Abstract
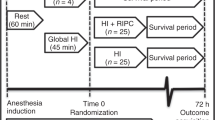
Perinatal asphyxia can lead to death and severe disability. Brain hypoxia-ischemia (HI) injury is the major pathophysiology contributing to death and severe disability after perinatal asphyxia. Here, seven-day old Sprague-Dawley rats were subjected to left brain HI. Dexmedetomidine was given intraperitoneally after the brain HI. Yohimbine or atipamezole, two α2 adrenergic receptor antagonists, were given 10 min before the dexmedetomidine injection. Neurological outcome was evaluated 7 or 28 days after the brain HI. Frontal cerebral cortex was harvested 6 h after the brain HI. Left brain HI reduced the left cerebral hemisphere weight assessed 7 days after the brain HI. This brain tissue loss was dose-dependently attenuated by dexmedetomidine. Dexmedetomidine applied within 1 h after the brain HI produced this effect. Dexmedetomidine attenuated the brain HI-induced brain tissue and cell loss as well as neurological and cognitive dysfunction assessed from 28 days after the brain HI. Dexmedetomidine postconditioning-induced neuroprotection was abolished by yohimbine or atipamezole. Brain HI increased tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin 1β in the brain tissues. This increase was attenuated by dexmedetomidine. Atipamezole inhibited this dexmedetomidine effect. Our results suggest that dexmedetomidine postconditioning reduces HI-induced brain injury in the neonatal rats. This effect may be mediated by α2 adrenergic receptor activation that inhibits inflammation in the ischemic brain tissues.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α2AR:
-
α2-adrenergic receptors
- DMSO:
-
dimethyl sulfoxide
- HI:
-
hypoxia-ischemia
- IL-1β:
-
interleukin-1β
- TNFα:
-
tumor necrosis factor α
References
Alblas J, van Corven EJ, Hordijk PL, Milligan G, Moolenaar WH (1993) Gi-mediated activation of the p21ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by alpha 2-adrenergic receptors expressed in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 268:22235–22238
Azzopardi DV, Strohm B, Edwards AD, Dyet L, Halliday HL, Juszczak E, Kapellou O, Levene M, Marlow N, Porter E, Thoresen M, Whitelaw A, Brocklehurst P (2009) Moderate hypothermia to treat perinatal asphyxial encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 361:1349–1358
Bang AT, Bang RA, Baitule SB, Reddy HM, Deshmukh MD (2005) Management of birth asphyxia in home deliveries in rural gadchiroli: the effect of two types of birth attendants and of resuscitating with mouth-to-mouth, tube-mask or bag-mask. J Perinatol 25(Suppl 1):S82–S91
Blum FE, Zuo Z (2013) Volatile anesthetics-induced neuroinflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses. Med Gas Res 3:16
Cosar M, Eser O, Fidan H, Sahin O, Buyukbas S, Ela Y, Yagmurca M, Ozen OA (2009) The neuroprotective effect of dexmedetomidine in the hippocampus of rabbits after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg Neurol 71:54–59
Eason MG, Liggett SB (1993) Human alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype distribution: widespread and subtype-selective expression of alpha 2C10, alpha 2C4, and alpha 2C2 mRNA in multiple tissues. Mol Pharmacol 44:70–75
Engelhard K, Werner C, Kaspar S, Mollenberg O, Blobner M, Bachl M, Kochs E (2002) Effect of the alpha2-agonist dexmedetomidine on cerebral neurotransmitter concentrations during cerebral ischemia in rats. Anesthesiology 96:450–457
Fisher M, Feuerstein G, Howells DW, Hurn PD, Kent TA, Savitz SI, Lo EH (2009) Update of the stroke therapy academic industry roundtable preclinical recommendations. Stroke 40:2244–2250
Goyagi T, Nishikawa T, Tobe Y, Masaki Y (2009) The combined neuroprotective effects of lidocaine and dexmedetomidine after transient forebrain ischemia in rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 53:1176–1183
Gu J, Sun P, Zhao H, Watts HR, Sanders RD, Terrando N, Xia P, Maze M, Ma D (2011) Dexmedetomidine provides renoprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Crit Care 15:R153
Hetman M, Kanning K, Cavanaugh JE, Xia Z (1999) Neuroprotection by brain-derived neurotrophic factor is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem 274:22569–22580
Hoffman WE, Kochs E, Werner C, Thomas C, Albrecht RF (1991) Dexmedetomidine improves neurologic outcome from incomplete ischemia in the rat. Anesthesiology 75:328–332
Huang R, Chen Y, Yu AC, Hertz L (2000) Dexmedetomidine-induced stimulation of glutamine oxidation in astrocytes: a possible mechanism for its neuroprotective activity. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:895–898
