Abstract
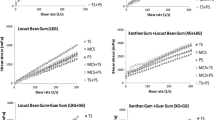
In this study, effects of different starches (tapioca (TS), wheat (WS), corn (CS), potato (PS), modified corn (MCS) and modified potato (MPS)) and gums (xanthan gum (XG), guar gum (GG), alginate (A), salep (S), locust bean gum (LBG) and carrageen (C)) on the rheological properties of model hot chocolate beverage were studied. Swelling power (SP) of the starches and water absorption capacity (WAC) of the gums were determined. Hot chocolate beverages showed pseudoplastic behaviour. Ostwald de Waele model accurately described flow behaviour of each beverage sample. K, n, R 2 values for Ostwald model were in the range of 4.8–160.3 mPa.sn, 0.5117–0.9745, 0.9972–0.9998, respectively. The highest synergic effect in the model was observed between the interaction of MCS and XG. The XG-PS, XG-TS, XG-CS combinations showed the highest K and viscosity values, respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.C. Da Silva Lannes, M.L. Medeiros, Int. J. Food Eng. 4(1), 1–11 (2008)
P. Achayuthakan, M. Suphantharika, Carbohydr. Polym. 71(1), 9–17 (2008)
D.M. Folkenberg, W.L.P. Bredie, M. Martens, J. Sensory Stud. 14, 181–195 (1999)
M. Yanes, L. Duran, E. Costell, J. Food Eng. 51(3), 229–234 (2002)
M.M. Raats, R. Shepherd, J. Sensory Stud. 7, 179–203 (1992)
G. Hough, R. Sanchez, T. Barbiery, E. Martinez, Food Qual. Pref. 8, 213–221 (1997)
R.M. Pangborn, Sensory attributes and acceptance of fat, sugar, and salt in dairy products, in Food Acceptability, ed. by D.M.H. Thomson (Elsevier Applied Science, London and New York, 1988)
A.C. Eliasson, M. Gudmundsson, Starch: Physicochemical and functional aspects, in Carbohydrates in Food, 2nd edn., ed. by A.-C. Eliasson (CRC, Boca Raton, 2006)
E. Dickinson, Food Hydrocoll. 17(1), 25–39 (2003)
A. Kayacier, M. Dogan, J. Food Eng. 72(3), 261–265 (2006)
M. Chaisawang, M. Suphantharika, Carbohydr. Polymer. 61(3), 288–295 (2005)
C. Kim, S.M. Lee, B. Yoo, Starch 58, 35–43 (2006)
H.M. Choi, B. Yoo, Starch-Starke 60, 263–269 (2008)
M. Alloncle, J.L. Doublier, Food Hydrocoll. 5(5), 455–467 (1991)
M. Alloncle, J. Lefebvre, G. Llamas, J.L. Doublier, Cereal Chem. 66(2), 90–93 (1989)
C.B. Closs, B. Conde-Petit, I.D. Roberts, V.B. Tolstoguzov, F. Escher, Carbohyd. Polymer. 39(1), 67–77 (1999)
P. Rayment, S.B. Ross-Murphy, P.R. Ellis, Carbohyd. Polymer. 28(2), 121–130 (1995)
D.D. Christianson, J.E. Hodge, D. Osborne, R.W. Detroy, Cereal Chem. 58, 513–517 (1981)
M.H. Lee, M.H. Baek, D.S. Cha, H.J. Park, S.T. Lim, Food Hydrocoll. 16(4), 345–352 (2002)
M. Dolz, M.J. Hernandez, J. Delegido, M.C. Alfaro, J. Food Eng. 81(1), 179–186 (2007)
G. Hough, R. Sanchez, Food Qual. Pref. 9, 197–204 (1998)
M.L. Tsai, C.F. Li, C.Y. Lii, Cereal Chem. 74, 750–757 (1997)
American Association of Cereal Chemists (AACC), Approved Methods of the AACC, 9th edn. (The Association, St Paul, 1995)
A. Ural, I. Kilic, Data Analysis with SPSS (Detay, Ankara, 2006)
M. Wotton, A. Bamunuarachchi, Starch 33, 159–161 (1978)
A.M. Hermansson, K. Swegmark, Trends Food Sci. Tech. 7, 345–353 (1996)
Y. Hibi, Starch 53, 227–234 (2001)
Y.J. Li, A.I. Yeh, J Food Eng. 50, 141–148 (2001)
S. Mishra, T.I. Rai, Food Hydrocoll. 20(5), 557–566 (2006)
R. Hoover, F. Sosulski, Starch 38, 149–155 (1986)
L.S. Sciarini, F. Maldonado, P.D. Ribotta, G.T. Perez, A.E. Leon, Food Hydrocoll. 23(2), 306–313 (2009)
H. Deue, H. Neukom, Adv. Chem. Ser. 11, 51–61 (1954)
I.C.M. Dea, A. Morrison, Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 31, 241–312 (1975)
F. Brown, K.R. Diller, Burns 34, 648–654 (2008)
M.A. Rao, Rheology of Fluid and Semisolid Foods—Principles and Application (An Aspen Publication, Gaithersburg, 1999)
G. Schramm, Rheology—Fundamentals and Applications, vol. 194 (Osrodek Wydawnictw Naukowych, Poznan, 1998)
M. Sikora, S. Kowalski, P. Tomasik, M. Sady, J. Food Eng. 79(4), 1144–1151 (2007)
J.M. Steffe, Rheological Methods in Food Process Engineering, 2nd edn. (Freeman, East Lansing, 1996)
Y.A. Bahnassey, W.M. Breene, Starch-Starke 46, 134–141 (1994)
J.A. Rojas, C.M. Rosell, C. Benedito de Barber, Food Hydrocoll. 13(1), 27–33 (1999)
S.B. Ross-Murphy, J. Rheol. 39, 1451–1463 (1995)
I.G. Mandala, E. Bayas, Food Hydrocoll. 18(2), 191–201 (2003)
V. Sudhakar, R.S. Singhal, P.R. Kulkarni, Food Chem. 55(3), 259–264 (1996)
X. Shi, J.N. BeMiller, Carbohyd. Polymer. 50(1), 7–18 (2002)
N.A. Abdulmola, M.W.N. Hember, R.K. Richardson, E.R. Morris, Carbohyd. Polymer. 31(1), 65–78 (1996)
F.W. Wood, Psychophysical Studies on the Consistency of Liquid Foods. S.C.L Monograph: Rheology and Texture of Food Stuffs (4CM9. Society of Chemical Industry, London, 1968)
M. Dogan, A. Kayacier, E. Ic, Food Hydrocoll. 21(3), 392–396 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dogan, M., Toker, O.S. & Goksel, M. Rheological Behaviour of Instant Hot Chocolate Beverage: Part 1. Optimization of the Effect of Different Starches and Gums. Food Biophysics 6, 512–518 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-011-9233-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-011-9233-0