Abstract
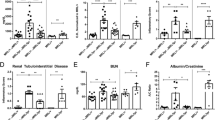
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that is frequently accompanied by diverse neuropsychiatric manifestations. An increased frequency of olfactory deficits has been recently reported as another marker of CNS involvement in SLE patients. Similarly, we observed that spontaneous development of lupus-like disease in MRL/lpr mice is accompanied by altered olfaction-related behaviors. However, it remained unclear whether the behavioral deficits are due to systemic autoimmunity, or the distinct genetic make-up. To address this question, we presently examine whether prolonged treatment with the immunosuppressive drug cyclophosphamide (CY) restores odor-guided behaviors in MRL/lpr mice. Over 12 weekends, MRL/lpr and control MRL +/+ males were given ad lib access to a sweetened CY solution or a vehicle. Their responsiveness to different scents was assessed at ages corresponding to mild, modest, and severe disease. Odor-guided exploratory behavior was further examined in the novel object test at 21 weeks of age, shortly before terminal assessment of immunopathology. In comparison to control groups, MRL/lpr mice exposed to CY exhibited normal spleen size and antibody levels, as well as increased responsiveness to an attractant and a novel object. However, CY treatment also exacerbated their aberrant response to a repellent, suggesting a dual mode of action on brain olfactory systems. The present results reveal that generalized immunosuppression modulates odor-guided behaviors in lupus-prone animals. Although key pathogenic mechanisms are not clear, the findings strengthen the construct validity of the MRL model by supporting the hypothesis that onset of systemic autoimmunity alters the activity of olfactory circuits.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander JJ, Quigg RJ (2007) Systemic lupus erythematosus and the brain: what mice are telling us. Neurochem Int 50(1):5–11
Balcombe JP, Barnard ND, Sandusky C (2004) Laboratory routines cause animal stress. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci 43(6):42–51
Ballok DA, Earls AM, Krasnik C, Hoffman SA, Sakic B (2004a) Autoimmune-induced damage of the midbrain dopaminergic system in lupus-prone mice. J Neuroimmunol 152(1–2):83–97
Ballok DA, Woulfe J, Sur M, Cyr M, Sakic B (2004b) Hippocampal damage in mouse and human forms of systemic autoimmune disease. Hippocampus 14(5):649–661
Denenberg VH, Mobraaten LE, Sherman GF, Morrison L, Schrott LM, Waters NS et al (1991) Effects of the autoimmune uterine/maternal environment upon cortical ectopias, behavior and autoimmunity. Brain Res 563:114–122
Dixon FJ, Andrews BS, Eisenberg RA, McConahey PJ, Theofilopoulos AN, Wilson CB (1978) Etiology and pathogenesis of a spontaneous lupus-like syndrome in mice. Arthritis Rheum 21:S64–SS7
Doty RL (1975) Intranasal trigeminal detection of chemical vapors by humans. Physiol Behav 14(6):855–859
Doty RL, Brugger WE, Jurs PC, Orndorff MA, Snyder PJ, Lowry LD (1978) Intranasal trigeminal stimulation from odorous volatiles: psychometric responses from anosmic and normal humans. Physiol Behav 20(2):175–185
Farrell M, Sakic B, Szechtman H, Denburg JA (1997) Effect of cyclophosphamide on leucocytic infiltration in the brain of MRL/lpr mice. Lupus 6(3):268–274
Grota LJ, Schachtman TR, Moynihan JA, Cohen N, Ader R (1989) Voluntary consumption of cyclophosphamide by Mrl mice. Brain Behav Immun 3:263–273
Grota LJ, Ader R, Moynihan JA, Cohen N (1990) Voluntary consumption of cyclophosphamide by nondeprived Mrl- lpr/lpr and Mrl +/+ mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 37:527–530
Gulinello M, Putterman C (2011) The MRL/lpr mouse strain as a model for neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:207504
Hanly JG, Urowitz MB, Siannis F, Farewell V, Gordon C, Bae SC et al (2008) Autoantibodies and neuropsychiatric events at the time of systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosis: results from an international inception cohort study. Arthritis Rheum 58(3):843–853
