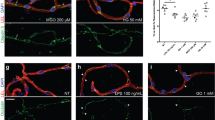
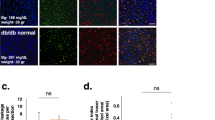
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disorder due to the inability properly to metabolize glucose associated with dysregulation of metabolic pathways of lipids and proteins resulting in structural and functional changes of various organ systems. DM has detrimental effects on the vasculature, resulting in the development of various cardiovascular diseases and stemming from microvascular injury. The blood brain barrier (BBB) is a highly specialized structure protecting the unique microenvironment of the brain. Endothelial cells, connected by junctional complexes and expressing numerous transporters, constitute the main cell type in the BBB. Other components, including pericytes, basement membrane, astrocytes and perivascular macrophages, join endothelial cells to form the neurovascular unit (NVU) and contribute to the proper function and integrity of the BBB. The role of the BBB in the pathogenesis of diabetic encephalopathy and other diabetes-related complications in the central nervous system is apparent. However, the mechanisms, timing and consequences of BBB injury in diabetes are not well understood. The importance of further studies related to barrier dysfunction in diabetes is dictated by its potential involvement in the cognitive demise associated with DM. This review summarizes the impact of DM on BBB/NVU integrity and function leading to neurological and cognitive complications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott NJ (2000) Inflammatory mediators and modulation of blood-brain barrier permeability. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20:131–147
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ (2010) Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis 37:13–25
Acharya NK, Levin EC, Clifford PM, Han M, Tourtellotte R, Chamberlain D, Pollaro M, Coretti NJ, Kosciuk MC, Nagele EP, Demarshall C, Freeman T, Shi Y, Guan C, Macphee CH, Wilensky RL, Nagele RG (2013) Diabetes and hypercholesterolemia increase blood-brain barrier permeability and brain amyloid deposition: beneficial effects of the LpPLA2 inhibitor darapladib. J Alzheimers Dis 35:179–198
Ahmed N (2005) Advanced glycation endproducts--role in pathology of diabetic complications. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 67:3–21
Alexandru N, Badila E, Weiss E, Cochior D, Stepien E, Georgescu A (2016) Vascular complications in diabetes: Microparticles and microparticle associated microRNAs as active players. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 472:1–10
Allen CL, Bayraktutan U (2009) Antioxidants attenuate hyperglycaemia-mediated brain endothelial cell dysfunction and blood-brain barrier hyperpermeability. Diabetes Obes Metab 11:480–490
Alvarez JI, Katayama T, Prat A (2013) Glial influence on the blood brain barrier. Glia 61:1939–1958
Arboleda-Velasquez JF, Valdez CN, Marko CK, D'Amore PA (2015) From pathobiology to the targeting of pericytes for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diab Rep 15:573
Argaw AT, Gurfein BT, Zhang Y, Zameer A, John GR (2009) VEGF-mediated disruption of endothelial CLN-5 promotes blood-brain barrier breakdown. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:1977–1982
Bates DO (2010) Vascular endothelial growth factors and vascular permeability. Cardiovasc Res 87:262–271
Bouchard P, Ghitescu LD, Bendayan M (2002) Morpho-functional studies of the blood-brain barrier in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetologia 45:1017–1025
Brownlee M (2001) Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 414:813–820
Ceriello A (2012) The emerging challenge in diabetes: the "metabolic memory". Vasc Pharmacol 57:133–138
Chen CH, Mayo JN, Gourdie RG, Johnstone SR, Isakson BE, Bearden SE (2015) The connexin 43/ZO-1 complex regulates cerebral endothelial F-actin architecture and migration. Am J Phys Cell Phys 309:C600–C607
Chronopoulos A, Tang A, Beglova E, Trackman PC, Roy S (2010) High glucose increases lysyl oxidase expression and activity in retinal endothelial cells: mechanism for compromised extracellular matrix barrier function. Diabetes 59:3159–3166
Dave KR, Tamariz J, Desai KM, Brand FJ, Liu A, Saul I, Bhattacharya SK, Pileggi A (2011) Recurrent hypoglycemia exacerbates cerebral ischemic damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Stroke 42:1404–1411
