Abstract
Objective
We conducted a retrospective analysis of two clinical trials in treatment-naïve patients (n = 402) with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) treated with axitinib. Our objective was to compare duration of treatment (DT) and clinical outcome in patients who achieved DT >18 months (longer DT) versus ≤18 months (shorter DT).
Patients and Methods
DT, objective response rate (ORR), tumor shrinkage, and overall survival (OS) were summarized for patients with longer and shorter DT.
Results
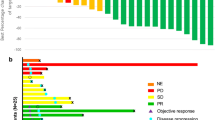
Overall, 152 patients (37.8%) had longer DT and 250 (62.2%) had shorter DT (median, 34.7 vs. 6.5 months, respectively). ORR in all 402 patients with advanced RCC was 43.5%. ORR was 75% for longer DT versus 24.4% for shorter DT (p < 0.0001). More patients with longer DT versus shorter DT had ≥10% tumor shrinkage at first scan (74.8% vs. 55.3%; p = 0.0001) and maximum on-study tumor shrinkage was greater in longer-DT versus shorter-DT group (−51.8% vs. –22.1%; p < 0.0001). Median OS was 32.6 months in the overall population while in the patients with longer DT the median was not reached. Treatment-related adverse events (AEs) grade ≥3 were more frequent in longer-DT versus shorter-DT and included hypertension (25.7% vs. 18.8%), diarrhea (15.1% vs. 4.4%), and weight decrease (11.2% vs. 3.2%); however, these AEs decreased over time in both groups. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0, favorable hematology values, no bone or liver metastases, and baseline tumor burden below the overall median were associated with longer DT.
Conclusions
Longer duration (>18 months) of axitinib treatment was associated with increased frequency of early tumor shrinkage, greater magnitude of tumor shrinkage, and a favorable OS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86. doi:10.1002/ijc.29210.
Znaor A, Lortet-Tieulent J, Laversanne M, Jemal A, Bray F. International variations and trends in renal cell carcinoma incidence and mortality. Eur Urol. 2015;67:519–30. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2014.10.002.
SEER Cancer Statistics Factsheets. Kidney and Renal Pelvis Cancer. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute 2016. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/kidrp.html Accessed July 27 2016.
Thorstenson A, Harmenberg U, Lindblad P, Holmstrom B, Lundstam S, Ljungberg B. Cancer characteristics and current treatments of patients with renal cell carcinoma in Sweden. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:456040. doi:10.1155/2015/456040.
Hu-Lowe DD, Zou HY, Grazzini ML, Hallin ME, Wickman GR, Amundson K, et al. Nonclinical antiangiogenesis and antitumor activities of axitinib (AG-013736), an oral, potent, and selective inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases 1, 2, 3. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:7272–83. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0652.
Inlyta® (axitinib) tablet, film coated [prescribing information]. New York: Pfizer Inc; 2012.
Rini BI, Escudier B, Tomczak P, Kaprin A, Szczylik C, Hutson TE, et al. Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;378:1931–9. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61613-9.
Hutson TE, Lesovoy V, Al-Shukri S, Stus VP, Lipatov ON, Bair AH, et al. Axitinib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: a randomised open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:1287–94. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70465-0.
Rini BI, Melichar B, Ueda T, Grunwald V, Fishman MN, Arranz JA, et al. Axitinib with or without dose titration for first-line metastatic renal-cell carcinoma: a randomised double-blind phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:1233–42. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70464-9.
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:205–16. doi:10.1093/jnci/92.3.205.
Molina AM, Jia X, Feldman DR, Hsieh JJ, Ginsberg MS, Velasco S, et al. Long-term response to sunitinib therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2013;11:297–302. doi:10.1016/j.clgc.2013.04.001.
Grunwald V, McKay RR, Krajewski KM, Kalanovic D, Lin X, Perkins JJ, et al. Depth of remission is a prognostic factor for survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2015;67:952–8. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2014.12.036.
