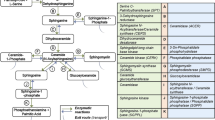
Abstract
Haloperidol is an effective antipsychotic drug for treatment of schizophrenia, but prolonged use can lead to debilitating side effects. To better understand the effects of long-term administration, we measured global metabolic changes in mouse brain following 3 mg/kg/day haloperidol for 28 days. These conditions lead to movement-related side effects in mice akin to those observed in patients after prolonged use. Brain tissue was collected following microwave tissue fixation to arrest metabolism and extracted metabolites were assessed using both liquid and gas chromatography mass spectrometry (MS). Over 300 unique compounds were identified across MS platforms. Haloperidol was found to be present in all test samples and not in controls, indicating experimental validity. Twenty-one compounds differed significantly between test and control groups at the p < 0.05 level. Top compounds were robust to analytical method, also being identified via partial least squares discriminant analysis. Four compounds (sphinganine, N-acetylornithine, leucine and adenosine diphosphate) survived correction for multiple testing in a non-parametric analysis using false discovery rate threshold < 0.1. Pathway analysis of nominally significant compounds (p < 0.05) revealed significant findings for sphingolipid metabolism (p = 0.015) and protein biosynthesis (p = 0.024). Altered sphingolipid metabolism is suggestive of disruptions to myelin. This interpretation is supported by our observation of elevated N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate in the haloperidol-treated mice (p = 0.004), a marker previously associated with demyelination. This study further demonstrates the utility of murine neurochemical metabolomics as a method to advance understanding of CNS drug effects.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberg K, Adkins DE, Bukszár J, Webb BT, Caroff SN, Miller DD, Sebat J, Stroup S, Fanous AH, Vladimirov VI, McClay JL, Lieberman JA, Sullivan PF, van den Oord EJ. (2010) Genome-wide association study of movement-related adverse antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry 67:279–282
Adams CE, Bergman H, Irving CB, Lawrie S (2013) Haloperidol versus placebo for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 11, CD003082
Armstrong MD (1979) N-delta-acetylornithine and S-methylcysteine in blood plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta 587:638–642
Benarroch EE (2008) N-acetylaspartate and N-acetylaspartylglutamate: neurobiology and clinical significance. Neurology 70:1353–1357
Bijlsma S, Bobeldijk I, Verheij ER, Ramaker R, Kochhar S, Macdonald IA, van Ommen B, Smilde AK (2006) Large-scale human metabolomics studies: a strategy for data (pre-) processing and validation. Anal Chem 78:567–574
Clayton TA, Lindon JC, Cloarec O, Antti H, Charuel C, Hanton G, Provost JP, le Net JL, Baker D, Walley RJ, Everett JR, Nicholson JK (2006) Pharmaco-metabonomic phenotyping and personalized drug treatment. Nature 440:1073–1077
Crowley JJ, Adkins DE, Pratt AL, Quackenbush CR, van den Oord EJ, Moy SS, Wilhelmsen KC, Cooper TB, Bogue MA, McLeod HL, Sullivan PF (2012a) Antipsychotic-induced vacuous chewing movements and extrapyramidal side effects are highly heritable in mice. Pharmacogenomics J 12:147–155
Crowley JJ, Kim Y, Szatkiewicz JP, Pratt AL, Quackenbush CR, Adkins DE, van den Oord E, Bogue MA, Yang H, Wang W, Threadgill DW, de Villena FP, McLeod HL, Sullivan PF (2012b) Genome-wide association mapping of loci for antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal symptoms in mice. Mamm Genome 23:322–335
de Graaf RA, Chowdhury GM, Brown PB, Rothman DL, Behar KL (2009) In situ 3D magnetic resonance metabolic imaging of microwave-irradiated rodent brain: a new tool for metabolomics research. J Neurochem 109:494–501
Dehaven CD, Evans AM, Dai H, Lawton KA (2010) Organization of GC/MS and LC/MS metabolomics data into chemical libraries. J Cheminform 2:9
