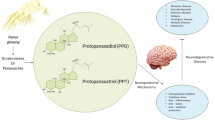
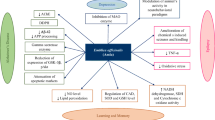
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease is a chronic, multifactorial and progressive neurologic condition that affects around six million people worldwide, normally over 60 years of age, and is characterized by neurodegeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. The species of the genus Panax, popularly named as “Ginseng”, are widely used as herbal remedies for their multiple beneficial effects, including their neurotherapeutic efficacies as protectors against major neurodegenerative diseases. The current review aims to report major findings and current knowledge on Ginseng and its major constituents as potential neuroprotective agents against Parkinson’s disease, focusing on its mechanisms of action and molecular targets. For that purpose, it includes all research works published in MEDLINE/PubMed within the last decade by utilizing the following combination of the keywords: “Ginseng, ginsenosides, neuroprotection and Parkinson’s disease”. As reported, most of the studies have been carried out on isolated compounds rather than extracts. The major ginsenosides investigated as neuroprotector agents for Parkinson’s disease are Rb1, Rg1, Rd and Re. Other minor components such as Notoginsenoside R2 and Pseudoginsenoside-F11 have also attracted remarkable interest as promising antiparkinson agents. These compounds exert their neuroprotective activity through different mechanisms including, among others, inhibition of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, decrease in toxins-induced apoptosis and nigral iron levels, and regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel activity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander GE (2004) Biology of Parkinson’s disease: pathogenesis and pathophysiology of a multisystem neurodegenerative disorder. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 6:259–280
Anglade P, Vyas S, Javoy-Agid F, Herrero MT, Michel PP, Marquez J, Mouatt-Prigent A, Ruberg M, Hirsch EC, Agid Y (1997) Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Histol Histopathol 12:25–31
Bae E, Han MJ, Choo M, Park S, Kim D (2002) Metabolism of 20(S)-and 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 by human intestinal bacteria and its relation to in vitro biological activities. Biol Pharm Bull 25:58–63
Baeg IH, So SH (2013) The world ginseng market and the ginseng (Korea). J Ginseng Res 37:1–7
Beamer CA, Shepherd DM (2012) Inhibition of TLR ligand- and interferon gamma-induced murine microglial activation by Panax notoginseng. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 7:465–476
Béraud D, Maguire-Zeiss KA (2012) Misfolded α-synuclein and Toll-like receptors: therapeutic targets for Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(Suppl1):S17–S20
Béraud D, Twomey M, Bloom B, Mittereder A, Ton V, Neitzke K, Chasovskikh S, Mhyre TR, Maguire-Zeiss KA (2011) α-Synuclein alters toll-like receptor expression. Front Neurosci 5:80
Beyfuss RL (1999) American ginseng production in woodlots. Agroforestry Notes (USDA-NAC) 3:1–4
Blumenthal M, Brinckmann J, Wollschlaeger B (2003) The ABC clinical guide to Herbs. New York, NY
Bocharov EV, Ivanova-Smolenskaya IA, Poleshchuk VV, Kucheryanu VG, Il’enko VA, Bocharova OA (2010) Therapeutic efficacy of the neuroprotective plant adaptogen in neurodegenerative disease (Parkinson’s disease as an example). Bull Exp Biol Med 149:682–684
Bostanci MO, Bagirici F (2008) Nitric oxide synthesis inhibition attenuates iron-induced neurotoxicity: a stereological study. Neurotoxicology 29:130–135
Chaudhuri KR, Healy DG, Schapira AH (2006) Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: diagnosis and management. Lancet Neurol 5:235–245
Chen XC, Chen Y, Zhu YG, Fang F, Chen LM (2002) Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 against MPTP-induced apoptosis in mouse substantia nigra neurons. Acta Pharmacol Sin 23:829–834
