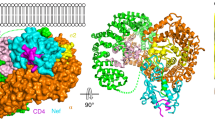
Abstract
Advances in the last several years have enhanced mechanistic understanding of Nef-induced CD4 and MHCI downregulation and have suggested a new paradigm for analyzing Nef function. In both of these cases, Nef acts by forming ternary complexes with significant contributions to stability imparted by non-canonical interactions. The mutational analyses and binding assays that have led to these conclusions are discussed. The recent progress has been dependent on conservative mutations and multi-protein binding assays. The poorly understood Nef functions of p21 activated protein kinase (PAK2) activation, enhancement of virion infectivity, and inhibition of immunoglobulin class switching are also likely to involve ternary complexes and non-canonical interactions. Hence, investigation of these latter Nef functions should benefit from a similar approach. Six historically used alanine substitutions for determining structure–function relationships of Nef are discussed. These are M20A, E62A/E63A/E64A/E65A (AAAA), P72A/P75A (AXXA), R106A, L164A/L165A, and D174A/D175A. Investigations of less-disruptive mutations in place of AAAA and AXXA have led to different interpretations of mechanism. Two recent examples of this alternate approach, F191I for studying PAK2 activation and D123E for the critical residue D123 are discussed. The implications of the new findings and the resulting new paradigm for Nef structure–function are discussed with respect to creating a map of Nef functions on the protein surface. We report the results of a PPI-Pred analysis for protein–protein interfaces. There are three predicted patches produced by the analysis which describe regions consistent with the currently known mutational analyses of Nef function.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agopian K, Wei BL, Garcia JV, Gabuzda D (2006) A hydrophobic binding surface on the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef core is critical for association with p21-activated kinase 2. J Virol 80:3050–3061
Agopian K, Wei BL, Garcia JV, Gabuzda D (2007) CD4 and MHC-I downregulation are conserved in primary HIV-1 Nef alleles from brain and lymphoid tissues, but Pak2 activation is highly variable. Virology 358:119–135
Aiken C, Krause L, Chen YL, Trono D (1996) Mutational analysis of HIV-1 Nef: identification of two mutants that are temperature-sensitive for CD4 downregulation. Virology 217:293–300
Akari H, Arold S, Fukumori T, Okazaki T, Strebel K, Adachi A (2000) Nef-induced major histocompatibility complex class I down-regulation is functionally dissociated from its virion incorporation, enhancement of viral infectivity, and CD4 down-regulation. J Virol 74:2907–2912
Anderson SJ, Lenburg M, Landau NR, Garcia JV (1994) The cytoplasmic domain of CD4 is sufficient for its down-regulation from the cell surface by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef. J Virol 68:3092–3101
Arold ST, Baur AS (2001) Dynamic Nef and Nef dynamics: how structure could explain the complex activities of this small HIV protein. Trends Biochem Sci 26:356–363
Arold S, Franken P, Strub MP, Hoh F, Benichou S, Benarous R, Dumas C (1997) The crystal structure of HIV-1 Nef protein bound to the Fyn kinase SH3 domain suggests a role for this complex in altered T cell receptor signaling. Structure 5:1361–1372
Arold S, Hoh F, Domergue S, Birck C, Delsuc MA, Jullien M, Dumas C (2000) Characterization and molecular basis of the oligomeric structure of HIV-1 nef protein. Protein Sci 9:1137–1148
Arora VK, Molina RP, Foster JL, Blakemore JL, Chernoff J, Fredericksen BL, Garcia JV (2000) Lentivirus Nef specifically activates Pak2. J Virol 74:11081–11087
