Abstract
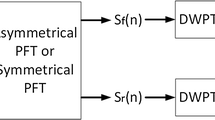
Quadrature signals are dual-channel signals obtained from the systems employing quadrature demodulation. Embolic Doppler ultrasound signals obtained from stroke-prone patients by using Doppler ultrasound systems are quadrature signals caused by emboli, which are particles bigger than red blood cells within circulatory system. Detection of emboli is an important step in diagnosing stroke. Most widely used parameter in detection of emboli is embolic signal-to-background signal ratio. Therefore, in order to increase this ratio, denoising techniques are employed in detection systems. Discrete wavelet transform has been used for denoising of embolic signals, but it lacks shift invariance property. Instead, dual-tree complex wavelet transform having near-shift invariance property can be used. However, it is computationally expensive as two wavelet trees are required. Recently proposed modified dual-tree complex wavelet transform, which reduces the computational complexity, can also be used. In this study, the denoising performance of this method is extensively evaluated and compared with the others by using simulated and real quadrature signals. The quantitative results demonstrated that the modified dual-tree-complex-wavelet-transform-based denoising outperforms the conventional discrete wavelet transform with the same level of computational complexity and exhibits almost equal performance to the dual-tree complex wavelet transform with almost half computational cost.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achim A, Bezerianos A, Tsakalides P (2001) Novel Bayesian multiscale method for speckle removal in medical ultrasound images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20(8):772–783
Ackerstaff RG, Babikian VL, Georgiadis D, Russell D, Siebler M, Spencer MP, Stump D (1995) Basic identification criteria of Doppler microembolic signals. Stroke 26:1123
Aydin N, Evans DH (1994) Implementation of directional Doppler techniques using a digital signal processor. Med Biol Eng Comput 32:157–164
Aydin N, Fan L, Evans DH (1994) Quadrature-to-directional format conversion of Doppler signals using digital methods. Physiol Meas 15:181–199
Aydin N, Marvasti F, Markus HS (2002) Effect of wavelet denoising on time-frequency and time-scale analysis of quadrature embolic signals. In: Proceedings of 24th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, Houston, pp 80–81
Aydin N, Marvasti F, Markus HS (2004) Embolic Doppler ultrasound signal detection using discrete wavelet transform. IEEE Trans Inf Tech Biomed 8(2):182–190
Boashash B (1992) Estimating and interpreting the instantaneous frequency of a signal: a tutorial review—part 2: algorithms and applications. Proc IEEE 80:539–568
Brigham EO (1974) The fast Fourier transform. Prentice Hall Inc, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Chang SG, Yu B, Vetterli M (2000) Adaptive wavelet thresholding for image denoising and compression. Trans Image Process 9(9):1532–1546
Cohen L (1989) Time-frequency distributions—a review. Proc IEEE 77(7):941–981
Donoho DL (1995) Denoising by soft-thresholding. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 41:613–647
Donoho DL, Johnstone IM (1994) Ideal spatial adaptation via wavelet shrinkage. Biometrika 81:425–455
Donoho DL, Johnstone IM (1995) Adapting to unknown smoothness via wavelet shrinkage. J Am Stat Assoc 90(432):1200–1224
Donoho DL, Johnstone IM (1998) Minimax estimation via wavelet shrinkage. Ann Stat 26(3):879–921
Evans DH, McDicken WN, Skidmore R, Woodcock JP (1989) Doppler Ultrasound: Physics, Instrumentation and Clinical Applications. Wiley, Chichester
Fan L, Evans DH, Naylor AR, Tortoli P (2004) Real-time identification and archival of microembolic Doppler signals using a knowledge-based system. Med Biol Eng Comput 42:193–204
Kingsbury NG (1998) The dual-tree complex wavelet transform: a new technique for shift invariance and directional filters. IEEE Digital Signal Process Workshop Bryce Canyon 86:319–322
Kingsbury NG (1999) Image processing with complex wavelets. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A 357:2543–2560
Krim H, Tucker D, Mallat S, Donoho D (1999) On denoising and best signal representation. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 45(7):2225–2238
Li H, Zhang Y, Xu D (2010) Noise and speckle reduction in Doppler blood flow spectrograms using an adaptive pulse-coupled neural network. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process. doi:10.1155/2010/918015
Markus H (1993) Transcranial Doppler detection of circulating cerebral emboli. A review. Stroke 24(8):1246–1250
Markus HS, Harrison MJ (1995) Microembolic signal detection using ultrasound. Stroke 26:1517–1519
Markus HS, Molloy J (1997) The use of a decibel threshold in the detection of embolic signals. Stroke 28:692–695
Markus HS, Reid G (1999) Frequency filtering improves ultrasonic embolic signal detection. Ultrasound Med Biol 25:857–860
Markus H, Loh A, Brown MM (1993) Computerized detection of cerebral emboli and discrimination from artifact using Doppler ultrasound. Stroke 24(11):1667–1672
Marvasti S, Gillies D, Marvasti F, Markus HS (2004) Online automated detection of cerebral embolic signals using a wavelet based system. Ultrasound in Med Biol 30:647–653
Marvasti S, Gillies D, Markus HS (2004) Novel intelligent wavelet filtering of embolic signals from TCD ultrasound. Conference record of the thirty-eighth Asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers, vol 2, pp 1580–1584
Pasti L, Walczak B, Massart DL, Reschiglian P (1999) Optimization of signal denoising in discrete wavelet transform. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 48:21–34
Selesnick IW, Baraniuk RG, Kingsbury NG (2005) The dual-tree complex wavelet transform. IEEE Signal Process Mag 22(6):123–151
Serbes G, Aydin N, (2009) A complex discrete wavelet transform for processing quadrature Doppler ultrasound signals. In: 9th international conference on information technology and applications in biomedicine ITAB 2009
Serbes G, Aydin N, (2010) Denoising performance of modified dual tree complex wavelet transform. In: 10th international conference on information technology and applications in biomedicine ITAB 2010, pp 1–4
Serbes G, Aydin N (2011) Modified dual tree complex wavelet transform for processing quadrature signals. Biomed Signal Process Control 6(3):301–306
Spencer MP, Thomas GI, Nicholls SC, Sauvage LR (1990) Detection of middle cerebral artery emboli during carotid endarterectomy using transcranial Doppler ultrasonography. Stroke 21:415–423
Taswell C (2000) The what, how, and why of wavelet shrinkage denoising. Comput Sci Eng 2(3):12–19
Yoon BJ, Vaidyanathan PP (2004) Wavelet-based denoising by customized thresholding. IEEE Int Conf Acoust Speech Signal Process 2:925–928
Zhang Y, Wang L, Gao Y, Chen J, Shi X (2007) Noise reduction in Doppler ultrasound signals using an adaptive decomposition algorithm. Med Eng Phys 29(6):699–707
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serbes, G., Aydin, N. Denoising performance of modified dual-tree complex wavelet transform for processing quadrature embolic Doppler signals. Med Biol Eng Comput 52, 29–43 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-013-1114-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-013-1114-x