Chen XC, Zhu YG, Zhu LA, Huang C, Chen Y, Chen LM, Fang F, Zhou YC, Zhao CH (2003) Ginsenoside Rg1 attenuates dopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by suppressing oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol 473:1–7
Chen XC, Zhou YC, Chen Y, Zhu YG, Fang F, Chen LM (2005) Ginsenoside Rg1 reduces MPTP-induced substantia nigra neuron loss by suppressing oxidative stress. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26:56–62
Chen F, Luo J, Kong L (2013) Determination of 10 ginsenosides in Panax ginseng of different harvest times based on HPLC fingerprints and principal component analysis. Nat Prod Res 27:851–854
Choi KT (2008) Botanical characteristics, pharmacological effects and medicinal components of Korean Panax ginseng C A Meyer. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29:1109–1118
Christensen LP (2009) Ginsenosides chemistry, biosynthesis, analysis, and potential health effects. Adv Food Nutr Res 55:1–99
Court WA, Reynolds LB, Hendel JG (1996) Influence of root age on the concentration of ginsenosides of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolium). Can J Plant Sci 76:853–855
Critchley E (1972) Clinical manifestations of essential tremor. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 35:365–372
Cruse-Sanders JM, Hamrick JL (2004) Genetic diversity in harvested and protected populations of wild American ginseng, Panax quinquefolius L. (Araliaceae). Am J Bot 91:540–548
Dexter DT, Jenner P (2013) Parkinson disease: from pathology to molecular disease mechanisms. Free Radic Biol Med 62:132–144
Di Monte DA, Lavasani M, Manning-Bog AB (2002) Environmental factors in Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 23:487–502
Dick FD, De Palma G, Ahmadi A, Scott NW, Prescott GJ, Bennett J, Semple S, Dick S, Counsell C, Mozzoni P, Haites N, Wettinger SB, Mutti A, Otelea M, Seaton A, Söderkvist P, Felice A (2007) Environmental risk factors for Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism: the Geoparkinson study. Occup Environ Med 64:666–672
Drui G, Carnicella S, Carcenac C, Favier M, Bertrand A, Boulet S, Savasta M (2014) Loss of dopaminergic nigrostriatal neurons accounts for the motivational and affective deficits in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 19:358–367
Duvoisin RC (1987) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease. Adv Neurol 45:307–312
Ebersbach G, Moreau C, Gandor F, Defebvre L, Devos D (2013) Clinical syndromes: Parkinsonian gait. Mov Disord 28:1552–1559
Forno LS (1996) Neuropathology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:259–272
Fuzzati N (2004) Analysis methods of ginsenosides. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 12:119–133
Gao QG, Chen WF, Xie JX, Wong MS (2009) Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells via IGF-I receptor and estrogen receptor pathways. J Neurochem 109:1338–1347
Ge KL, Chen WF, Xie JX, Wong MS (2010) Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against 6-OHDA-induced toxicity in MES23.5 cells via Akt and ERK signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 127:118–123
Giasson BI, Lee VM (2003) Are ubiquitination pathways central to Parkinson’s disease? Cell 114:1–8
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Murray IV, Chen Q, Souza JM, Hurtig HI, Ischiropoulos H, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2000) Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective alpha-synuclein nitration in synucleinopathy lesions. Science 290:985–989
Gui Y, Gil SK, Ryu GH (2012) Effects of extrusion conditions on the physicochemical properties of extruded red ginseng. Prev Nutr Food Sci 17:203–209
Gum SI, Cho MK (2013) Korean red ginseng extract prevents APAP-induced hepatotoxicity through metabolic enzyme regulation: the role of ginsenoside Rg3, a protopanaxadiol. Liver Int 33:1071–1084
Hallett PJ, Standaert DG (2004) Rationale for and use of NMDA receptor antagonists in Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol Ther 102:155–174
He B, Chen P, Yang J, Yun Y, Zhang X, Yang R, Shen Z (2012) Neuroprotective effect of 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg(3) against transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett 526:106–111
