Abstract
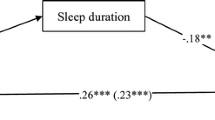
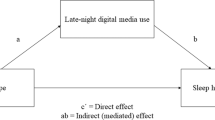
Adolescents increasingly use electronic media as a night-time activity, amid concerns about the potential negative impact on sleep and daytime functioning. The present study examined electronic media use and pathological media use in relation to sleep activity in a normative sample of Australian adolescents. A total of 1,287 high school students aged 12–18 years (50 % female) were recruited from seven secondary schools in South Australia. Adolescents completed a questionnaire assessing electronic media use, pathological media use, and sleep factors. Adolescents reported non-optimal sleep duration on weekday (71 %) and weekend nights (53 %). One in five adolescents reported nightly bedtime delay as a consequence of electronic media use. Adolescent pathological media users reported significantly more sleep problems than their non-pathological peers. These data contribute to current knowledge of how electronic media use may negatively affect adolescent sleep patterns, particularly in regard to sleep displacement and sleep-onset latency effects. Further research is needed in light of the increasing accessibility and uptake of portable electronic media devices, as well as the growing use of media as a sleeping aid, among young people.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison, S. E., von Wahlde, L., Shockley, T., & Gabbard, G. O. (2006). The development of the self in the era of the internet and role-playing fantasy games. American Journal of Psychiatry, 163, 381–385.
Andraessen, C. S., Tosheim, T., Brunborg, G. S., & Pallesen, S. (2011). Development of a Facebook addiction scale. Psychological Reports, 110, 501–517.
Australian Communications and Media Authority. (2008). Internet use and social networking by young people. Retrieved 20/02/2013 from: http://www.acma.gov.au/webwr/_assets/main/lib310665/no1_internet_use_social_networking_young_people.pdf
Bahammam, A., Bin Saeed, A., Al-Faris, E., & Shaikh, S. (2006). Sleep duration and its correlates in a sample of Saudi elementary school children. Singapore Medical Journal, 47, 875–881.
Bakken, I. J., Wenzel, H. G., Gotestam, K. G., Johansson, A., & Oren, A. (2009). Internet addiction among Norwegian adults: a stratified probability sample study. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 50, 121–127.
Beard, K. W. (2005). Internet addiction: a review of current assessment techniques and potential assessment questions. Cyber Psychology & Behavior, 8, 7–14.
Brunborg, G. S., Mentzoni, R. A., Molde, H., et al. (2011). The relationship between media use in the bedroom, sleep habits and symptoms of insomnia. Journal of Sleep Research, 20, 569–575.
Cain, N., & Gradisar, M. (2010). Electronic media use and sleep in school-aged children and adolescents: a review. Sleep Medicine, 11, 735–742.
Cheung, L. M., & Wong, W. S. (2011). The effects of insomnia and Internet addiction on depression in Hong Kong Chinese adolescents: an exploratory cross-sectional analysis. Journal of Sleep Research, 20, 311–317.
Choi, K., Son, H., Park, M., Han, J., Kim, K., Lee, B., & Gwak, H. (2009). Internet overuse and excessive daytime sleepiness in adolescents. Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 63, 455–462.
Choo, H., Gentile, D. A., Sim, T., Li, Dongdong, L., Khoo, A., & Liau, A. K. (2010). Pathological video-gaming among Singaporean youth. Annals Academy of Medicine, 39, 822–829.
Durkin, K., & Barber, B. (2002). Not so doomed: computer game play and positive adolescent development. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 23, 373–392.
Dworak, M., Schierl, T., Bruns, T., & Strüder, H. K. (2007). Impact of singular excessive computer game and television exposure on sleep patterns and memory performance of school-aged children. Pediatrics, 120, 978–985.
Eggermont, S., & Van den Bulck, J. (2006). Nodding off or switching off? The use of popular media as a sleep aid in secondary-school children. Journal of Pediatrics and Child Health, 42, 428–433.
Espie, C. A., Inglis, S. J., Tessier, S., & Harvey, L. (2001). The clinical effectiveness of cognitive behaviour therapy for chronic insomnia: Implementation and evaluation of a sleep clinic in general medical practice. Behavior, Research & Therapy, 39, 45–60.
Ferguson, C. J., Coulson, M., & Barnett, J. (2011). A meta-analysis of pathological gaming prevalence and comorbidity with mental health, academic and social problems. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 45, 1573–1578.