Davidson TL, Monnot A, Neal AU, Martin AA, Horton JJ, Zheng W (2012) The effects of a high-energy diet on hippocampal-dependent discrimination performance and blood-brain barrier integrity differ for diet-induced obese and diet-resistant rats. Physiol Behav 107:26–33
Dias IH, Griffiths HR (2014) Oxidative stress in diabetes - circulating advanced glycation end products, lipid oxidation and vascular disease. Ann Clin Biochem 51:125–127
Dinapoli VA, Benkovic SA, Li X, Kelly KA, Miller DB, Rosen CL, Huber JD, O'Callaghan JP (2010) Age exaggerates proinflammatory cytokine signaling and truncates signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 signaling following ischemic stroke in the rat. Neuroscience 170:633–644
Ding C, He Q, Li PA (2005) Diabetes increases expression of ICAM after a brief period of cerebral ischemia. J Neuroimmunol 161:61–67
Fanning AS, Little BP, Rahner C, Utepbergenov D, Walther Z, Anderson JM (2007) The unique-5 and -6 motifs of ZO-1 regulate tight junction strand localization and scaffolding properties. Mol Biol Cell 18:721–731
Gandhi GK, Ball KK, Cruz NF, Dienel GA (2010) Hyperglycaemia and diabetes impair gap junctional communication among astrocytes. ASN Neuro 2:e00030
Hawkins BT, Lundeen TF, Norwood KM, Brooks HL, Egleton RD (2007) Increased blood-brain barrier permeability and altered tight junctions in experimental diabetes in the rat: contribution of hyperglycaemia and matrix metalloproteinases. Diabetologia 50:202–211
Huber JD, VanGilder RL, Houser KA (2006) Streptozotocin-induced diabetes progressively increases blood-brain barrier permeability in specific brain regions in rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H2660–H2668
Janelidze S, Hertze J, Nagga K, Nilsson K, Nilsson C, Swedish Bio FSG, Wennstrom M, van Westen D, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Hansson O (2017) Increased blood-brain barrier permeability is associated with dementia and diabetes but not amyloid pathology or APOE genotype. Neurobiol Aging 51:104–112
Junker U, Jaggi C, Bestetti G, Rossi GL (1985) Basement membrane of hypothalamus and cortex capillaries from normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Acta Neuropathol 65:202–208
Kim LA, Wong LL, Amarnani DS, Bigger-Allen AA, Hu Y, Marko CK, Eliott D, Shah VA, McGuone D, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Gai X, D'Amore PA, Arboleda-Velasquez JF (2015) Characterization of cells from patient-derived fibrovascular membranes in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Mol Vis 21:673–687
Kwan P, Brodie MJ (2005) Potential role of drug transporters in the pathogenesis of medically intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia 46:224–235
Liu H, Xu X, Yang Z, Deng Y, Liu X, Xie L (2006) Impaired function and expression of P-glycoprotein in blood-brain barrier of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Brain Res 1123:245–252
Lu QY, Chen W, Lu L, Zheng Z, Xu X (2014) Involvement of RhoA/ROCK1 signaling pathway in hyperglycemia-induced microvascular endothelial dysfunction in diabetic retinopathy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:7268–7277
Mankovsky BN, Ziegler D (2004) Stroke in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 20:268–287
McCorry D, Nicolson A, Smith D, Marson A, Feltbower RG, Chadwick DW (2006) An association between type 1 diabetes and idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Ann Neurol 59:204–206
McCuskey PA, McCuskey RS (1984) In vivo and electron microscopic study of the development of cerebral diabetic microangiography. Microcirc Endothel Lymphat 1:221–244
Min LJ, Mogi M, Shudou M, Jing F, Tsukuda K, Ohshima K, Iwanami J, Horiuchi M (2012) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation with angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade is pivotal for the prevention of blood-brain barrier impairment and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetic mice. Hypertension 59:1079–1088
Minamizono A, Tomi M, Hosoya K (2006) Inhibition of dehydroascorbic acid transport across the rat blood-retinal and -brain barriers in experimental diabetes. Biol Pharm Bull 29:2148–2150
Mogi M, Horiuchi M (2011) Neurovascular coupling in cognitive impairment associated with diabetes mellitus. Circ J 75:1042–1048
Mooradian AD (1997) Central nervous system complications of diabetes mellitus--a perspective from the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 23:210–218
Norhammar A, Tenerz A, Nilsson G, Hamsten A, Efendic S, Ryden L, Malmberg K (2002) Glucose metabolism in patients with acute myocardial infarction and no previous diagnosis of diabetes mellitus: a prospective study. Lancet 359:2140–2144