Atkins KM, Thomas L, Youker RT, Harriff MJ, Pissani F, You H, Thomas G (2008) HIV-1 Nef binds PACS-2 to assemble a multikinase cascade that triggers major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) down-regulation: analysis using short interfering rna and knock-out mice. J Biol Chem 283:11772–11784
Bailey JR, O’Connell K, Yang HC, Han Y, Xu J, Jilek B, Williams TM, Ray SC, Siliciano RF, Blankson JN (2008) Transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from a patient who developed AIDS to an elite suppressor. J Virol 82:7395–7410
Bailey JR, Brennan TP, O’Connell KA, Siliciano RF, Blankson JN (2009) Evidence of CD8+ T-cell-mediated selective pressure on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 nef in HLA-B*57+ elite suppressors. J Virol 83:88–97
Baugh LL, Garcia JV, Foster JL (2008) Functional characterization of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef acidic domain. J Virol 82:9657–9667
Baur AS, Sass G, Laffert B, Willbold D, Cheng-Mayer C, Peterlin BM (1997) The N-terminus of Nef from HIV-1/SIV associates with a protein complex containing Lck and a serine kinase. Immunity 6:283–291
Blagoveshchenskaya AD, Thomas L, Feliciangeli SF, Hung CH, Thomas G (2002) HIV-1 Nef downregulates MHC-I by a PACS-1- and PI3K-regulated ARF6 endocytic pathway. Cell 111:853–866
Bonifacino JS, Traub LM (2003) Signals for sorting of transmembrane proteins to endosomes and lysosomes. Annu Rev Biochem 72:395–447
Boursier JP, Alcover A, Herve F, Laisney I, Acuto O (1993) Evidence for an extended structure of the T-cell co-receptor CD8 alpha as deduced from the hydrodynamic properties of soluble forms of the extracellular region. J Biol Chem 268:2013–2020
Bresnahan PA, Yonemoto W, Ferrell S, Williams-Herman D, Geleziunas R, Greene WC (1998) A dileucine motif in HIV-1 Nef acts as an internalization signal for CD4 downregulation and binds the AP-1 clathrin adaptor. Curr Biol 8:1235–1238
Bresnahan PA, Yonemoto W, Greene WC (1999) Cutting edge: SIV Nef protein utilizes both leucine- and tyrosine-based protein sorting pathways for down-regulation of CD4. J Immunol 163:2977–2981
Briggs SD, Sharkey M, Stevenson M, Smithgall TE (1997) SH3-mediated Hck tyrosine kinase activation and fibroblast transformation by the Nef protein of HIV-1. J Biol Chem 272:17899–17902
Briggs SD, Scholtz B, Jacque JM, Swingler S, Stevenson M, Smithgall TE (2001) HIV-1 Nef promotes survival of myeloid cells by a Stat3-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 276:25605–25611
Carl S, Iafrate AJ, Lang SM, Stolte N, Stahl-Hennig C, Matz-Rensing K, Fuchs D, Skowronski J, Kirchhoff F (2000) Simian immunodeficiency virus containing mutations in N-terminal tyrosine residues and in the PxxP motif in Nef replicates efficiently in rhesus macaques. J Virol 74:4155–4164
Casartelli N, Giolo G, Neri F, Haller C, Potesta M, Rossi P, Fackler OT, Doria M (2006) The Pro78 residue regulates the capacity of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein to inhibit recycling of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules in an SH3-independent manner. J Gen Virol 87:2291–2296
Chaudhuri R, Lindwasser OW, Smith WJ, Hurley JH, Bonifacino JS (2007) Downregulation of CD4 by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef is dependent on clathrin and involves direct interaction of Nef with the AP2 clathrin adaptor. J Virol 81:3877–3890
Chaudhuri R, Mattera R, Lindwasser OW, Robinson MS, Bonifacino JS (2009) A basic patch on alpha-adaptin is required for binding of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef and cooperative assembly of a CD4-Nef-AP-2 complex. J Virol 83:2518–2530
Cohen GB, Rangan VS, Chen BK, Smith S, Baltimore D (2000) The human thioesterase II protein binds to a site on HIV-1 Nef critical for CD4 down-regulation. J Biol Chem 275:23097–23105