Hirsch EC, Breidert T, Rousselet E, Hunot S, Hartmann A, Michel PP (2003) The role of glial reaction and inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Ann NY Acad Sci 991:214–228
Horsfall L, Petersen I, Walters K, Schrag A (2013) Time trends in incidence of Parkinson’s disease diagnosis in UK primary care. J Neurol 260:1351–1357
Hou JP (1977) The chemical constituents of ginseng plants. Comp Med East West 5:123–145
Hu S, Han R, Mak S, Han Y (2011) Protection against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+)-induced apoptosis by water extract of ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) in SH-SY5Y cells. J Ethnopharmacol 135:34–42
Hwang YP, Jeong HG (2010) Ginsenoside Rb1 protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress by increasing heme oxygenase-1 expression through an estrogen receptor-related PI3K/Akt/Nrf2-dependent pathway in human dopaminergic cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 242:18–28
Jenner P (2003) Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53:S26–S36
Jia L, Zhao Y (2009) Current evaluation of the millennium phytomedicine—ginseng (I): etymology, pharmacognosy, phytochemistry, market and regulations. Curr Med Chem 16:2475–2484
Jia L, Zhao Y, Liang XJ (2009) Current evaluation of the millennium phytomedicine- ginseng (II): Collected chemical entities, modern pharmacology, and clinical applications emanated from traditional Chinese medicine. Curr Med Chem 16:2924–2942
Jiang F, DeSilva S, Turnbull J (2000) Beneficial effect of ginseng root in SOD-1 (G93A) transgenic mice. J Neurol Sci 180:52–54
Jie YH, Cammisuli S, Baggiolini M (1984) Immunomodulatory effects of Panax Ginseng C.A. Meyer in the mouse. Agents Actions 15:386–391
Kakizoe T (2000) Asian studies of cancer chemoprevention: latest clinical results. Eur J Cancer 36:1303–1309
Kalia LV, Kalia SK, McLean PJ, Lozano AM, Lang AE (2013) α-Synuclein oligomers and clinical implications for Parkinson disease. Ann Neurol 73:155–169
Kenarova B, Neychev H, Hadjiivanova C, Petkov VD (1990) Immunomodulating activity of ginsenoside Rg1 from Panax ginseng. Jpn J Pharmacol 54:447–454
Kim DH (2012) Chemical diversity of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquifolium, and Panax notoginseng. J Ginseng Res 36:1–15
Kim JY, Germolec DR, Luster MI (1990) Panax ginseng as a potential immunomodulator: studies in mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 12:257–276
Kim HJ, Chun YJ, Park JD, Kim SI, Roh JK, Jeong TC (1997) Protection of rat liver microsomes against carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation by redginseng saponin through cytochrome P450 inhibition. Planta Med 63:415–418
Kim TD, Paik SR, Yang CH (2002) Structural and functional implications of C-terminal regions of alpha-synuclein. Biochemistry 41:13782–13790
Kim EH, Jang MH, Shin MC, Shin MS, Kim CJ (2003) Protective effect of aqueous extract of ginseng radix against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 26:1668–1673
Kim MH, Byon YY, Ko EJ, Song JY, Yun YS, Shin T, Joo HG (2009) Immunomodulatory activity of ginsan, a polysaccharide of Panax ginseng, on dendritic cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 13:169–173
Kim S, Shim S, Choi DS, Kim JH, Kwon YB, Kwon J (2011) Modulation of LPS-stimulated astroglial activation by ginseng total saponins. J Ginseng Res 35:80–85
Kim KH, Song K, Yoon SH, Shehzad O, Kim YS, Son JH (2012) Rescue of PINK1 protein null-specific mitochondrial complex IV deficits by ginsenoside Re activation of nitric oxide signaling. J Biol Chem 287:44109–44120
Kitts D, Hu C (2000) Efficacy and safety of ginseng. Public Health Nutr 3:473–485
Konno C, Murakami M, Oshima Y, Hikino H (1985) Isolation and hypoglycemic activity of panaxans Q, R, S, T and U, glycans of Panax ginseng roots. J Ethnopharmacol 14:69–74
Krige D, Carroll MT, Cooper JM, Marsden CD, Schapira AH (1992) Platelet mitochondrial function in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 32:782–788