Oltmanns KM, Melchert UH, Scholand-Engler HG, Schultes B, Schweiger U, Peters A (2008) Divergent effects of hyper- and hypoglycemia on circulating vascular endothelial growth factor in humans. Metabolism 57:90–94
Pasquier F, Boulogne A, Leys D, Fontaine P (2006) Diabetes mellitus and dementia. Diabete Metab 32:403–414
Patrick P, Price TO, Diogo AL, Sheibani N, Banks WA, Shah GN (2015) Topiramate protects Pericytes from Glucotoxicity: role for mitochondrial CA VA in Cerebromicrovascular disease in diabetes. J Endocrinol Diabetes 2(2). http://www.symbiosisonlinepublishing.com/endocrinology-diabetes/endocrinology-diabetes23.php
Peng F, Wu D, Gao B, Ingram AJ, Zhang B, Chorneyko K, McKenzie R, Krepinsky JC (2008) RhoA/rho-kinase contribute to the pathogenesis of diabetic renal disease. Diabetes 57:1683–1692
Peng H, Luo P, Li Y, Wang C, Liu X, Ye Z, Li C, Lou T (2013) Simvastatin alleviates hyperpermeability of glomerular endothelial cells in early-stage diabetic nephropathy by inhibition of RhoA/ROCK1. PLoS One 8:e80009
Persidsky Y (1999) Model systems for studies of leukocyte migration across the blood - brain barrier. J Neuro-Oncol 5:579–590
Persidsky Y, Ghorpade A, Rasmussen J, Limoges J, Liu XJ, Stins M, Fiala M, Way D, Kim KS, Witte MH, Weinand M, Carhart L, Gendelman HE (1999) Microglial and astrocyte chemokines regulate monocyte migration through the blood-brain barrier in human immunodeficiency virus-1 encephalitis. Am J Pathol 155:1599–1611
Persidsky Y, Ramirez SH, Haorah J, Kanmogne GD (2006a) Blood-brain barrier: structural components and function under physiologic and pathologic conditions. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 1:223–236
Persidsky Y, Heilman D, Haorah J, Zelivyanskaya M, Persidsky R, Weber GA, Shimokawa H, Kaibuchi K, Ikezu T (2006b) Rho-mediated regulation of tight junctions during monocyte migration across the blood-brain barrier in HIV-1 encephalitis (HIVE). Blood 107:4770–4780
Persidsky Y, Hill J, Zhang M, Dykstra H, Winfield M, Reichenbach NL, Potula R, Mukherjee A, Ramirez SH, Rom S (2016) Dysfunction of brain pericytes in chronic neuroinflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36:794–807
Poittevin M, Bonnin P, Pimpie C, Riviere L, Sebrie C, Dohan A, Pocard M, Charriaut-Marlangue C, Kubis N (2015) Diabetic microangiopathy: impact of impaired cerebral vasoreactivity and delayed angiogenesis after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion on stroke damage and cerebral repair in mice. Diabetes 64:999–1010
Prakash R, Johnson M, Fagan SC, Ergul A (2013) Cerebral neovascularization and remodeling patterns in two different models of type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 8:e56264
Prasad S, Sajja RK, Naik P, Cucullo L (2014) Diabetes mellitus and blood-brain barrier dysfunction: an overview. Aust J Pharm 2:125
Reichel V, Burghard S, John I, Huber O (2011) P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein expression and function at the blood-brain barrier and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier (choroid plexus) in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Brain Res 1370:238–245
Safiah Mokhtar S, MV P, WSL S, Imran Yusof M, Wan Sulaiman WA, Zaharil Mat Saad A, Suppian R, Ghulam Rasool AH (2013) Reduced expression of prostacyclin synthase and nitric oxide synthase in subcutaneous arteries of type 2 diabetic patients. Tohoku J Exp Med 231:217–222
Sahin D, Ilbay G, Ates N (2003) Changes in the blood-brain barrier permeability and in the brain tissue trace element concentrations after single and repeated pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in rats. Pharmacol Res 48:69–73
Schober E, Otto KP, Dost A, Jorch N, Holl R, German/Austrian DPVI, the BCND (2012) Association of epilepsy and type 1 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents: is there an increased risk for diabetic ketoacidosis? J Pediatr 160(662–666):e661
Serban AI, Stanca L, Geicu OI, Munteanu MC, Dinischiotu A (2016) RAGE and TGF-beta1 cross-talk regulate extracellular matrix turnover and cytokine synthesis in AGEs exposed fibroblast cells. PLoS One 11:e0152376
Shah GN, Morofuji Y, Banks WA, Price TO (2013) High glucose-induced mitochondrial respiration and reactive oxygen species in mouse cerebral pericytes is reversed by pharmacological inhibition of mitochondrial carbonic anhydrases: implications for cerebral microvascular disease in diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 440:354–358