Coleman SH, Madrid R, Van Damme N, Mitchell RS, Bouchet J, Servant C, Pillai S, Benichou S, Guatelli JC (2006) Modulation of cellular protein trafficking by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef: role of the acidic residue in the ExxxLL motif. J Virol 80:1837–1849
Collins KL, Chen BK, Kalams SA, Walker BD, Baltimore D (1998) HIV-1 Nef protein protects infected primary cells against killing by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature 391:397–401
Costa LJ, Chen N, Lopes A, Aguiar RS, Tanuri A, Plemenitas A, Peterlin BM (2006) Interactions between Nef and AIP1 proliferate multivesicular bodies and facilitate egress of HIV-1. Retrovirology 3:33
Craig HM, Pandori MW, Guatelli JC (1998) Interaction of HIV-1 Nef with the cellular dileucine-based sorting pathway is required for CD4 down-regulation and optimal viral infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:11229–11234
daSilva LL, Sougrat R, Burgos PV, Janvier K, Mattera R, Bonifacino JS (2009) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein targets CD4 to the multivesicular body pathway. J Virol 83:6578–6590
Dikeakos JD, Atkins KM, Thomas L, Emert-Sedlak L, Byeon IJ, Jung J, Ahn J, Wortman MD, Kukull B, Saito M, Koizumi H, Williamson DM, Hiyoshi M, Barklis E, Takiguchi M, Suzu S, Gronenborn AM, Smithgall TE, Thomas G (2010) Small molecule inhibition of HIV-1-induced MHC-I down-regulation identifies a temporally regulated switch in Nef action. Mol Biol Cell 21:3279–3292
Erdtmann L, Janvier K, Raposo G, Craig HM, Benaroch P, Berlioz-Torrent C, Guatelli JC, Benarous R, Benichou S (2000) Two independent regions of HIV-1 Nef are required for connection with the endocytic pathway through binding to the mu 1 chain of AP1 complex. Traffic 1:871–883
Fackler OT, Luo W, Geyer M, Alberts AS, Peterlin BM (1999) Activation of Vav by Nef induces cytoskeletal rearrangements and downstream effector functions. Mol Cell 3:729–739
Fackler OT, Alcover A, Schwartz O (2007) Modulation of the immunological synapse: a key to HIV-1 pathogenesis? Nat Rev Immunol 7:310–317
Fleis R, Filzen T, Collins KL (2002) Species-specific effects of HIV-1 Nef-mediated MHC-I downmodulation. Virology 303:120–129
Foster JL, Garcia JV (2007) Role of Nef in HIV-1 replication and pathogenesis. Adv Pharmacol 55:389–409
Foster JL, Molina RP, Luo T, Arora VK, Huang Y, Ho DD, Garcia JV (2001) Genetic and functional diversity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype B Nef primary isolates. J Virol 75:1672–1680
Freeburn RW, Wright KL, Burgess SJ, Astoul E, Cantrell DA, Ward SG (2002) Evidence that SHIP-1 contributes to phosphatidylinositol 3, 4, 5-trisphosphate metabolism in T lymphocytes and can regulate novel phosphoinositide 3-kinase effectors. J Immunol 169:5441–5450
Goldsmith MA, Warmerdam MT, Atchison RE, Miller MD, Greene WC (1995) Dissociation of the CD4 downregulation and viral infectivity enhancement functions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef. J Virol 69:4112–4121
Gorry PR, McPhee DA, Verity E, Dyer WB, Wesselingh SL, Learmont J, Sullivan JS, Roche M, Zaunders JJ, Gabuzda D, Crowe SM, Mills J, Lewin SR, Brew BJ, Cunningham AL, Churchill MJ (2007) Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of attenuated, nef-deleted HIV-1 strains in vivo. Retrovirology 4:66
Gruenberg J, Maxfield FR (1995) Membrane transport in the endocytic pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7:552–563
Greenberg M, DeTulleo L, Rapoport I, Skowronski J, Kirchhausen T (1998a) A dileucine motif in HIV-1 Nef is essential for sorting into clathrin-coated pits and for downregulation of CD4. Curr Biol 8:1239–1242
Greenberg ME, Iafrate AJ, Skowronski J (1998b) The SH3 domain-binding surface and an acidic motif in HIV-1 Nef regulate trafficking of class I MHC complexes. EMBO J 17:2777–2789
