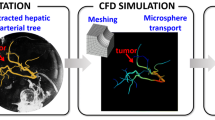
Abstract
Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) using Yttrium-90 loaded glass microspheres injected in the hepatic artery is an emerging, minimally invasive therapy of liver cancer. A personalized intervention can lead to high concentration dose in the tumor, while sparing the surrounding parenchyma. We propose a computational model for patient-specific simulation of entire hepatic arterial tree, based on liver, tumors, and arteries segmentation on patient’s tomography. Segmentation of hepatic arteries down to a diameter of 0.5 mm is semi-automatically performed on 3D cone-beam CT angiography. The liver and tumors are extracted from CT-scan at portal phase by an active surface method. Once the images are registered through an automatic multimodal registration, extracted data are used to initialize a numerical model simulating liver vascular network. The model creates successive bifurcations from given principal vessels, observing Poiseuille’s and matter conservation laws. Simulations provide a coherent reconstruction of global hepatic arterial tree until vessel diameter of 0.05 mm. Microspheres distribution under simple hypotheses is also quantified, depending on injection site. The patient-specific character of this model may allow a personalized numerical approximation of microspheres final distribution, opening the way to clinical optimization of catheter placement for tumor targeting.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreana L, Isgrȯ G, Marelli L, Davies N, Yu D, Navalkissoor S, Burroughs AK (2012) Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by intra-arterial infusion of radio-emitter compounds: trans-arterial radio-embolisation of HCC. Cancer Treat Rev 38(6):641–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2011.11.004
Andrews JC, Walker-Andrews SC, Juni JE, Warber S, Ensminger WD (1989) Modulation of liver tumor blood flow with hepatic arterial epinephrine: a spect study. Radiology 173(3):645–647
Behrens T, Rohr K, Stiehl HS (2003) Robust segmentation of tubular structures in 3-D medical images by parametric object detection and tracking. Syst Man. Cybern Part B Cybern IEEE Trans 33(4):554–561. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2003.814305
Childress EM, Kleinstreuer C (2014) Computationally Efficient Particle Release Map Determination for Direct Tumor-Targeting in a Representative Hepatic Artery System. J Biomech Eng 136(1):11,012–11,018. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4025881
Childress EM, Kleinstreuer C, Kennedy AS (2012) A New Catheter for Tumor-Targeting With Radioactive Microspheres in Representative Hepatic Artery Systems-Part II: Solid Tumor-Targeting in a Patient-Inspired Hepatic Artery System. J Biomech Eng 134(5):051,005. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4006685
Esneault S, Lafon C, Dillenseger JL (2010) Liver vessels segmentation using a hybrid geometrical moments/graph cuts method. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(2):276–283
Ficher A (1963). The liver. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4832-2824-2.50013-3
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285(21):1182–1186
Frangi AF, Niessen WJ, Vincken KL, Viergever MA (1998) Multiscale vessel enhancement filtering. Medial Image Comput Comput Assist Invervention 1496:130–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2004.08.001
Garin E, Lenoir L, Edeline J, Laffont S, Mesbah H, Porée P, Sulpice L, Boudjema K, Mesbah M, Guillygomarc A, Quehen E, Pracht M, Raoul JL, Clement B, Rolland Y, Boucher E (2013) Boosted selective internai radiation therapy with 90Y-loaded glass microspheres (B-SIRT) for hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a new personalized promising concept. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 20(7):1057–1068
GroupHealth (2013) Clinical Review Criteria. SIRT (Selective Internal Radiation Therapy) Therasphere and SIR Sphere for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jimenez-Carretero D, Santos A, Kerkstra S, Rudyanto RD, Ledesma-Carbayo MJ (2013) 3D Frangi-based lung vessel enhancement filter penalizing airways. In: 2013 IEEE 10th International Symposium Biomedicine of Imaging (ISBI). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2013.6556627, pp 926–929
Jurczuk K, Kretowski M, Eliat PA, Saint-Jalmes H, Bézy-Wendling J (2014) In Silico Modeling of Magnetic Resonance Flow Imaging in Complex Vascular Networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 33(11):2191–2209. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25020068
Kamiya A, Togawa T (1972) Optimal branching structure of the vascular tree. Bull Math Biophys 34 (4):431–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02476705
Kretowski M, Rolland Y, Bézy-Wendling J, Coatrieux JL (2003) Physiologically based modeling of 3-D vascular networks and CT scan angiography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 22(2):248–57. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12716001
Ledzewicz U, Maurer H, Schättler H (2011) Optimal and suboptimal protocols for a mathematical model for tumor anti-angiogenesis in combination with chemotherapy. Math Biosci Eng 8(2):307–323
Martini F, Nath JL, Bartholomew EF (2012) Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology. Pearson
Mescam M, Eliat PA, Fauvel C, de Certaines JD, Bėzy-Wendling J (2007) A physiologically based pharmacokinetic model of vascular-extravascular exchanges during liver carcinogenesis: application to MRI contrast agents. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2(5):215–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmmi.147, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17874424
Murthy R, Nunez R, Szklaruk J, Erwin W, Madoff DC, Gupta S, Ahrar K, Wallace MJ, Cohen A, Coldwell DM, Kennedy AS, Hicks ME (2005) Yttrium-90 microsphere therapy for hepatic malignancy: devices, indications, technical considerations, and potential complications. Radiographics 25 (Suppl 1):S41–S55. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.25si055515
Olufsen MS (1998) Modeling of the arterial system with reference to an anesthesia simulator. PhD thesis, Roskilde University
Pluim JPW, Maintz JBA, Viergever MA (2003) Mutual-information-based registration of medical images: a survey. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 22(8):986–1004. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2003.815867
Raoul JL, Sangro B, Forner A, Mazzaferro V, Piscaglia F, Bolondi L, Lencioni R (2011) Evolving strategies for the management of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: available evidence and expert opinion on the use of transarterial chemoembolization. Cancer Treat Rev 37(3):212–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.07.006
Reska D, Boldak C, Kretowski M (2012) Fast 3D segmentation of hepatic images combining region and boundary criteria. Image Process Commun 17(4):31–38
Reska D, Jurczuk K, Boldak C, Kretowski M (2014) MESA: Complete approach for design and evaluation of segmentation methods using real and simulated tomographic images. Biocybern Biomed Eng 34(3):146–158
Smistad E, Elster AC, Lindseth F (2014) GPU accelerated segmentation and centerline extraction of tubular structures from medical images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 9(4):561–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0956-x
Styner M, Brechbuhler C, Székely G, Gerig G (2000) Parametric estimate of intensity inhomogeneities applied to MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 19(3)
Zamir M, Chee H (1986) Branching characteristics of human coronary arteries. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 64 (6):661–668. https://doi.org/10.1139/y86-109
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Etienne Garin for his contribution to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simoncini, C., Jurczuk, K., Reska, D. et al. Towards a patient-specific hepatic arterial modeling for microspheres distribution optimization in SIRT protocol. Med Biol Eng Comput 56, 515–529 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1703-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1703-1