treated with targeted therapy agents: characterization of survival outcome and application of the International mRCC Database Consortium criteria. Cancer. 2013;119(16):2999–3006. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.28151.
Heng DY, Mackenzie MJ, Vaishampayan UN, Bjarnason GA, Knox JJ, Tan MH, et al. Primary anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma: clinical characteristics, risk factors, and subsequent therapy. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(6):1549–55. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdr533.
Saito K, Kihara K. C-reactive protein as a biomarker for urological cancers. Nat Rev Urol. 2011;8(12):659–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2011.145.
McKay RR, Kroeger N, Xie W, Lee JL, Knox JJ, Bjarnason GA, et al. Impact of bone and liver metastases on patients with renal cell carcinoma treated with targeted therapy. Eur Urol. 2014;65(3):577–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2013.08.012.
Ishihara H, Tachibana H, Takagi T, Yoshida K, Kondo T, Tanabe K. Effect of improved systemic therapy on patient survival in metastatic non-clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Urol. 2021;28(5):605–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.14523.
Seydel F, Delecluse S, Zeier M, Holland-Letz T, Haag GM, Berger AK, et al. Efficacy and safety of checkpoint inhibitor treatment in patients with advanced renal or urothelial cell carcinoma and concomitant chronic kidney disease: a retrospective cohort study. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(7):1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071623.
Osmán-García I, Congregado-Ruiz CB, Lendínez-Cano G, Baena-Villamarin C, Conde-Sanchez JM, Medina-López RA. Outcomes and safety of biweekly and monthly nivolumab in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma and dialysis: three case reports and literature review. Urol Int. 2020;104(3–4):323–6. https://doi.org/10.1159/000504515.
Strohbehn IA, Lee M, Seethapathy H, Chute D, Rahma O, Guidon A, et al. Safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients on dialysis: a retrospective case series. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;76(2):299–302. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.02.451.
Tachibana H, Kondo T, Ishihara H, Takagi T, Tanabe K. Safety and efficacy of nivolumab in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma and end-stage renal disease at 2 centers. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2019;17(4):e772–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2019.04.004.
Desai K, Brown L, Wei W, Tucker M, Kao C, Kinsey E, et al. A multi-institutional, retrospective analysis of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma to bone treated with combination ipilimumab and nivolumab. Target Oncol. 2021;16(5):633–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-021-00832-3.
Santoni M, Massari F, Bracarda S, Grande E, Matrana MR, Rizzo M, et al. Cabozantinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma primary refractory to first-line immunocombinations or tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Eur Urol Focus. 2022;S2405–4569(22):00049–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2022.02.004.
Carter BW, Bhosale PR, Yang WT. Immunotherapy and the role of imaging. Cancer. 2018;124(14):2906–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.31349.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Ms. Nobuko Hata, from the Department of Urology, Tokyo Women’s Medical University, for secretarial assistance and to the patients from the participating institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No external funding was used in the preparation of this article.
Conflict of interest
Toshio Takagi received a speaker honorarium from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ono Pharmaceutical. Tsunenori Kondo received a speaker honorarium from Pfizer, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Ono Pharmaceutical. Hiroki Ishihara, Yuki Nemoto, Kazutaka Nakamura, Hidekazu Tachibana, Hironori Fukuda, Kazuhiko Yoshida, Hirohito Kobayashi, Junpei Iizuka, Hiroaki Shimmura, Yasunobu Hashimoto, and Kazunari Tanabe declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Boards of Tokyo Women’s Medical University, Tokyo Women’s Medical University Medical Center East, Saiseikai Kawaguchi General Hospital, Saiseikai Kurihashi Hospital, and Jyoban Hospital (ID: 2020-0009). This study conforms to the ethical guidelines of the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki. The requirement for written informed consent was waived because of the retrospective observational nature of the study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design, data collection, and data analysis. HI wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all authors critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content and approved the version to be published.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishihara, H., Nemoto, Y., Nakamura, K. et al. Changes in Real-World Outcomes in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma from the Molecular-Targeted Therapy Era to the Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Era. Targ Oncol 17, 307–319 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-022-00879-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-022-00879-w