Grzesiek S, Stahl SJ, Wingfield PT, Bax A (1996a) The CD4 determinant for downregulation by HIV-1 Nef directly binds to Nef. Mapping of the Nef binding surface by NMR. Biochemistry 35:10256–10261
Grzesiek S, Bax A, Clore GM, Gronenborn AM, Hu JS, Kaufman J, Palmer I, Stahl SJ, Wingfield PT (1996b) The solution structure of HIV-1 Nef reveals an unexpected fold and permits delineation of the binding surface for the SH3 domain of Hck tyrosine protein kinase. Nat Struct Biol 3:340–345
Grzesiek S, Bax A, Hu JS, Kaufman J, Palmer I, Stahl SJ, Tjandra N, Wingfield PT (1997) Refined solution structure and backbone dynamics of HIV-1 Nef. Protein Sci 6:1248–1263
Haller C, Rauch S, Fackler OT (2007) HIV-1 Nef employs two distinct mechanisms to modulate Lck subcellular localization and TCR induced actin remodeling. PLoS ONE 2:e1212
Hanna Z, Kay DG, Cool M, Jothy S, Rebai N, Jolicoeur P (1998a) Transgenic mice expressing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in immune cells develop a severe AIDS-like disease. J Virol 72:121–132
Hanna Z, Kay DG, Rebai N, Guimond A, Jothy S, Jolicoeur P (1998b) Nef harbors a major determinant of pathogenicity for an AIDS-like disease induced by HIV-1 in transgenic mice. Cell 95:163–175
Hanna Z, Weng X, Kay DG, Poudrier J, Lowell C, Jolicoeur P (2001) The pathogenicity of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 Nef in CD4C/HIV transgenic mice is abolished by mutation of its SH3-binding domain, and disease development is delayed in the absence of Hck. J Virol 75:9378–9392
Henikoff S, Henikoff JG (1992) Amino acid substitution matrices from protein blocks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10915–10919
Hung CH, Thomas L, Ruby CE, Atkins KM, Morris NP, Knight ZA, Scholz I, Barklis E, Weinberg AD, Shokat KM, Thomas G (2007) HIV-1 Nef assembles a Src family kinase-ZAP-70/Syk-PI3K cascade to downregulate cell-surface MHC-I. Cell Host Microbe 1:121–133
Iafrate AJ, Bronson S, Skowronski J (1997) Separable functions of Nef disrupt two aspects of T cell receptor machinery: CD4 expression and CD3 signaling. EMBO J 16:673–684
Iafrate AJ, Carl S, Bronson S, Stahl-Hennig C, Swigut T, Skowronski J, Kirchhoff F (2000) Disrupting surfaces of nef required for downregulation of CD4 and for enhancement of virion infectivity attenuates simian immunodeficiency virus replication in vivo. J Virol 74:9836–9844
Karkkainen S, Hiipakka M, Wang JH, Kleino I, Vaha-Jaakkola M, Renkema GH, Liss M, Wagner R, Saksela K (2006) Identification of preferred protein interactions by phage-display of the human Src homology-3 proteome. EMBO Rep 7:186–191
Kestler HW 3rd, Ringler DJ, Mori K, Panicali DL, Sehgal PK, Daniel MD, Desrosiers RC (1991) Importance of the nef gene for maintenance of high virus loads and for development of AIDS. Cell 65:651–662
Kienzle N, Freund J, Kalbitzer HR, Mueller-Lantzsch N (1993) Oligomerization of the Nef protein from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1. Eur J Biochem 214:451–457
Kim MO, Suh HS, Si Q, Terman BI, Lee SC (2006) Anti-CD45RO suppresses human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in microglia: role of Hck tyrosine kinase and implications for AIDS dementia. J Virol 80:62–72
Kimpton J, Emerman M (1992) Detection of replication-competent and pseudotyped human immunodeficiency virus with a sensitive cell line on the basis of activation of an integrated beta-galactosidase gene. J Virol 66:2232–2239
Kirchhoff F, Schindler M, Bailer N, Renkema GH, Saksela K, Knoop V, Muller-Trutwin MC, Santiago ML, Bibollet-Ruche F, Dittmar MT, Heeney JL, Hahn BH, Munch J (2004) Nef proteins from simian immunodeficiency virus-infected chimpanzees interact with p21-activated kinase 2 and modulate cell surface expression of various human receptors. J Virol 78:6864–6874