Kumar KR, Lohmann K, Klein C (2012) Genetics of Parkinson disease and other movement disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 25:466–474
Lang AE, Lozano AM (1998) Parkinson´s disease. N Eng J Med 339: 1044–1053
Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2006) Mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease linked to pathological alpha-synuclein: new targets for drug discovery. Neuron 52:33–38
Lee MS, Yang EJ, Kim JI, Ernst E (2009) Ginseng for cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. J Alzheimers Dis 18:339–344
Leung KW, Wong AS (2010) Pharmacology of ginsenosides: a literature review. Chin Med 5:20
Leung KW, Yung KK, Mak NK, Chan YS, Fan TP, Wong RN (2007) Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside-Rg1 in primary nigral neurons against rotenone toxicity. Neuropharmacology 52:827–835
Lewis WH (2003) Medical botany: plants affecting human health. USA
Li YB, Wang SL (2009) The effect of TSPG in vivo on transplantation of neural stem cells in treatment of Parkinson’s disease mouse. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 25:133–137
Li W, Gu C, Zhang H, Awang DVC, Fitzloff JF, Fong HHS, van Breemen RB (2000) Use of high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to distinguish Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer (Asian ginseng) and Panax quinquefolius L. (North American ginseng). Anal Chem 72:5417–5422
Li J, Ichikawa T, Jin Y, Hofseth LJ, Nagarkatti P, Nagarkatti M, Windust A, Cui T (2010) An essential role of Nrf2 in American ginseng-mediated anti-oxidative actions in cardiomyocytes. J Ethnopharmacol 130:222–230
Li J, Shao ZH, Xie JT, Wang CZ, Ramachandran S, Yin JJ, Aung H, Li CQ, Qin G, Vanden Hoek T, Yuan CS (2012) The effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on JNK in oxidative injury in cardiomyocytes. Arch Pharm Res 35:1259–1267
Li J, Wei Q, Zuo GW, Xia J, You ZM, Li CL, Chen DL (2014) Ginsenoside Rg1 induces apoptosis through inhibition of the EpoR-Mediated JAK2/STAT5 signalling pathway in the TF-1/ Epo human leukemia cell line. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15:2453–2459
Lim TS, Na K, Choi EM, Chung JY, Hwang JK (2004) Immunomodulating activities of polysaccharides isolated from Panax ginseng. J Med Food 7:1–6
Lim W, Mudge KW, Vermeylen F (2005) Effects of population, age, and cultivation methods on ginsenoside content of wild American ginseng (Panax quinquefolium). J Agric Food Chem 53:8498–8505
Lim KH, Kang CW, Choi JY, Kim JH (2013) Korean red ginseng induced cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia in Guinea Pig. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 17:283–289
Lin WM, Zhang YM, Moldzio R, Rausch WD (2007) Ginsenoside Rd attenuates neuroinflammation of dopaminergic cells in culture. J Neural Transm Suppl 72:105–112
Liu Q, Kou JP, Yu BY (2011) Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in PC12 cells via inhibiting NF-κB activation. Neurochem Int 58:119–125
Liu JP, Wang F, Li PY, Lu D (2012) A new ocotillol-type triterpenoid saponin from red American ginseng. Nat Prod Res 26:731–735
Lü JM, Yao Q, Chen C (2009) Ginseng compounds: an update on their molecular mechanisms and medical applications. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 7:293–302
Luk KC, Song C, O’Brien P, Stieber A, Branch JR, Brunden KR, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2009) Exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils seed the formation of Lewy body-like intracellular inclusions in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:20051–20056
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B, O'Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012a) Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science 16:949–953
Luk KC, Kehm VM, Zhang B, O'Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012b) Intracerebral inoculation of pathological α-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative α-synucleinopathy in mice. J Exp Med 209:975–986
