Abstract
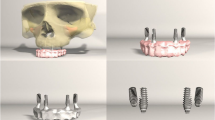
This study aims to evaluate the stress values, created in peri-implant region as a consequence of loading on fixed hybrid dentures that was planned with different implant numbers, lengths, or tilting angulations. Thirteen three-dimensional (3D) finite element analysis models were generated with four, five, or seven implants (group A, B, and C). Except the distal implants, all implants were modeled at 4.1 mm (diameter) and 11.5 mm (length) in size. Distal implants were configured to be in five different lengths (6, 8, 11.5, 13, and 16 mm) and three different implant inclination degrees (0°, 30°, and 45°). A 150-N load was applied vertically on prosthesis. Released stresses were evaluated comparatively. The lowest von Mises stress values were found in group C, in the 11.5-mm implant model. Tilting the distal implants 30° caused higher stress values. In 45°-tilting implant models, lower stress values were recorded according to the 30°-tilting models. The ideal implant number is seven for an edentulous maxilla. Tilting the implants causes higher stress values. A 45° inclination of implant causes lower stress values according to the 30° models due to a shorter cantilever. The ideal implant length is 11.5 mm.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chou HY, Muftu S, Bozkaya D (2010) Combined effects of implant insertion depth and alveolar bone quality on periimplant bone strain induced by a wide-diameter, short implant and a narrow-diameter, long implant. J Prosthet Dent 104(5):293–300
Chang SH, Lin CL, Hsue SS, Lin YS, Huang SR (2012) Biomechanical analysis of the effects of implant diameter and bone quality in short implants placed in the atrophic posterior maxilla. Med Eng Phys 34(2):153–160
Woo I, Le BT (2004) Maxillary sinus floor elevation: review of anatomy and two techniques. Implant Dent 13(1):28–32
Graziani F, Donos N, Needleman I, Gabriele M, Tonetti M (2004) Comparison of implant survival following sinus floor augmentation procedures with implants placed in pristine posterior maxillary bone: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 15(6):677–682
Li T, Yang X, Zhang D, Zhou H, Shao J, Ding Y, Kong L (2012) Analysis of the biomechanical feasibility of a wide implant in moderately atrophic maxillary sinus region with finite element method. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 114(2):1–8
Almeida EO, Rocha EP, Freitas Junior AC, Anchieta RB, Poveda R, Gupta N, Coelho PG (2015) Tilted and short implants supporting fixed prosthesis in an atrophic maxilla: a 3D-FEA biomechanical evaluation. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 17(1):332–342
Saleh Saber F, Ghasemi S, Koodaryan R, Babaloo A, Abolfazli N (2015) The comparison of stress distribution with different implant numbers and inclination angles in all-on-four and conventional methods in maxilla: a finite element analysis. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects 9(4):246–253
Hernandez-Alfaro F, Sancho-Puchades M, Guijarro-Martinez R (2013) Total reconstruction of the atrophic maxilla with intraoral bone grafts and biomaterials: a prospective clinical study with cone beam computed tomography validation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 28(1):241–251
Chiapasco M, Casentini P, Zaniboni M (2009) Bone augmentation procedures in implant dentistry. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 24(7):237–259
Zampelis A, Rangert B, Heijl L (2007) Tilting of splinted implants for improved prosthodontic support: a two-dimensional finite element analysis. J Prosthet Dent 97(6):35–43
Regev E, Smith A, Perrott DH, Pogrel MA (1995) Maxillary sinus complications related to endosseous implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 10(4):451–461
Malo P, Nobre M, Rangert B (2007) Short implants placed one-stage in maxillae and mandibles: a 2-year retrospective clinical study. Clin Implant Dent and Relat Res 9(1):15–21
Das Neves FD, Fones D, Bernardes SR, Do Prado CJ, Neto AJ (2006) Short implants. An analysis of longitudinal studies. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 21(1):86–93
Van Assche N, Michels S, Quirynen M, Naert I (2011) Extra short dental implants supporting an overdenture in the edentulous maxilla: a proof of concept. Clin Oral Implants Res 23(5):567–576
Romeo E, Bivio A, Mosca D, Scanferla M, Ghisolfi M, Storelli S (2010) The use of short dental implants in clinical practice: literature review. Minerva Stomatol 59(1–2):23–31
Davarpanah M, Martinez H, Kebir M, Etienne D, Tecucianu JF (2001) Wide-diameter implants: new concepts. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 21(2):149–159
Cavalli N, Barbaro B, Spasari D, Azzola F, Ciatti A, Francetti L (2012) Tilted implants for full-arch rehabilitations in completely edentulous maxilla: a retrospective study. Int J Dent 2012(2012):e180379