Kirchhoff F, Schindler M, Specht A, Arhel N, Munch J (2008) Role of Nef in primate lentiviral immunopathogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:2621–2636
Kistner A, Gossen M, Zimmermann F, Jerecic J, Ullmer C, Lubbert H, Bujard H (1996) Doxycycline-mediated quantitative and tissue-specific control of gene expression in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10933–10938
Klippel A, Escobedo MA, Wachowicz MS, Apell G, Brown TW, Giedlin MA, Kavanaugh WM, Williams LT (1998) Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is sufficient for cell cycle entry and promotes cellular changes characteristic of oncogenic transformation. Mol Cell Biol 18:5699–5711
Kohn AD, Barthel A, Kovacina KS, Boge A, Wallach B, Summers SA, Birnbaum MJ, Scott PH, Lawrence JC Jr, Roth RA (1998) Construction and characterization of a conditionally active version of the serine/threonine kinase Akt. J Biol Chem 273:11937–11943
Krady JK, Basu A, Levison SW, Milner RJ (2002) Differential expression of protein tyrosine kinase genes during microglial activation. Glia 40:11–24
Kwak YT, Raney A, Kuo LS, Denial SJ, Temple BR, Garcia JV, Foster JL (2010) Self-association of the Lentivirus protein. Nef Retrovirology 7:77
Laguette N, Benichou S, Basmaciogullari S (2009a) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef incorporation into virions does not increase infectivity. J Virol 83:1093–1104
Laguette N, Bregnard C, Bouchet J, Benmerah A, Benichou S, Basmaciogullari S (2009b) Nef-induced CD4 endocytosis in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 host cells: role of p56lck kinase. J Virol 83:7117–7128
Laguette N, Bregnard C, Benichou S, Basmaciogullari S (2010) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type-1, HIV-2 and simian immunodeficiency virus Nef proteins. Mol Aspects Med 31(5):418–433
Lang SM, Iafrate AJ, Stahl-Hennig C, Kuhn EM, Nisslein T, Kaup FJ, Haupt M, Hunsmann G, Skowronski J, Kirchhoff F (1997) Association of simian immunodeficiency virus Nef with cellular serine/threonine kinases is dispensable for the development of AIDS in rhesus macaques. Nat Med 3:860–865
Lee CH, Saksela K, Mirza UA, Chait BT, Kuriyan J (1996) Crystal structure of the conserved core of HIV-1 Nef complexed with a Src family SH3 domain. Cell 85:931–942
Li SS (2005) Specificity and versatility of SH3 and other proline-recognition domains: structural basis and implications for cellular signal transduction. Biochem J 390:641–653
Lindwasser OW, Smith WJ, Chaudhuri R, Yang P, Hurley JH, Bonifacino JS (2008) A diacidic motif in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef is a novel determinant of binding to AP-2. J Virol 82:1166–1174
Liu LX, Heveker N, Fackler OT, Arold S, Le Gall S, Janvier K, Peterlin BM, Dumas C, Schwartz O, Benichou S, Benarous R (2000) Mutation of a conserved residue (D123) required for oligomerization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein abolishes interaction with human thioesterase and results in impairment of Nef biological functions. J Virol 74:5310–5319
Lock M, Greenberg ME, Iafrate AJ, Swigut T, Muench J, Kirchhoff F, Shohdy N, Skowronski J (1999) Two elements target SIV Nef to the AP-2 clathrin adaptor complex, but only one is required for the induction of CD4 endocytosis. EMBO J 18:2722–2733
Lu X, Yu H, Liu SH, Brodsky FM, Peterlin BM (1998) Interactions between HIV1 Nef and vacuolar ATPase facilitate the internalization of CD4. Immunity 8:647–656
Lubben NB, Sahlender DA, Motley AM, Lehner PJ, Benaroch P, Robinson MS (2007) HIV-1 Nef-induced down-regulation of MHC class I requires AP-1 and clathrin but not PACS-1 and is impeded by AP-2. Mol Biol Cell 18:3351–3365
Luo T, Anderson SJ, Garcia JV (1996) Inhibition of Nef- and phorbol ester-induced CD4 degradation by macrolide antibiotics. J Virol 70:1527–1534