Evans AM, DeHaven CD, Barrett T, Mitchell M, Milgram E (2009) Integrated, nontargeted ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry platform for the identification and relative quantification of the small-molecule complement of biological systems. Anal Chem 81:6656–6667
Frolkis A, Knox C, Lim E, Jewison T, Law V, Hau DD, Liu P, Gautam B, Ly S, Guo AC, Xia J, Liang Y, Shrivastava S, Wishart DS (2010) SMPDB: the small molecule pathway database. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D480–487
Gao K, Kemp DE, Ganocy SJ, Gajwani P, Xia G, Calabrese JR (2008) Antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal side effects in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia: a systematic review. J Clin Psychopharmacol 28:203–209
Ghose S, Gleason KA, Potts BW, Lewis-Amezcua K, Tamminga CA (2009) Differential expression of metabotropic glutamate receptors 2 and 3 in schizophrenia: a mechanism for antipsychotic drug action? Am J Psychiatry 166:812–820
Glazer WM (2000) Extrapyramidal side effects, tardive dyskinesia, and the concept of atypicality. J Clin Psychiatry 61(Suppl 3):16–21
Hastings J, de Matos P, Dekker A, Ennis M, Harsha B, Kale N, Muthukrishnan V, Owen G, Turner S, Williams M, Steinbeck C (2013) The ChEBI reference database and ontology for biologically relevant chemistry: enhancements for 2013. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D456–463
Hoekstra D, Maier O, van der Wouden JM, Slimane TA, van IJzendoorn SC (2003) Membrane dynamics and cell polarity: the role of sphingolipids. J Lipid Res 44:869–877
Hsin-tung E, Simpson G (2000) Medication-induced movement disorders. In: Sadock BJ (ed) Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry (Kaplan H. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Ikarashi Y, Sasahara T, Maruyama Y (1985) Postmortem changes in catecholamines, indoleamines, and their metabolites in rat brain regions: prevention with 10-kW microwave irradiation. J Neurochem 45:935–939
Jessen F, Fingerhut N, Sprinkart AM, Kuhn KU, Petrovsky N, Maier W, Schild HH, Block W, Wagner M, Traber F (2013) N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) and N-acetylaspartate (NAA) in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 39:197–205
Kaddurah-Daouk R, Kristal BS, Weinshilboum RM (2008) Metabolomics: a global biochemical approach to drug response and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 48:653–683
Kolodziejczyk K, Hamilton NB, Wade A, Karadottir R, Attwell D (2009) The effect of N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate and N-acetyl-aspartate on white matter oligodendrocytes. Brain 132:1496–1508
Leucht S, Cipriani A, Spineli L, Mavridis D, Orey D, Richter F, Samara M, Barbui C, Engel RR, Geddes JR, Kissling W, Stapf MP, Lassig B, Salanti G, Davis JM (2013) Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet 382:951–962
Levy M, Futerman AH (2010) Mammalian ceramide synthases. IUBMB Life 62:347–356
Login GR, Dvorak AM (1994) Application of microwave fixation techniques in pathology to neuroscience studies: a review. J Neurosci Methods 55:173–182
Lopez-Munoz F, Alamo C (2009) The consolidation of neuroleptic therapy: Janssen, the discovery of haloperidol and its introduction into clinical practice. Brain Res Bull 79:130–141
Ma D, Guest PC, Bahn S (2009) Metabonomic studies of schizophrenia and psychotropic medications: focus on alterations in CNS energy homeostasis. Bioanalysis 1:1615–1626
Marsden CD, Jenner P (1980) The pathophysiology of extrapyramidal side-effects of neuroleptic drugs. Psychol Med 10:55–72
Martin R, Sospedra M (2014) Sphingosine-1 phosphate and central nervous system. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 378:149–170
McClay JL, Adkins DE, Vunck SA, Batman AM, Vann RE, Clark SL, Beardsley PM, van den Oord EJ (2013) Large-scale neurochemical metabolomics analysis identifies multiple compounds associated with methamphetamine exposure. Metabolomics 9:392–402
McLoughlin GA, Ma D, Tsang TM, Jones DN, Cilia J, Hill MD, Robbins MJ, Benzel IM, Maycox PR, Holmes E, Bahn S (2009) Analyzing the effects of psychotropic drugs on metabolite profiles in rat brain using 1H NMR spectroscopy. J Proteome Res 8:1943–1952