Rossetti PH, Bonachela WC, Rossetti LM (2010) Relevant anatomic and biomechanical studies for implant possibilities on the atrophic maxilla: critical appraisal and literature review. J Prosthodont 19(6):449–457
Drago CJ (1992) Rates of osseointegration of dental implants with regard to anatomical location. J Prosthodont 1(1):29–31
Viceconti M, Baleani M, De Lollis A, Toni A (1998) An FEA-based protocol for the pre-clinical validation of custom-made hip implants. J Med Eng Technol 22(6):257–262
Geng JP, Tan KB, Liu GR (2001) Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: a review of the literature. J Prosthet Dent 85(6):585–598
Moriwaki H, Yamaguchi S, Nakano T, Yamanishi Y, Imazato S, Yatani H (2016) Influence of implant length and diameter, Bicortical anchorage, and sinus augmentation on bone stress distribution: three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 31(4):84–91
YJ L, Chang SH, Ye JT, Ye YS, YS Y (2015) Finite element analysis of bone stress around micro-implants of different diameters and lengths with application of a single or composite torque force. PLoS One 10(12):e0144744
Baggi L, Cappelloni I, Di Girolama M, Maceri F, Vairo G (2008) The influence of implant diameter and length on stress distribution of osseointegrated implants related to crestal bone geometry: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Prosthet Dent 100(6):422–431
Assuncao WG, Barao VA, Tabata LF, Gomes EA, Delben JA, dos Santos PH (2009) Biomechanics studies in dentistry: bioengineering applied in oral implantology. J Craniofac Surg 20(4):1173–1177
Bourauel C, Aitlahrach M, Heinemann F, Hasan I (2012) Biomechanical finite element analysis of small diameter and short dental implants: extensive study of commercial implants. Biomed Tech (Berl) 57(1):21–32
Silva GC, Mendonca JA, Lopes LR, Landre J (2010) Stress patterns on implants in prostheses supported by four or six implants: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 25(2):239–246
Gümrükçü Z, Korkmaz YT, Korkmaz FM (2017) Biomechanical evaluation of implant-supported prosthesis with various tilting implant angles and bone types in atrophic maxilla: a finite element study. Comput Biol Med 86(2017):47–54
Lekholm U, Zarb GA, Albrektsson T (1985) Patient selection and preparation. Tissue-integrated prostheses. Chicago Quintessence Int:199–209
Correa S, Ivancik J, Isaza JF, Naranjo M (2012) Evaluation of the structural behavior of three and four implant-supported fixed prosthetic restorations by finite element analysis. J Prosthodont Res 56(2):110–119
Misch CE (2009) Dental implant prosthesis, 2nd edn. Nobel, İstanbul, pp 281–308
Kong L, Gu Z, Hu K, Zhou H, Liu Y, Liu B (2009) Optimization of the implant diameter and length in type B/2 bone for improved biomechanical properties: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. Adv Eng Softw 40(9):935–940
Kitamura E, Stegaroiu R, Nomura S, Miyakawa O (2005) Influence of marginal bone resorption on stress around an implant—a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Oral Rehabil 32(4):279–286
Pirner S, Tingelhoff K, Wagner I, Westphal R, Rilk M, Wahl FM, Bootz F, Eichhorn KW (2009) CT-based manual segmentation and evaluation of paranasal sinuses. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266(4):507–518
Tepper G, Haas R, Zechner W, Krach W, Watzek G (2002) Three-dimensional finite element analysis of implant stability in the atrophic posterior maxilla: a mathematical study of the sinus floor augmentation. Clin Oral Implants Res 13(6):657–665
Rismanchian M, Bajoghli F, Mostajeran Z, Fazel A, Eshkevari P (2009) Effect of implants on maximum bite force in edentulous patients. J Oral Implantol 35(4):196–200
Ferrario VF, Sforza C, Serrao G, Dellavia C, Tartaglia GM (2004) Single tooth bite forces in healthy young adults. J Oral Rehabil 31(1):18–22
Petrie CS, Williams JL (2005) Comparative evaluation of implant designs: influence of diameter, length, and taper on strains in the alveolar crest. A three-dimensional finite-element analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 16(4):486–494
Bozkaya D, Muftu S, Muftu A (2004) Evaluation of load transfer characteristics of five different implants in compact bone at different load levels by finite elements analysis. J Prosthet Dent 92(6):523–530
Eraslan O, Sevimay M, Usumez A, Eslitascıoglu G (2005) Effects of cantilever design and material on stress distribution in fixed partial dentures—a finite element analysis. J Oral Rehabil 32(4):273–2788
Lin CL, Kuo YC, Lin TS (2005) Effects of dental implant length and bone quality on biomechanical responses in bone around implants: a 3-D non-linear finite element analysis. Biomed Eng Appl Basis Commun 17(1):44–49