Foundation, N. S. (2006). 2006 sleep in America poll. Washington DC: National Sleep Foundation.
Gaina, A., Sekine, M., Kanayama, H., Sengoku, K., Yamagami, T., & Kagamimori, S. (2005). Short-long sleep latency and associated factors in Japanese junior high school children. Sleep and Biological Rhythms, 3, 162–165.
Gentile, D. A. (2009). Pathological video-game use among youth ages 8 to 18: a national study. Psychological Science, 20, 594–602.
Griffiths, M. D., Kuss, D. J., & King, D. L. (2012). Video game addiction: Past, present and future. Current Psychiatry Reviews, 8, 308–318.
Hussain, Z., & Griffiths, M. D. (2009). The attitudes, feelings and experiences of online gamers: a qualitative analysis. Cyber Psychology and Behavior, 12, 747–753.
Ivarsson, M., Anderson, M., Akerstedt, T., & Lindblad, F. (2009). Playing a violent television game affects heart rate variability. Acta Paediatrica, 98, 166–172.
King, D. L., & Delfabbro, P. H. (2013). Issues for DSM-5: video-gaming disorder? Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 47, 20–22.
King, D. L., Delfabbro, P. H., Griffiths, M. D., & Gradisar, M. (2011). Assessing clinical trials of internet addiction treatment: a systematic review and CONSORT evaluation. Clinical Psychology Review, 31, 1110–1116.
King, D. L., Delfabbro, P. H., & Griffiths, M. D. (2012a). Clinical interventions for technology-based problems: excessive internet and video game use. Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy: An International Quarterly, 26, 43–56.
King, D. L., Delfabbro, P. H., Griffiths, M. D., & Gradisar, M. (2012b). Cognitive-behavioral approaches to outpatient treatment of Internet addiction in children and adolescents. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 68, 1185–1195.
King, D. L., Delfabbro, P. H., Zwaans, T., & Kaptsis, D. (2013a). Clinical features and axis I comorbidity of Australian adolescent pathological internet and video-game users. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 47, 1058–1067.
King, D. L., Gradisar, M., Drummond, A., Lovato, N., Wessel, J., Micic, G., Douglas, P., & Delfabbro, P. H. (2013b). The impact of prolonged violent video-gaming on adolescent sleep: an experimental study. Journal of Sleep Research, 22, 137–143.
King, D. L., Haagsma, M. C., Delfabbro, P. H., Gradisar, M., & Griffiths, M. D. (2013c). Toward a consensus definition of pathological video-gaming: a systematic review of psychometric assessment tools. Clinical Psychology Review, 33, 331–342.
King, D. L., Delfabbro, P. H., Kaptsis, D., & Zwaans, T. (2014). Adolescent simulated gambling via digital and social media: an emerging problem. Computers in Human Behavior, 31, 305–313.
Kouimtsidis, C., Reynolds, M., Drummond, C., Davis, P., & Tarrier, N. (2007). Cognitive-behavioural therapy in the treatment of addiction. West Sussex: Wiley.
Kuss, D. J., & Griffiths, M. D. (2012). Online gaming addiction in adolescence: a literature review of empirical research. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 1, 3–22.
Li, S., Jin, X., Wu, S., Jiang, F., Yan, C., & Shen, X. (2007). The impact of media use on sleep patterns and sleep disorders among school-aged children in China. Sleep, 30, 361–367.
Mentzoni, R. A., Brunborg, G. S., Molde, H., Myrseth, H., Mår Skouverøe, K. J., Hetland, J., & Pallesen, S. (2011). Problematic video game use: estimated prevalence and associations with mental and physical health. Cyber Psychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 14, 591–596.
National Sleep Foundation. (2011). 2011 Sleep in America Poll: Communications Technology in the bedroom. Washington, DC: The Foundation. Available from: http://www.sleepfoundation.org/2011poll
Oka, Y., Suzuki, S., & Inoue, Y. (2008). Bedtime activities, sleep environments, and sleep/wake patterns of Japanese elementary school children. Behavioral Sleep Medicine, 6, 220–233.
Porter, G., Starcevic, V., Berle, D., & Fenech, P. (2010). Recognising problem video game use. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 44, 120–128.
Punamaki, R., Wallenius, M., Nygard, C., Saarni, L., & Rimpela, A. (2007). Use of information and communication technology (ICT) and perceived health in adolescence: the role of sleeping habits and waking-time tiredness. Journal of Adolescence, 30, 569–585.