Hirohata S, Arinuma Y, Takayama M, Yoshio T (2007) Association of cerebrospinal fluid anti-ribosomal p protein antibodies with diffuse psychiatric/neuropsychological syndromes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 9(3):R44
Jeltsch-David H, Muller S (2014) Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus and cognitive dysfunction: the MRL-lpr mouse strain as a model. Autoimmun Rev 13(9):963–973
Kapadia M, Stanojcic M, Earls AM, Pulapaka S, Lee J, Sakic B (2012) Altered olfactory function in the MRL model of CNS lupus. Behav Brain Res 234(2):303–311
Katzav A, Solodeev I, Brodsky O, Chapman J, Pick CG, Blank M et al (2007) Induction of autoimmune depression in mice by anti-ribosomal P antibodies via the limbic system. Arthritis Rheum 56(3):938–948
Katzav A, Ben-Ziv T, Chapman J, Blank M, Reichlin M, Shoenfeld Y (2008) Anti-P ribosomal antibodies induce defect in smell capability in a model of CNS -SLE (depression). J Autoimmun 31(4):393–398
Kim A, Feng P, Ohkuri T, Sauers D, Cohn ZJ, Chai J et al (2012) Defects in the peripheral taste structure and function in the MRL/lpr mouse model of autoimmune disease. PLoS One 7(4):e35588
Kivity S, Tsarfaty G, Agmon-Levin N, Blank M, Manor D, Konen E et al (2010) Abnormal olfactory function demonstrated by manganese-enhanced MRI in mice with experimental neuropsychiatric lupus. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1193(1):70–77
Kivity S, Agmon-Levin N, Zandman-Goddard G, Chapman J, Shoenfeld Y (2015) Neuropsychiatric lupus: a mosaic of clinical presentations. BMC Med 4(13):43
Lee JY, Huerta PT, Zhang J, Kowal C, Bertini E, Volpe BT et al (2009) Neurotoxic autoantibodies mediate congenital cortical impairment of offspring in maternal lupus. Nat Med 15(1):91–96
Loheswaran G, Stanojcic M, Xu L, Sakic B (2010) Autoimmunity as a principal pathogenic factor in the refined model of neuropsychiatric lupus. Clin Exp Neurol 1:141–152
Loheswaran G, Kapadia M, Gladman M, Pulapaka S, Xu L, Stanojcic M et al (2013) Altered neuroendocrine status at the onset of CNS lupus-like disease. Brain Behav Immun 32:86–93
Marchese M, Cowan D, Head E, Ma D, Karimi K, Ashthorpe V et al (2014) Autoimmune manifestations in the 3xTg-AD model of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 39(1):191–210
Matus S, Burgos PV, Bravo-Zehnder M, Kraft R, Porras OH, Farias P et al (2007) Antiribosomal-P autoantibodies from psychiatric lupus target a novel neuronal surface protein causing calcium influx and apoptosis. J Exp Med 204(13):3221–3234
Meijer MK, Spruijt BM, van Zutphen LF, Baumans V (2006) Effect of restraint and injection methods on heart rate and body temperature in mice. Lab Anim 40(4):382–391
Nery FG, Borba EF, Viana VS, Hatch JP, Soares JC, Bonfa E et al (2008) Prevalence of depressive and anxiety disorders in systemic lupus erythematosus and their association with anti-ribosomal P antibodies. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32(3):695–700
Pinching A (1977) Clinical testing of olfaction reassessed. Brain J Neurol 100(2):377–388
Ryabinin AE, Wang YM, Finn DA (1999) Different levels of Fos immunoreactivity after repeated handling and injection stress in two inbred strains of mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 63(1):143–151
Sakic B (2012) The MRL model: an invaluable tool in studies of autoimmunity-brain interactions. Methods Mol Biol 934:277–299
Sakic B, Szechtman H, Keffer M, Talangbayan H, Stead R, Denburg JA (1992) A behavioral profile of autoimmune lupus-prone MRL mice. Brain Behav Immun 6:265–285
Sakic B, Szechtman H, Denburg SD, Carbotte RM, Denburg JA (1993) Spatial learning during the course of autoimmune disease in MRL mice. Behav Brain Res 54:57–66
Sakic B, Szechtman H, Talangbayan H, Denburg SD, Carbotte RM, Denburg JA (1994) Disturbed emotionality in autoimmune MRL-lpr mice. Physiol Behav 56(3):609–617
Sakic B, Szechtman H, Denburg SD, Denburg JA (1995) Immunosuppressive treatment prevents behavioral deficit in autoimmune MRL-lpr mice. Physiol Behav 58(4):797–802