Rini BI, Tomita Y, Melichar B, Ueda T, Grünwald V, Fishman MN, et al. Overall survival analysis from a randomized phase II study of axitinib with or without dose titration in first-line metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2016;14:499–503. doi:10.1016/j.clgc.2016.04.005.
Hutson TE, Al-Shukri S, Stus VP, Lipatov ON, Shparyk Y, Bair AH, et al. Axitinib versus sorafenib in first-line metastatic renal cell carcinoma: overall survival from a randomized phase III trial. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017;15:72–6. doi:10.1016/j.clgc.2016.05.008.
Grünwald V, Lin X, Kalanovic D, Simantov R. Early tumour shrinkage: a tool for the detection of early clinical activity in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2016;70:1006–15. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2016.05.010.
Choueiri TK, Garcia JA, Elson P, Khasawneh M, Usman S, Golshayan AR, et al. Clinical factors associated with outcome in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. Cancer. 2007;110:543–50. doi:10.1002/cncr.22827.
Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Bukowski R, Rini BI, Hutson TE, Barrios CH, et al. Prognostic factors for survival in 1059 patients treated with sunitinib for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:2470–7. doi:10.1038/bjc.2013.236.
Cohen RB, Oudard S. Antiangiogenic therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma: management of treatment-related toxicities. Invest New Drugs. 2012;30:2066–79. doi:10.1007/s10637-012-9796-8.
Eisen T, Sternberg CN, Robert C, Mulders P, Pyle L, Zbinden S, et al. Targeted therapies for renal cell carcinoma: review of adverse event management strategies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104:93–113. doi:10.1093/jnci/djr511.
Rini BI, Escudier B, Hariharan S, Roberts WG, Tarazi J, Rosbrook B, et al. Long-term safety with axitinib in previously treated patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2015;13:540–7 e1-7. doi:10.1016/j.clgc.2015.07.001.
Donskov F, Michaelson MD, Puzanov I, Davis MP, Bjarnason GA, Motzer RJ, et al. Sunitinib-associated hypertension and neutropenia as efficacy biomarkers in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients. Br J Cancer. 2015;113:1571–80. doi:10.1038/bjc.2015.368.
Rini BI, Cohen DP, Lu DR, Chen I, Hariharan S, Gore ME, et al. Hypertension as a biomarker of efficacy in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011;103:763–73. doi:10.1093/jnci/djr128.
Rini BI, Schiller JH, Fruehauf JP, Cohen EE, Tarazi JC, Rosbrook B, et al. Diastolic blood pressure as a biomarker of axitinib efficacy in solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:3841–9. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2806.
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by Vardit Dror, PhD, of Engage Scientific Solutions and was funded by Pfizer Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by Pfizer Inc.
Conflicts of Interest
JC Tarazi, B Rosbrook, AH Bair, S Hariharan and L Cisar are full-time employees of and declare stocks from Pfizer Inc.
BI Rini received research funding and consulting fees from Pfizer.
V Gruenwald received consulting fees and honoraria from Pfizer Oncology, Roche Pharma, GSK and Novartis Oncology, research funding from Wyeth Oncology, and a lecture honorarium from Bayer.
E Jonasch received research funding and consulting fees from Pfizer.
MN Fishman received research funding and honoraria from Aveo, Altor Biosciences, Bayer, Genentech, GSK, and Pfizer; research funding from BMS, Eisai and Exelixis; honoraria from Alkermes, and Prometheus; and has served on speakers bureaus for Bayer, Exelixis, GSK, Novartis, Pfizer, and Prometheus.
Y Tomita received honoraria and research funding from Pfizer and Novartis.
MD Michaelson received research funding and consulting fees from Pfizer, Novartis, and Exelixis.
TE Hutson received consulting fees and research funding from Pfizer, Exelexis, Eisai, Novartis, and BMS.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rini, B.I., Gruenwald, V., Jonasch, E. et al. Long-term Duration of First-Line Axitinib Treatment in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Targ Oncol 12, 333–340 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-017-0487-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-017-0487-4