Madrid R, Janvier K, Hitchin D, Day J, Coleman S, Noviello C, Bouchet J, Benmerah A, Guatelli J, Benichou S (2005) Nef-induced alteration of the early/recycling endosomal compartment correlates with enhancement of HIV-1 infectivity. J Biol Chem 280:5032–5044
Manninen A, Hiipakka M, Vihinen M, Lu W, Mayer BJ, Saksela K (1998) SH3-Domain binding function of HIV-1 Nef is required for association with a PAK-related kinase. Virology 250:273–282
Marsh M, Pelchen-Matthews A (1996) Endocytic and exocytic regulation of CD4 expression and function. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 205:107–135
Maxfield FR, McGraw TE (2004) Endocytic recycling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:121–132
Melkus MW, Estes JD, Padgett-Thomas A, Gatlin J, Denton PW, Othieno FA, Wege AK, Haase AT, Garcia JV (2006) Humanized mice mount specific adaptive and innate immune responses to EBV and TSST-1. Nat Med 12:1316–1322
Noviello CM, Benichou S, Guatelli JC (2008) Cooperative binding of the class I major histocompatibility complex cytoplasmic domain and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef to the endosomal AP-1 complex via its mu subunit. J Virol 82:1249–1258
O’Neill E, Baugh LL, Novitsky VA, Essex ME, Garcia JV (2006a) Intra- and intersubtype alternative Pak2-activating structural motifs of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef. J Virol 80:8824–8829
O’Neill E, Kuo LS, Krisko JF, Tomchick DR, Garcia JV, Foster JL (2006b) Dynamic evolution of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 pathogenic factor, Nef. J Virol 80:1311–1320
Pelchen-Matthews A, da Silva RP, Bijlmakers MJ, Signoret N, Gordon S, Marsh M (1998) Lack of p56lck expression correlates with CD4 endocytosis in primary lymphoid and myeloid cells. Eur J Immunol 28:3639–3647
Pereyra F et al (2010) The major genetic determinants of HIV-1 control affect HLA class I peptide presentation. Science 330(6010):1551–1557
Picard C, Greenway A, Holloway G, Olive D, Collette Y (2002) Interaction with simian Hck tyrosine kinase reveals convergent evolution of the Nef protein from simian and human immunodeficiency viruses despite differential molecular surface usage. Virology 295:320–327
Piguet V, Gu F, Foti M, Demaurex N, Gruenberg J, Carpentier JL, Trono D (1999) Nef-induced CD4 degradation: a diacidic-based motif in Nef functions as a lysosomal targeting signal through the binding of beta-COP in endosomes. Cell 97:63–73
Pizzato M, Helander A, Popova E, Calistri A, Zamborlini A, Palu G, Gottlinger HG (2007) Dynamin 2 is required for the enhancement of HIV-1 infectivity by Nef. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:6812–6817
Poe JA, Smithgall TE (2009) HIV-1 Nef dimerization is required for Nef-mediated receptor downregulation and viral replication. J Mol Biol 394:329–342
Preusser A, Briese L, Baur AS, Willbold D (2001) Direct in vitro binding of full-length human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein to CD4 cytoplasmic domain. J Virol 75:3960–3964
Pritchard CA, Samuels ML, Bosch E, McMahon M (1995) Conditionally oncogenic forms of the A-Raf and B-Raf protein kinases display different biological and biochemical properties in NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol 15:6430–6442
Pulkkinen K, Renkema GH, Kirchhoff F, Saksela K (2004) Nef associates with p21-activated kinase 2 in a p21-GTPase-dependent dynamic activation complex within lipid rafts. J Virol 78:12773–12780
Qiao X, He B, Chiu A, Knowles DM, Chadburn A, Cerutti A (2006) Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Nef suppresses CD40-dependent immunoglobulin class switching in bystander B cells. Nat Immunol 7:302–310
Rahim MM, Chrobak P, Hu C, Hanna Z, Jolicoeur P (2009) Adult AIDS-like disease in a novel inducible human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef transgenic mouse model: CD4+ T-cell activation is Nef dependent and can occur in the absence of lymphophenia. J Virol 83:11830–11846