Luo FC, Wang SD, Li K, Nakamura H, Yodoi J, Bai J (2010) Panaxatriol saponins extracted from Panax notoginseng induces thioredoxin-1 and prevents 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion-induced neurotoxicity. J Ethnopharmacol 127:419–423
Luo FC, Wang SD, Qi L, Song JY, Lv T, Bai J (2011) Protective effect of panaxatriol saponins extracted from Panax notoginseng against MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol 133:448–453
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Boyes BE, McGeer EG (1988) Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Neurology 38:1285–1291
McNaught KS, Belizaire R, Jenner P, Olanow CW, Isacson O (2002) Selective loss of 20S proteasome α-subunits in the substantia nigra pars compacta in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 326:155–158
McNaught KS, Belizaire R, Isacson O, Jenner P, Olanow CW (2003) Altered proteasomal function in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 179:38–46
McNaught KS, Perl DP, Brownell AL, Olanow CW (2004) Systemic exposure to proteasome inhibitors causes a progressive model of Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 56:149–162
Meng XB, Sun GB, Wang M, Sun J, Qin M, Sun XB (2013) P90RSK and Nrf2 activation via MEK1/2-ERK1/2 pathways mediated by notoginsenoside R2 to prevent 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptotic death in SH-SY5Y cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. doi:10.1155/2013/971712
Mhyre TR, Boyd JT, Hamill RW, Maguire-Zeiss KA (2012) Parkinson’s disease. Subcell Biochem 65:389–455
Moore DJ, Zhang L, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2003) A missense mutation (L166P) in DJ-1, linked to familial Parkinson’s disease, confers reduced protein stability and impairs homo-oligomerization. J Neurochem 87:1558–1567
Moore DJ, West AB, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2005) Molecular pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 28:57–87
Mosley RL, Benner EJ, Kadiu I, Thomas M, Boska MD, Hasan K, Laurie C, Gendelmana HE (2006) Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neurosci Res 6:261–281
Musende AG, Eberding A, Wood CA, Adomat H, Fazli L, Hurtado-Coll A, Jia W, Bally MB, Tomlinson Guns ES (2012) A novel oral dosage formulation of the ginsenoside aglycone protopanaxadiol exhibits therapeutic activity against a hormone-insensitive model of prostate cancer. Anticancer Drugs 23:543–552
Nah SY (2014) Ginseng ginsenoside pharmacology in the nervous system: involvement in the regulation of ion channels and receptors. Front Physiol 19:98
Ng TB, Yeung HW (1985) Hypoglycemic constituents of Panax ginseng. Gen Pharmacol 16:549–552
Olanow CV, Tatton WG (1999) Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson´s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 22:123–144
Oshima Y, Konno C, Hikino H (1985) Isolation and hypoglycemic activity of panaxans I, J, K and L, glycans of Panax ginseng roots. J Ethnopharmacol 14:255–259
Oshima Y, Sato K, Hikino H (1987) Isolation and hypoglycemic activity of quinquefolans A, B, and C, glycans of Panax quinquefolium roots. J Nat Prod 50:188–190
Park J, Cho J (2009) Anti-inflammatory effects of ginsenosides from Panax ginseng and their structural analogs. Afr J Biotechnol 8:3682–3690
Park SJ, Lee JR, Jo MJ, Park SM, Ku SK, Kim SC (2013) Protective effects of Korean red ginseng extract on cadmium-induced hepatic toxicity in rats. J Ginseng Res 37:37–44
Parker WD Jr, Boyson SJ, Parks JK (1989) Abnormalities of the electron transport chain in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 26:719–723
Perier C, Tieu K, Guegan C, Caspersen C, Jackson-Lewis V, Carelli V (2005) Complex I deficiency primes Bax-dependent neuronal apoptosis through mitochondrial oxidative damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:19126–19131
Perier C, Bove J, Wu DC, Dehay B, Choi DK, Jackson-Lewis V, Rathke-Hartlieb S, Bouillet P, Strasser A, Schulz JB, Przedborski S, Vila M (2007) Two molecular pathways initiate mitochondria-dependent dopaminergic neurodegeneration in experimental Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:8161–8166