Huang Y, Lu Y, Zhang L, Yan J, Jiang J, Jiang H (2014) Perineural dexmedetomidine attenuates inflammation in rat sciatic nerve via the NF-kappaB pathway. Int J Mol Sci 15:4049–4059
Iadecola C, Anrather J (2011) The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat Med 17:796–808
Kamibayashi T, Maze M (2000) Clinical uses of alpha2 -adrenergic agonists. Anesthesiology 93:1345–1349
Karlsson BR, Loberg EM, Steen PA (1995) Dexmedetomidine, a potent alpha 2-agonist, does not affect neuronal damage following severe forebrain ischaemia in the rat. Eur J Anaesthesiol 12:281–285
Kim HK, Zornow MH, Strnat MA, Maze M (1996) Dexmedetomidine does not attenuate increases in excitatory amino acids after transient global ischemia in the rabbit. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 8:230–236
Kuhmonen J, Pokorny J, Miettinen R, Haapalinna A, Jolkkonen J, Riekkinen P, Sivenius J (1997) Neuroprotective effects of dexmedetomidine in the gerbil hippocampus after transient global ischemia. Anesthesiology 87:371–377
Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A, Hofer M (2009) Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: therapeutic approaches. J Transl Med 7:97
Laudenbach V, Mantz J, Lagercrantz H, Desmonts JM, Evrard P, Gressens P (2002a) Effects of alpha(2)-adrenoceptor agonists on perinatal excitotoxic brain injury: comparison of clonidine and dexmedetomidine. Anesthesiology 96:134–141
Laudenbach V, Mantz J, Lagercrantz H, Desmonts J-M, Evrard P, Gressens P (2002b) Effects of a2-adrenoceptor agonists on perinatal excitotoxic brain injury. Anesthesiology 96:134–141
Li H, Yin J, Li L, Deng J, Feng C, Zuo Z (2013) Isoflurane postconditioning reduces ischemia-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation and interleukin 1beta production to provide neuroprotection in rats and mice. Neurobiol Dis 54:216–224
Li J, Sheng W, Feng C, Zuo Z (2012) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates brain abeta increase and improves long-term neurological outcome in rats after transient focal brain ischemia. Neurobiol Dis 45:564–572
Li L, Zuo Z (2009) Isoflurane preconditioning improves short-term and long-term neurological outcome after focal brain ischemia in adult rats. Neurosci 164:497–506
Lin D, Zuo Z (2011) Isoflurane induces hippocampal cell injury and cognitive impairments in adult rats. Neuropharmacology 61:1354–1359
Lynch JK, Nelson KB (2001) Epidemiology of perinatal stroke. Curr Opin Pediatr 13:499–505
Ma D, Hossain M, Rajakumaraswamy N, Arshad M, Sanders RD, Franks NP, Maze M (2004) Dexmedetomidine produces its neuroprotective effect via the alpha 2 A-adrenoceptor subtype. Eur J Pharmacol 502:87–97
Ma MC, Qian H, Ghassemi F, Zhao P, Xia Y (2005) Oxygen-sensitive {delta}-opioid receptor-regulated survival and death signals: novel insights into neuronal preconditioning and protection. J Biol Chem 280:16208–16218
Maier C, Steinberg GK, Sun GH, Zhi GT, Maze M (1993) Neuroprotection by the alpha 2-adrenoreceptor agonist dexmedetomidine in a focal model of cerebral ischemia. Anesthesiology 79:306–312
Millan MJ, Newman-Tancredi A, Audinot V, Cussac D, Lejeune F, Nicolas JP, Coge F, Galizzi JP, Boutin JA, Rivet JM, Dekeyne A, Gobert A (2000) Agonist and antagonist actions of yohimbine as compared to fluparoxan at alpha(2)-adrenergic receptors (AR)s, serotonin (5-HT)(1 A), 5-HT(1B), 5-HT(1D) and dopamine D(2) and D(3) receptors. Significance for the Modulation of Frontocortical Monoaminergic Transmission and Depressive States Synapse 35:79–95
Minino AM, Heron MP, Murphy SL, Kochanek KD (2007) Deaths: final data for 2004. Natl Vital Stat Rep 55:1–119
Nakano T, Okamoto H (2009) Dexmedetomidine-induced cerebral hypoperfusion exacerbates ischemic brain injury in rats. J Anesth 23:378–384
Philipp M, Brede M, Hein L (2002) Physiological significance of alpha(2)-adrenergic receptor subtype diversity: one receptor is not enough. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283:R287–R295
Qian XL, Zhang W, Liu MZ, Zhou YB, Zhang JM, Han L, Peng YM, Jiang JH, Wang QD (2015) Dexmedetomidine improves early postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged mice. Eur J Pharmacol 746:206–212
Rajakumaraswamy N, Ma D, Hossain M, Sanders RD, Franks NP, Maze M (2006) Neuroprotective interaction produced by xenon and dexmedetomidine on in vitro and in vivo neuronal injury models. Neurosci Lett 409:128–133