Sakic B, Denburg JA, Denburg SD, Szechtman H (1996) Blunted sensitivity to sucrose in autoimmune MRL-lpr mice: a curve-shift study. Brain Res Bull 41(5):305–311
Sakic B, Szechtman H, Braciak TA, Richards CD, Gauldie J, Denburg JA (1997a) Reduced preference for sucrose in autoimmune mice: a possible role of interleukin-6. Brain Res Bull 44(2):155–165
Sakic B, Szechtman H, Denburg JA (1997b) Neurobehavioral alteration in autoimmune mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21(3):327–340
Sakic B, Gurunlian L, Denburg SD (1998a) Reduced aggressiveness and low testosterone levels in autoimmune MRL-lpr males. Physiol Behav 63(2):305–309
Sakic B, Szechtman H, Denburg JA, Gorny G, Kolb B, Whishaw IQ (1998b) Progressive atrophy of pyramidal neuron dendrites in autoimmune MRL-lpr mice. J Neuroimmunol 87(1–2):162–170
Sakic B, Kolb B, Whishaw IQ, Gorny G, Szechtman H, Denburg JA (2000) Immunosuppression prevents neuronal atrophy in lupus-prone mice: evidence for brain damage induced by autoimmune disease? J Neuroimmunol 111(1–2):93–101
Sanchez-Andrade G, Kendrick KM (2009) The main olfactory system and social learning in mammals. Behav Brain Res 200(2):323–335
Shiraki M, Fujiwara M, Tomura S (1984) Long term administration of cyclophosphamide in MRL/1 mice. I. The effects on the development of immunological abnormalities and lupus nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol 55:333–339
Shoenfeld N, Agmon-Levin N, Flitman-Katzevman I, Paran D, Katz BS, Kivity S et al (2009) The sense of smell in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 60(5):1484–1487
Sled JG, Spring S, van Eede M, Lerch JP, Ullal S, Sakic B (2009) Time course and nature of brain atrophy in the MRL mouse model of central nervous system lupus. Arthritis Rheum 60(6):1764–1774
Soudry Y, Lemogne C, Malinvaud D, Consoli SM, Bonfils P (2011) Olfactory system and emotion: common substrates. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 128(1):18–23
Stanojcic M, Loheswaran G, Xu L, Hoffman SA, Sakic B (2010) Intrathecal antibodies and brain damage in autoimmune MRL mice. Brain Behav Immun 24:289–297
Stock AD, Wen J, Doerner J, Herlitz LC, Gulinello M, Putterman C (2015) Neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus persists despite attenuation of systemic disease in MRL/lpr mice. J Neuroinflammation 12:205
Theofilopoulos AN (1992) Murine models of lupus. In: Lahita RG (ed) Systemic lupus erythematosus, 2nd edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 121–194
Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Brannan CI, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Nagata S (1992a) Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis. Nature 356:314–317
Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Brannan CI, Itoh N, Yonehara S, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA et al (1992b) The cDNA structure, expression, and chromosomal assignment of the mouse Fas antigen. J Immunol 148(4):1274–1279
Wen J, Doerner J, Chalmers S, Stock A, Wang H, Gullinello M et al (2016) B cell and/or autoantibody deficiency do not prevent neuropsychiatric disease in murine systemic lupus erythematosus. J Neuroinflammation 13(1):73
Williams S, Sakic B, Hoffman SA (2010) Circulating brain-reactive autoantibodies and behavioral deficits in the MRL model of CNS lupus. J Neuroimmunol 218(1–2):73–82
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Bhargav Thakar and Yitian Ma at EuroImmun Canada (Mississauga, ON) for assistance with behavioral scoring and ELISA assays, respectively. This study was supported by an Ontario Mental Health Foundation research grant to B. S as well as personal grants from The Father Sean O’Sullivan Research Foundation (St. Joseph’s Healthcare, Hamilton) and Ontario Graduate Scholarship to M.K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapadia, M., Zhao, H., Ma, D. et al. Sustained Immunosuppression Alters Olfactory Function in the MRL Model of CNS Lupus. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 12, 555–564 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-017-9745-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-017-9745-6