Perier C, Bové J, Vila M (2012) Mitochondria and programmed cell death in Parkinson’s disease: apoptosis and beyond. Antioxid Redox Signal 16:883–895
Petrucelli L, O’Farrell C, Lockhart PJ, Baptista M, Kehoe K, Vink L, Choi P, Wolozin B, Farrer M, Hardy J, Cookson MR (2002) Parkin protects against the toxicity associated with mutant alpha-synuclein: proteasome dysfunction selectively affects catecholaminergic neurons. Neuron 36:1007–1019
Pizzorno JE, Murray MT (2012) Natural medicine. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier, St. Louis
Qi LW, Wang CZ, Yuan CS (2011) Ginsenosides from American ginseng: chemical and pharmacological diversity. Phytochemistry 72:689–699
Qian M, Yi L, Song-Lin L, Jie Y, Ping-Hu Z, Qiang W (2014) Chemical profiles and anticancer effects of saponin fractions of different polarity from the leaves of Panax notoginseng. Chin J Nat Med 12:30–37
Radad K, Gille G, Moldzio R, Saito H, Ishige K, Rausch WD (2004a) Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 effects on survival and neurite growth of MPP + -affected mesencephalic dopaminergic cells. J Neural Transm 111:37–45
Radad K, Gille G, Moldzio R, Saito H, Rausch WD (2004b) Ginsenosides Rb1 and Rg1 effects on mesencephalic dopaminergic cells stressed with glutamate. Brain Res 1021:41–53
Radad K, Moldzio R, Rausch WD (2011) Ginsenosides and their CNS targets. CNS Neurosci Ther 17:761–768
Rhule A, Navarro S, Smith JR, Shepherd DM (2006) Panax notoginseng attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory mediators in RAW264.7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol 106:121–128
Rinwa P, Kumar A (2014) Modulation of nitrergic signalling pathway by American ginseng attenuates chronic unpredictable stress-induced cognitive impairment, neuroinflammation, and biochemical alterations. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 387:129–141
Runkel ST, Bull AF (2009) Wildflowers of Iowa woodlands. University of Iowa Press, Iowa
Scaglione F, Ferrara F, Dugnani S, Falchi M, Santoro G, Fraschini F (1990) Immunomodulatory effects of two extracts of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Drugs Exp Clin Res 16:537–542
Schapira AH (2008) Mitochondria in the aetiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 7:97–109
Schapira AH (2011) Mitochondrial pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Mt Sinai J Med 78:872–881
Schapira AH, Cooper JM, Dexter D, Clark JB, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1990) Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 54:823–827
Schlag EM, McIntosh MS (2006) Ginsenoside content and variation among and within American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) populations. Phytochemistry 67:1510–1519
Shao ZH, Xie JT, Vanden Hoek TL, Mehendale S, Aung H, Li CQ, Qin Y, Schumacker PT, Becker LB, Yuan CS (2004) Antioxidant effects of American ginseng berry extract in cardiomyocytes exposed to acute oxidant stress. Biochim Biophys Acta 1670:165–171
Shashidharan P, Good PF, Hsu A, Perl DP, Brin MF, Olanow CW (2000) TorsinA accumulation in Lewy bodies in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 877:379–381
Sherer TB, Betarbet R, Greenamyre JT (2002) Environment, mitochondria, and Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscientist 8:192–197
Shi C, Zhang Y, Zhang Z (2009) Effect of phosphorylated-ERK1/2 on inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in the substantia nigra of mice with MPTP-induced Parkinson disease. J South Med Univ 29:60–63
Shi J, Xue W, Zhao WJ, Li KX (2013) Pharmacokinetics and dopamine/acetylcholine releasing effects of ginsenoside Re in hippocampus and mPFC of freely moving rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34:214–220
Shibata S, Tanaka O, NagaI M, Ishit T (1963) Studies on the constituents of Japanese and Chinese crude drugs. XII. panaxadiol, a sapogenin of ginseng roots. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 11:762–765
Shibata S, Ando T, Tanaka O, Meguro Y, Sôma K, Iida Y (1965a) Saponins and sapogenins of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer and some other Panax spp. Yakugaku Zasshi 85:753–755