Sanders RD, Sun P, Patel S, Li M, Maze M, Ma D (2010) Dexmedetomidine provides cortical neuroprotection: impact on anaesthetic-induced neuroapoptosis in the rat developing brain. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 54:710–716
Schaub MC, Hefti MA, Zaugg M (2006) Integration of calcium with the signaling network in cardiac myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 41:183–214
Schoeler M, Loetscher PD, Rossaint R, Fahlenkamp AV, Eberhardt G, Rex S, Weis J, Coburn M (2012) Dexmedetomidine is neuroprotective in an in vitro model for traumatic brain injury. BMC Neurol 12:20
Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, Fanaroff AA, Poole WK, Wright LL, Higgins RD, Finer NN, Carlo WA, Duara S, Oh W, Cotten CM, Stevenson DK, Stoll BJ, Lemons JA, Guillet R, Jobe AH (2005) Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med 353:1574–1584
Spera PA, Ellison JA, Feuerstein GZ, Barone FC (1998) IL-10 reduces rat brain injury following focal stroke. Neurosci Lett 251:189–192
Sran SK, Baumann RJ (1988) Outcome of neonatal strokes. Am J Dis Child 142:1086–1088
Sreenan C, Bhargave R, Robertson CM (2000) Cerebral infarction in the term new-born: clinical presentation and long-term outcome. J Pediatrics 137:351–355
Vannucci RC, Vannucci SJ (2005) Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: evolution of an animal model. Dev Neurosci 27:81–86
Walker SM, Howard RF, Keay KA, Fitzgerald M (2005) Developmental age influences the effect of epidural dexmedetomidine on inflammatory hyperalgesia in rat pups. Anesthesiology 102:1226–1234
Wang Z, Zhao H, Peng S, Zuo Z (2013) Intranasal pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate decreases brain inflammatory mediators and provides neuroprotection after brain hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal rats. Exp Neurol 249:74–82
Wang Z, Feng C, Zhao H, Ren X, Peng S, Zuo Z (2015) Autoregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by RNA interference provides neuroprotection in neonatal rats. Theranostics 5:504–514
Yager JY, Ashwal S (2009) Animal models of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Pediatr Neurol 40:156–167
Yin J, Li H, Feng C, Zuo Z (2014) Inhibition of brain ischemia-caused notch activation in microglia may contribute to isoflurane postconditioning-induced neuroprotection. CNS & Neurological Disorders - Drug Targets 13:718–732
Zhao P, Zuo Z (2004) Isoflurane preconditioning induces neuroprotection that is inducible nitric oxide synthase-dependent in the neonatal rats. Anesthesiology 101:695–702
Zhao P, Peng L, Li L, Xu X, Zuo Z (2007) Isoflurane preconditioning improves long-term neurologic outcome after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Anesthesiology 107:963–970
Zhu YM, Wang CC, Chen L, Qian LB, Ma LL, Yu J, Zhu MH, Wen CY, Yu LN, Yan M (2013) Both PI3K/akt and ERK1/2 pathways participate in the protection by dexmedetomidine against transient focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Brain Res 1494:1–8
Zornow MH, Fleischer JE, Scheller MS, Nakakimura K, Drummond JC (1990) Dexmedetomidine, an alpha 2-adrenergic agonist, decreases cerebral blood flow in the isoflurane-anesthetized dog. Anesth Analg 70:624–630
Zuo Z, Wang Y, Huang Y (2006) Isoflurane preconditioning protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against in vitro simulated ischemia-reperfusion through the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 542:84–91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Grant Support
This study was supported by a grant (R01 GM098308 to Z Zuo) from the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, by a grant from the International Anesthesia Research Society (2007 Frontiers in Anesthesia Research Award to Z Zuo), Cleveland, OH, by a Grant-in-Aid from the American Heart Association Mid-Atlantic Affiliate (10GRNT3900019 to Z Zuo), Baltimore, MD, and the Robert M. Epstein Professorship endowment, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
The research was performed in the Department of Anesthesiology, University of Virginia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, X., Ma, H. & Zuo, Z. Dexmedetomidine Postconditioning Reduces Brain Injury after Brain Hypoxia-Ischemia in Neonatal Rats. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 11, 238–247 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-016-9658-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-016-9658-9