Shao B, Bayraktutan U (2013) Hyperglycaemia promotes cerebral barrier dysfunction through activation of protein kinase C-beta. Diabetes Obes Metab 15:993–999
Shimizu F, Sano Y, Tominaga O, Maeda T, Abe MA, Kanda T (2013) Advanced glycation end-products disrupt the blood-brain barrier by stimulating the release of transforming growth factor-beta by pericytes and vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase-2 by endothelial cells in vitro. Neurobiol Aging 34:1902–1912
Stamatovic SM, Shakui P, Keep RF, Moore BB, Kunkel SL, Van Rooijen N, Andjelkovic AV (2005) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:593–606
Starr JM, Wardlaw J, Ferguson K, MacLullich A, Deary IJ, Marshall I (2003) Increased blood-brain barrier permeability in type II diabetes demonstrated by gadolinium magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:70–76
Summers WK (2004) Alzheimer's disease, oxidative injury, and cytokines. J Alzheimers Dis 6:651–657 discussion 673-681
Suzuki A, Ishiyama C, Hashiba K, Shimizu M, Ebnet K, Ohno S (2002) aPKC kinase activity is required for the asymmetric differentiation of the premature junctional complex during epithelial cell polarization. J Cell Sci 115:3565–3573
Tarallo S, Beltramo E, Berrone E, Porta M (2012) Human pericyte-endothelial cell interactions in co-culture models mimicking the diabetic retinal microvascular environment. Acta Diabetol 49(Suppl 1):S141–S151
TG B (1989) Epileptic seizures and the blood-brain barrier., Neuwelt, EA edn. Plenum Medical Book Company, New York and London
Tien T, Muto T, Barrette K, Challyandra L, Roy S (2014) Downregulation of Connexin 43 promotes vascular cell loss and excess permeability associated with the development of vascular lesions in the diabetic retina. Mol Vis 20:732–741
Wang J, Li G, Wang Z, Zhang X, Yao L, Wang F, Liu S, Yin J, Ling EA, Wang L, Hao A (2012a) High glucose-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species in cultured astrocytes. Neuroscience 202:58–68
Wang S, Cao C, Chen Z, Bankaitis V, Tzima E, Sheibani N, Burridge K (2012b) Pericytes regulate vascular basement membrane remodeling and govern neutrophil extravasation during inflammation. PLoS One 7:e45499
Wegmann F, Petri B, Khandoga AG, Moser C, Khandoga A, Volkery S, Li H, Nasdala I, Brandau O, Fassler R, Butz S, Krombach F, Vestweber D (2006) ESAM supports neutrophil extravasation, activation of rho, and VEGF-induced vascular permeability. J Exp Med 203:1671–1677
Winkler EA, Bell RD, Zlokovic BV (2011) Central nervous system pericytes in health and disease. Nat Neurosci 14:1398–1405
Xie X, Lan T, Chang X, Huang K, Huang J, Wang S, Chen C, Shen X, Liu P, Huang H (2013) Connexin43 mediates NF-kappaB signalling activation induced by high glucose in GMCs: involvement of c-Src. Cell Commun Signal 11:38
Xu Z, Zeng W, Sun J, Chen W, Zhang R, Yang Z, Yao Z, Wang L, Song L, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Wang C, Gong L, Wu B, Wang T, Zheng J, Gao F (2016) The quantification of blood-brain barrier disruption using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in aging rhesus monkeys with spontaneous type 2 diabetes mellitus. Neuroimage. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.07.017
Yoo DY, Yim HS, Jung HY, Nam SM, Kim JW, Choi JH, Seong JK, Yoon YS, Kim DW, Hwang IK (2016a) Chronic type 2 diabetes reduces the integrity of the blood-brain barrier by reducing tight junction proteins in the hippocampus. J Vet Med Sci 78:957–962
Yoo S, Ahn H, Park YK (2016b) High dietary fructose intake on cardiovascular disease related parameters in growing rats. Nutrients 9(1):11
Yorulmaz H, Kaptan E, Seker FB, Oztas B (2015) Type 1 diabetes exacerbates blood-brain barrier alterations during experimental epileptic seizures in an animal model. Cell Biochem Funct 33:285–292
Zhong Y, Wang JJ, Zhang SX (2012) Intermittent but not constant high glucose induces ER stress and inflammation in human retinal pericytes. Adv Exp Med Biol 723:285–292
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported in part by the National Institutes of Health grants: DA013429, MH65151, AA015913, MH106967 (YP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bogush, M., Heldt, N.A. & Persidsky, Y. Blood Brain Barrier Injury in Diabetes: Unrecognized Effects on Brain and Cognition. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 12, 593–601 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-017-9752-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-017-9752-7