Van Staden RC, Guan H, Loo YC (2006) Application of the finite element method in dental implant research. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 9(4):257–270
Quirynen M, Naert I, van Steenberghe D (1992) Fixture design and overload influence marginal bone loss and fixture success in the Branemark system. Clin Oral Implants Res 3(3):104–111
Martinez H, Davarpanah M, Missika P, Calletti R, Lazzara R (2001) Optimal implant stabilization in low density bone. Clin Oral Implants Res 12(5):423–432
Koca OL, Eskitascioglu G, Usumez A (2005) Three-dimensional finite-element analysis of functional stresses in different bone locations produced by implants placed in the maxillary posterior region of the sinus floor. J Prosthet Dent 93(1):38–44
Taylor TD, Agar JR, Vogiatzi T (2000) Implant prosthodontics: current perspective and future directions. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 15(1):66–75
Iplikcioglu H, Akca K, Cehreli MC, Sahin S (2003) Comparison of non-linear finite element stress analysis with in vitro strain gauge measurements on a Morse taper implant. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 18(2):258–265
Mansat P, Briot J, Mansat M, Swider P (2007) Evaluation of the glenoid implant survival using a biomechanical finite element analysis: influence of the implant design, bone properties, and loading location. J Shoulder Elb Surg 16(3):79–83
Simsek B, Erkmen E, Yılmaz D, Eser A (2006) Effects of different inter-implant distances on the stress distribution around endosseous implants in posterior mandible: a 3D finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys 28(3):199–213
Mercian P, Borak L, Valasek J, Kaiser J, Florian Z, Wolff J (2014) Finite element analysis of dental implant loading on atrophic and non-atrophic cancellous and cortical mandibular bone—a feasibility study. J Biomech 47(16):3830–3836
Chun HJ, Park DN, Han CH, Heo SJ, Heo MS, Koak JY (2005) Stress distributions in maxillary bone surrounding overdenture implants with different overdenture attachments. J Oral Rehabil 32(3):193–205
Barao VA, Assuncao WG, Tabata LF, Delben JA, Gomes EA, De Sousa EA, Rocha EP (2009) Finite element analysis to compare complete denture and implant-retained overdentures with different attachment systems. J Craniofac Surg 20(4):1066–1067
Takahashi T, Shimamura I, Sakurai K (2010) Influence of number and inclination angle of implants on stress distribution in mandibular cortical bone with All-on-4 concept. J Prosthodont Res 54(4):179–184
El-Anwar MI, El-Zawahry MM (2011) A three dimensional finite element study on dental implant design. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 9(1):77–82
Küçükkurt S, Alpaslan G, Kurt A (2017) Biomechanical comparison of sinus floor elevation and alternative treatment methods for dental implant placement. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 20(3):284–293
Francetti L, Romeo D, Corbella S, Taschieri S, Del Fabbro M (2012) Bone level changes around axial and tilted implants in full-arch fixed immediate restorations. Interim results of a prospective study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 14(5):646–654
Cehreli MC, Iplikcioglu H, Bilir OG (2002) The influence of the location of load transfer on strains around implants supporting four unit cement-retained fixed prostheses: in vitro evaluation of axial versus off-set loading. J Oral Rehabil 29(4):394–400
De Vico G, Bonin M, Spinelli D, Schiavetti R, Sannino G, Pozzi A, Ottria L (2011) Rationale for tilted implants: FEA considerations and clinical reports. J Oral Implantol 4:23–33
Naini RB, Nokar S, Borghei H, Alikhasi M (2011) Tilted or parallel implant placement in the completely edentulous mandible? A three-dimensional finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 26(4):776–781
Ogawa T, Dhaliwal S, Naert I, Mine A, Kronstrom M, Sasaki K, Duyck J (2010) Impact of implant number, distribution and prosthesis material on loading on implants supporting fixed prostheses. J Oral Rehabil 37(7):525–531
Pierrisnard L, Renouard F, Renault P, Barquins M (2003) Influence of implant length and bicortical anchorage on implant stress distribution. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 5(4):254–262
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank to Mechanical Engineer Sinan Köse for his valuable contributions to this study.
Funding
This study was funded by the Scientific Research Project Fund of Karadeniz Technical University, Trabzon, Turkey (Grant number: 2014-11400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gümrükçü, Z., Korkmaz, Y.T. Influence of implant number, length, and tilting degree on stress distribution in atrophic maxilla: a finite element study. Med Biol Eng Comput 56, 979–989 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1737-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1737-4