Shibata S, Tanaka O, Soma K, Aando T, Iida Y, Nakamura H (1965b) Studies on saponins and sapogenins of ginseng. the structure of panaxatriol. Tetrahedron Lett 42:207–213
Shin HR, Kim JY, Yun TK, Morgan G, Vainio H (2000) The cancer-preventive potential of Panax ginseng: a review of human and experimental evidence. Canc Causes Contr 11:565–576
Shin TJ, Hwang SH, Choi SH, Lee BH, Kang J, Kim HJ, Zukin RS, Rhim H, Nah SY (2012) Effects of protopanaxatriol-ginsenoside metabolites on rat N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor-mediated ion currents. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 16:113–118
Siddiqi MH, Siddiqi MZ, Ahn S, Kang S, Kim YJ, Sathishkumar N, Yang DU, Yang DC (2013) Ginseng saponins and the treatment of osteoporosis: mini literature review. J Ginseng Res 37:261–268
Small E (2013) North American cornucopia: Top 100 indigenous food plants (Agricultural Science Book) Taylor & Francis
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Summers AP, Koob TJ, Brainerd EL (1998) The ubiquitin pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 395:451–452
Surh YJ, Na HK, Lee JY, Keum YS (2001) Molecular mechanisms underlying anti-tumor promoting activities of heat-processed Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J Korean Med Sci 16:S38–S41
Taylor JM, Main BS, Crack PJ (2013) Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress: coconspirators in the pathology of Parkinson´s disease. Neurochem Int 62:803–819
Van Kampen J, Robertson H, Hagg T, Drobitch R (2003) Neuroprotective actions of the ginseng extract G115 in two rodent models of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 184:521–529
Van Kampen JM, Baranowski DB, Shaw CA, Kay DG (2014) Panax ginseng is neuroprotective in a novel progressive model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Gerontol 50:95–105
Venderova K, Park DS (2012) Programmed cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2(8) doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009365
Vila M, Jackson-Lewis V, Vukosavic S, Djaldetti R, Liberatore G, Offen D, Korsmeyer SJ, Przedborski S (2001) Bax ablation prevents dopaminergic neurodegeneration in the 1-methyl- 4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:2837–2842
Von Coelln R, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2004) Parkin-associated Parkinson’s disease. Cell Tissue Res 318:175–184
Wang X, Sakuma T, Asafu-Adjaye E, Shiu GK (1999) Determination of ginsenosides in plant extracts from Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius L. by LC/MS/MS. Anal Chem 71:1579–1584
Wang A, Wang CZ, Wu JA, Osinski J, Yuan CS (2005) Determination of major ginsenosides in Panax quinquefolius (American ginseng) using high-performance liquid chromatography. Phytochem Anal 16:272–277
Wang Y, Pan JY, Xiao XY, Lin RC, Cheng YY (2006) Simultaneous determination of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng with different growth ages using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Phytochem Anal 17:424–430
Wang J, Jiang H, Xie JX (2007) Ferroportin1 and hephaestin are involved in the nigral iron accumulation of 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Eur J Neurosci 25:2766–2772
Wang J, Xu HM, Yang HD, Du XX, Jiang H, Xie JX (2009) Rg1 reduces nigral iron levels of MPTP-treated C57BL6 mice by regulating certain iron transport proteins. Neurochem Int 4:43–48
Wang Q, Zheng H, Zhang ZF, Zhang YX (2008) Ginsenoside Rg1 modulates COX-2 expression in the substantia nigra of mice with MPTP-induced Parkinson disease through the P38 signaling pathway. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 28:1594–1598
Wang C, Li YZ, Wang XR, Lu ZR, Shi DZ, Liu XH (2012) Panax quinquefolium saponins reduce myocardial hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by inhibiting excessive endoplasmic reticulum stress. Shock 37:228–233