Meltzer HY (2013) Update on typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs. Annu Rev Med 64:393–406
Meltzer HY, Stahl SM (1976) The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia: a review. Schizophr Bull 2:19–76
Ohta T, Masutomi N, Tsutsui N, Sakairi T, Mitchell M, Milburn MV, Ryals JA, Beebe KD, Guo L (2009) Untargeted metabolomic profiling as an evaluative tool of fenofibrate-induced toxicology in Fischer 344 male rats. Toxicol Pathol 37:521–535
Okada T, Kajimoto T, Jahangeer S, Nakamura S (2009) Sphingosine kinase/sphingosine 1-phosphate signalling in central nervous system. Cell Signal 21:7–13
Olszewski RT, Bzdega T, Neale JH (2012) mGluR3 and not mGluR2 receptors mediate the efficacy of NAAG peptidase inhibitor in validated model of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 136:160–161
Patti GJ, Yanes O, Siuzdak G (2012) Innovation: metabolomics: the apogee of the omics trilogy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:263–269
Peluso MJ, Lewis SW, Barnes TR, Jones PB (2012) Extrapyramidal motor side-effects of first- and second-generation antipsychotic drugs. Br J Psychiatry 200:387–392
Rosebush PI, Mazurek MF (1999) Neurologic side effects in neuroleptic-naive patients treated with haloperidol or risperidone. Neurology 52:782–785
Slotte JP (2013) Biological functions of sphingomyelins. Prog Lipid Res 52:424–437
Soares-Weiser K, Fernandez HH (2007) Tardive dyskinesia. Semin Neurol 27:159–169
Suhre K et al (2011) Human metabolic individuality in biomedical and pharmaceutical research. Nature 477:54–60
Takanashi J, Saito S, Aoki I, Barkovich AJ, Ito Y, Inoue K (2012) Increased N-acetylaspartate in model mouse of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. J Magn Reson Imaging 35:418–425
Turrone P, Remington G, Nobrega JN (2002) The vacuous chewing movement (VCM) model of tardive dyskinesia revisited: is there a relationship to dopamine D(2) receptor occupancy? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26:361–380
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G (2001) Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:5116–5121
van den Oord EJ, Sullivan PF (2003) False discoveries and models for gene discovery. Trends Genet 19:537–542
van der Knaap MS, Linnankivi T, Paetau A, Feigenbaum A, Wakusawa K, Haginoya K, Kohler W, Henneke M, Dinopoulos A, Grattan-Smith P, Brockmann K, Schiffmann R, Blaser S (2007) Hypomyelination with atrophy of the basal ganglia and cerebellum: follow-up and pathology. Neurology 69:166–171
van Os J, Kapur S (2009) Schizophrenia. Lancet 374:635–645
Xia J, Wishart DS (2011) Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nat Protoc 6:743–760
Xia J, Mandal R, Sinelnikov IV, Broadhurst D, Wishart DS (2012) MetaboAnalyst 2.0–a comprehensive server for metabolomic data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 40:W127–133
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the assistance of Danny Alexander, Edward Karoly and John Luster at Metabolon, Inc, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina. We also acknowledge the assistance of Lindsey King and Krista Scoggins at Virginia Commonwealth University in expediting the experiments. This work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health to EJvdO (R21DA021411) and a NARSAD (National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Depression, now the Brain Research Foundation) Young Investigator Award to JLM. Both JLM and EJvdO are also partly supported by grant 1R01MH097283 from the US National Institute of Mental Health.
Conflict of Interest
After working on this project, REV left Virginia Commonwealth University and is now an employee of Eli Lilly. All other authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McClay, J.L., Vunck, S.A., Batman, A.M. et al. Neurochemical Metabolomics Reveals Disruption to Sphingolipid Metabolism Following Chronic Haloperidol Administration. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 10, 425–434 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-015-9605-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-015-9605-1