Rauch S, Pulkkinen K, Saksela K, Fackler OT (2008) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef recruits the guanine exchange factor Vav1 via an unexpected interface into plasma membrane microdomains for association with p21-activated kinase 2 activity. J Virol 82:2918–2929
Rhee SS, Marsh JW (1994) HIV-1 Nef activity in murine T cells. CD4 modulation and positive enhancement. J Immunol 152:5128–5134
Roeth JF, Collins KL (2006) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef: adapting to intracellular trafficking pathways. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70:548–563
Rose JJ, Janvier K, Chandrasekhar S, Sekaly RP, Bonifacino JS, Venkatesan S (2005) CD4 down-regulation by HIV-1 and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) Nef proteins involves both internalization and intracellular retention mechanisms. J Biol Chem 280:7413–7426
Saksela K, Cheng G, Baltimore D (1995) Proline-rich (PxxP) motifs in HIV-1 Nef bind to SH3 domains of a subset of Src kinases and are required for the enhanced growth of Nef + viruses but not for down-regulation of CD4. EMBO J 14:484–491
Sawai ET, Baur A, Struble H, Peterlin BM, Levy JA, Cheng-Mayer C (1994) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef associates with a cellular serine kinase in T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:1539–1543
Sawai ET, Baur AS, Peterlin BM, Levy JA, Cheng-Mayer C (1995) A conserved domain and membrane targeting of Nef from HIV and SIV are required for association with a cellular serine kinase activity. J Biol Chem 270:15307–15314
Schaefer MR, Wonderlich ER, Roeth JF, Leonard JA, Collins KL (2008) HIV-1 Nef targets MHC-I and CD4 for degradation via a final common beta-COP-dependent pathway in T cells. PLoS Pathog 4:e1000131
Schindler M, Rajan D, Specht A, Ritter C, Pulkkinen K, Saksela K, Kirchhoff F (2007) Association of Nef with p21-activated kinase 2 is dispensable for efficient human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication and cytopathicity in ex vivo-infected human lymphoid tissue. J Virol 81:13005–13014
Simmen T, Nobile M, Bonifacino JS, Hunziker W (1999) Basolateral sorting of furin in MDCK cells requires a phenylalanine-isoleucine motif together with an acidic amino acid cluster. Mol Cell Biol 19:3136–3144
Singh RK, Lau D, Noviello CM, Ghosh P, Guatelli JC (2009) An MHC-I cytoplasmic domain/HIV-1 Nef fusion protein binds directly to the micro subunit of the AP-1 endosomal coat complex. PLoS ONE 4:e8364
Stolp B, Reichman-Fried M, Abraham L, Pan X, Giese SI, Hannemann S, Goulimari P, Raz E, Grosse R, Fackler OT (2009) HIV-1 Nef interferes with host cell motility by deregulation of Cofilin. Cell Host Microbe 6:174–186
Swigut T, Iafrate AJ, Muench J, Kirchhoff F, Skowronski J (2000) Simian and human immunodeficiency virus Nef proteins use different surfaces to downregulate class I major histocompatibility complex antigen expression. J Virol 74:5691–5701
Swigut T, Alexander L, Morgan J, Lifson J, Mansfield KG, Lang S, Johnson RP, Skowronski J, Desrosiers R (2004) Impact of Nef-mediated downregulation of major histocompatibility complex class I on immune response to simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol 78:13335–13344
Thoulouze MI, Sol-Foulon N, Blanchet F, Dautry-Varsat A, Schwartz O, Alcover A (2006) Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 infection impairs the formation of the immunological synapse. Immunity 24:547–561
Trible RP, Emert-Sedlak L, Smithgall TE (2006) HIV-1 Nef selectively activates Src family kinases Hck, Lyn, and c-Src through direct SH3 domain interaction. J Biol Chem 281:27029–27038