Rehbein, F., Kleimann, M., & Mossle, T. (2010). Prevalence and risk factors of video game dependency in adolescence: results of a German nationwide survey. Cyber Psychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 13, 269–277.
Rideout, V. J., Foehr, U. G., & Roberts, D. F. (2010). Generation M: Media in the lives of 8- to 18-year-olds. Report published by the Kaiser Family Foundation. Retrieved online from: http://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED527859
Schochat, T., Flint-Bretner, O., & Tzischinksy, O. (2010). Sleep patterns, electronic media exposure and daytime sleep-related behaviours among Israeli adolescents. Acta Paediatrica, 99, 1396–1400.
Short, M. A., Gradisar, M., Lack, L. C., Wright, H. R., & Dohnt, H. (2013). The sleep patterns and well-being of Australian adolescents. Journal of Adolescence, 36, 103–110.
Sim, T., Gentile, D. A., Bricolo, F., et al. (2012). A conceptual review of research on the pathological use of computers, video games, and the Internet. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 10, 748–769.
Smyth, J. M. (2007). Beyond self-selection in video game play: an experimental examination of the consequences of massively multiplayer online role-playing game play. Cyber Psychology & Behavior, 10, 717–721.
Strasberger, V. C., Jordan, A. B., & Donnerstein, E. (2010). Health effects of media on children and adolescents. Pediatrics, 125, 756–767.
Subrahmanyam, K., Greenfield, P., Kraut, R., & Gross, E. (2001). The impact of computer use on children’s and adolescents’ development. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 22, 7–30.
Suganuma, N., Kikachi, T., Yanagi, K., Yamamura, S., Morishima, H., Adachi, H., Kumango, T., Mikami, A., Sugita, Y., & Takeda, M. (2007). Using electronic media before sleep can curtail sleep time and result in self-perceived insufficient sleep. Sleep and Biological Rhythms, 5, 204–214.
Tazawa, Y., & Okada, K. (2001). Physical signs associated with excessive television-game playing and sleep deprivation. Pediatrics International, 43, 647–650.
Tejeiro, R. A., Gomez-Vallecillo, J. L., Pelegrina, M., Wallace, A., & Emberley, E. (2012). Risk factors associated with the abuse of video games in adolescents. Psychology, 3, 310–314.
Thomas, N. J., & Martin, F, H. (2010). Video-arcade game, computer game and Internet activities of Australian students: participation habits and prevalence of addiction. Australian Journal of Psychology, 62, 59–66.
Van den Bulck, J. (2003). Text messaging as a cause of sleep interruption in adolescents: evidence from a cross-sectional study. Journal of Sleep Research, 12, 263.
Van den Bulck, J. (2004). Television viewing, computer game playing, and internet use and self-reported time to bed and time out of bed in secondary-school children. Sleep, 27, 101–104.
†Van Rooij, A. J., Schoenmakers, T. M., Vermulst, A. A., van de Eijnden, R. J. J. M., & van de Mheen, D. (2010). Online video game addiction: Identification of addicted adolescent gamers. Addiction, 106, 205–212.
Weaver, E., Gradisar, M., Dohnt, H., Lovato, N., & Douglas, P. (2010). The effect of pre-sleep video-game playing on adolescent sleep. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 6, 184–189.
Wolniczak, I., Ca’ceres-DelAguila, J. A., Palma-Ardiles, G., Arroyo, K. J., Solıs-Visscher, R., et al. (2013). Association between facebook dependence and poor sleep quality: a study in a sample of undergraduate students in Peru. PLoS ONE, 8, e59087. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059087.
Yen, J. Y., Ko, C. H., Yen, C. F., Chen, S. H., Chung, W. L., & Chen, C. C. (2008). Psychiatric symptoms in adolescents with Internet addiction: comparison with substance use. Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 62, 9–16.
Acknowledgements
With thanks to the students who participated in this study, and the teachers and principals for assistance with data collection. We are grateful to Dr Michael Gradisar for his assistance with development of the sleep questionnaire.
Declaration of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Financial Disclosure
This study received financial support from a 2013 RIBG Small Research Grant funded by the School of Psychology, The University of Adelaide.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
King, D.L., Delfabbro, P.H., Zwaans, T. et al. Sleep Interference Effects of Pathological Electronic Media Use during Adolescence. Int J Ment Health Addiction 12, 21–35 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-013-9461-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-013-9461-2