Wang JY, Yang JY, Wang F, Fu SY, Hou Y, Jiang B, Ma J, Song C, Wu CF (2013) Neuroprotective effect of pseudoginsenoside-f11 on a rat model of Parkinson’s disease induced by 6-hydroxydopamine. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. doi:10.1155/2013/152798
Warner TT, Schapira AH (2003) Genetic and environmental factors in the cause of Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53:16–23
Wen J, Nowicke JW (1999) Pollen ultrastructure of Panax (the ginseng genus, Araliaceae), an eastern Asian and eastern North American disjunct genus. Am J Bot 86:1624–1636
Willis AW (2013) Parkinson disease in the elderly adult. Mo Med 110:406–410
Willis AW, Evanoff BA, Lian M, Criswell SR, Racette BA (2010) Geographic and ethnic variation in Parkinson disease: a population-based study of US Medicare beneficiaries. Neuroepidemiology 34:143–151
Wooten GF, Currie LJ, Bovbjerg VE, Lee JK, Patrie J (2004) Are men at greater risk for Parkinson’s disease than women? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:637–639
Xia R, Mao ZH (2012) Progression of motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Bull 28:39–48
Xie JT, Shao ZH, Vanden Hoek TL, Chang WT, Li J, Mehendale S, Wang CZ, Hsu CW, Becker LB, Yin JJ, Yuan CS (2006) Antioxidant effects of ginsenoside Re in cardiomyocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 532:201–207
Xu BB, Liu CQ, Gao X, Zhang WQ, Wang SW, Cao YL (2005) Possible mechanisms of the protection of ginsenoside Re against MPTP-induced apoptosis in substantia nigra neurons of Parkinson’s disease mouse model. J Asian Nat Prod Res 7:215–224
Xu L, Chen WF, Wong MS (2009) Ginsenoside Rg1 protects dopaminergic neurons in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease through the IGF-I receptor signalling pathway. Br J Pharmacol 158:738–748
Xu H, Jiang H, Wang J, Xie J (2010a) Rg1 protects the MPP + -treated MES23.5 cells via attenuating DMT1 up-regulation and cellular iron uptake. Neuropharmacology 58:488–494
Xu H, Jiang H, Wang J, Xie J (2010b) Rg1 protects iron-induced neurotoxicity through antioxidant and iron regulatory proteins in 6-OHDA-treated MES23.5 cells. J Cell Biochem 111:1537–1545
Yang L, Zhang J, Zheng K, Shen H, Chen X (2014) Long-term ginsenoside Rg1 supplementation improves age-related cognitive decline by promoting synaptic plasticity associated protein expression in C57BL/6 J mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 69:282–294
Yap KY, Chan SY, Weng Chan Y, Sing Lim C (2005) Overview on the analytical tools for quality control of natural product-based supplements: a case study of ginseng. Assay Drug Dev Technol 3:683–699
Ye R, Kong X, Yang Q, Zhang Y, Han J, Li P, Xiong L, Zhao G (2011a) Ginsenoside rd in experimental stroke: superior neuroprotective efficacy with a wide therapeutic window. Neurotherapeutics 8:515–525
Ye R, Kong X, Yang Q, Zhang Y, Han J, Zhao G (2011b) Ginsenoside Rd attenuates redox imbalance and improves stroke outcome after focal cerebral ischemia in aged mice. Neuropharmacology 61:815–824
Ye R, Zhao G, Liu X (2013) Ginsenoside Rd for acute ischemic stroke: translating from bench to bedside. Expert Rev Neurother 13:603–613
Yun TK (2001) Brief introduction of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J Korean Med Sci 16:S3–S5
Zhou W, Chai H, Lin PH, Lumsden AB, Yao Q, Chen CJ (2004) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of ginseng root for cardiovascular disease. Med Sci Monit 10:RA187–RA192
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a doctoral grant from the Spanish Ministry of Education, Culture and Sports (FPU), awarded to Carlos Fernandez Moriano (N° FPU12/03824).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Elena González-Burgos, Carlos Fernandez-Moriano and M. Pilar Gómez-Serranillos contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González-Burgos, E., Fernandez-Moriano, C. & Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Potential Neuroprotective Activity of Ginseng in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 10, 14–29 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-014-9569-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-014-9569-6