Trible RP, Emert-Sedlak L, Wales TE, Ayyavoo V, Engen JR, Smithgall TE (2007) Allosteric loss-of-function mutations in HIV-1 Nef from a long-term non-progressor. J Mol Biol 374:121–129
Tuazon PT, Spanos WC, Gump EL, Monnig CA, Traugh JA (1997) Determinants for substrate phosphorylation by p21-activated protein kinase (gamma-PAK). Biochemistry 36:16059–16064
Van den Broeke C, Radu M, Chernoff J, Favoreel HW (2010) An emerging role for p21-activated kinases (Paks) in viral infections. Trends Cell Biol 20(3):160–169
Walk SF, Alexander M, Maier B, Hammarskjold ML, Rekosh DM, Ravichandran KS (2001) Design and use of an inducibly activated human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef to study immune modulation. J Virol 75:834–843
Wei BL, Denton PW, O’Neill E, Luo T, Foster JL, Garcia JV (2005) Inhibition of lysosome and proteasome function enhances human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Virol 79:5705–5712
Williams M, Roeth JF, Kasper MR, Filzen TM, Collins KL (2005) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef domains required for disruption of major histocompatibility complex class I trafficking are also necessary for coprecipitation of Nef with HLA-A2. J Virol 79:632–636
Wiskerchen M, Cheng-Mayer C (1996) HIV-1 Nef association with cellular serine kinase correlates with enhanced virion infectivity and efficient proviral DNA synthesis. Virology 224:292–301
Wonderlich ER, Williams M, Collins KL (2008) The tyrosine binding pocket in the adaptor protein 1 (AP-1) mu1 subunit is necessary for Nef to recruit AP-1 to the major histocompatibility complex class I cytoplasmic tail. J Biol Chem 283:3011–3022
Xu W, Santini PA, Sullivan JS, He B, Shan M, Ball SC, Dyer WB, Ketas TJ, Chadburn A, Cohen-Gould L, Knowles DM, Chiu A, Sanders RW, Chen K, Cerutti A (2009) HIV-1 evades virus-specific IgG2 and IgA responses by targeting systemic and intestinal B cells via long-range intercellular conduits. Nat Immunol 10:1008–1017
Yamada T, Kaji N, Odawara T, Chiba J, Iwamoto A, Kitamura Y (2003) Proline 78 is crucial for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef to down-regulate class I human leukocyte antigen. J Virol 77:1589–1594
Yang OO, Nguyen PT, Kalams SA, Dorfman T, Gottlinger HG, Stewart S, Chen IS, Threlkeld S, Walker BD (2002) Nef-mediated resistance of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to antiviral cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Virol 76:1626–1631
Ye H, Choi HJ, Poe J, Smithgall TE (2004) Oligomerization is required for HIV-1 Nef-induced activation of the Src family protein-tyrosine kinase, Hck. Biochemistry 43:15775–15784
Yi L, Rosales T, Rose JJ, Chaudhury B, Knutson JR, Venkatesan S (2010) HIV-1 Nef binds a subpopulation of MHC-I throughout its trafficking itinerary and down-regulates MHC-I by perturbing both anterograde and retrograde trafficking. J Biol Chem 285:30884–30905
Youker RT, Shinde U, Day R, Thomas G (2009) At the crossroads of homoeostasis and disease: roles of the PACS proteins in membrane traffic and apoptosis. Biochem J 421:1–15
Zarrinpar A, Bhattacharyya RP, Lim WA (2003) The structure and function of proline recognition domains. Sci STKE 2003:RE8.
Zazopoulos E, Haseltine WA (1993) Disulfide bond formation in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef protein. J Virol 67:1676–1680
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by grant AI33331 from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health, USA and UNC CFAR P30 AI504410.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foster, J.L., Denial, S.J., Temple, B.R.S. et al. Mechanisms of HIV-1 Nef Function and Intracellular Signaling. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 6, 230–246 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9262-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9262-y