Abstract
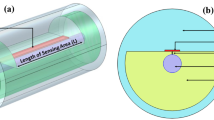
A finite element method is used to analyze the performance of a microstructured optical fiber-based surface plasmon resonance sensors aimed for biomedical applications, such as the detection of blood carried species. Birefringence obtained by removing of a row of holes in a two-ring hexagonal lattice of holes in a gold covered silica fiber leads to a relatively high sensitivity of the fiber optical response to a refractive index of the analyte surrounding the fiber. This fiber structure supports two types (I and II) of resonant modes. In these modes, there is an opposite variation of some sensing parameters with the increase of the refractive index of the analyte between 1.36 and 1.39. Thus, for a smaller value (1.36) of the refractive index of the analyte n a, the resonance spectral width δλ 0.5 is large for the core mode I and small for the core mode II but for a larger value (1.39) of n a, δλ 0.5 is small for the core mode I and large for the core mode II. Also, for n a = 1.36, the amplitude sensitivity S A is small for the core mode I and large for the core mode II but for n a = 1.39, S A is large for the core mode I and small for the core mode II. By adjusting the radius of the gold layer, the proposed sensor shows high spectral sensitivity S λ and narrow δλ 0.5 at the same resonance wavelength and n a (1.39) where the figure of merit (FOM) is very large in comparison with the most recently published values.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Skorobogatiy M (2009) Microstructured and photonic bandgap fibers for applications in the resonant bio-and chemical sensors. J Sens 524237:1–20. doi:10.1155/2009/524237
Popescu VA, Puscas NN, Perrone G (2012) Power absorption efficiency of a new microstructured plasmon optical fiber. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29(11):3039–3046. doi:10.1364/JOSAB.29.003039
Popescu VA, Puscas NN, Perrone G (2014) Strong power absorption in a new microstructured holey fiber-based plasmonic sensor. J Opt Soc Am B 31(5):1062–1070. doi:10.1364/JOSAB.31.001062
Rifat AA, Mahdiraji GA, Sua YM, Shee YG, Ahmed R, Chow DM, Adikan FRM (2015) Surface plasmon resonance photonic crystal fiber biosensor: a practical sensing approach. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 27(15):1628–1631. doi:10.1109/LPT.2015.2432812
Luan N, Wang R, Lv W, Yao J (2015) Surface plasmon resonance sensor based on Dshaped microstructured optical fiber with hollow core. Opt Express 23(7):8576–8582. doi:10.1364/OE.23.008576
Peng L, Shi F, Zhou G, Hou Z, Xia C (2015) A surface plasmon biosensor based on a D-shaped microstructured optical fiber with rectangular lattice. IEEE Photon J 7(5):1–9. doi:10.1109/JPHOT.2015.2488278
Shuai B, Xia L, Zhang Y, Liu D (2012) A multi-core holey fiber based plasmonic sensor with large detection range and high linearity. Opt Express 20(6):5974–5986. doi:10.1364/OE.20.005974
Zhang Y, Xia L, Zhou C, Yu X, Liu H, Liu D, Zhang Y (2011) Microstructured fiber based plasmonic index sensor with optimized accuracy and calibration relation in large dynamic range. Opt Commun 284(18):4161–4166. doi:10.1016/j.optcom.2011.04.053
Sharma AK, Rajan R, Gupta BD (2007) Influence of dopants on the performance of a fiber optic surface plasmon resonance sensor. Opt Commun 274(2):320–326
Verma RK, Sharma AK, Gupta BD (2008) Surface plasmon resonance based tapered fiber optic sensor with different taper profiles. Opt Commun 281:1486–1491
Ghatak AK, Thyagarajan K (1999) Introduction to fiber optics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Vial A, Grimault AS, Macías D, Barchiesi D, Chapelle ML (2005) Improved analytical fit of gold dispersion: application to the modeling of extinction spectra with a finite-difference time-domain method. Phys Rev B 71:085416. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.71.085416
Shalabney A, Abdulhalim I (2012) Figure-of-merit enhancement of surface plasmon resonance sensors in the spectral interrogation. Opt Lett 37(7):1175–1177. doi:10.1364/OL.37.001175
Sardar D, Levy L (1998) Optical properties of whole blood. Lasers Med Sci 13(2):106–111. doi:10.1007/s101030050062
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Popescu, V.A., Puscas, N.N. & Perrone, G. Simulation of the Sensing Performance of a Plasmonic Biosensor Based on Birefringent Solid-Core Microstructured Optical Fiber. Plasmonics 12, 905–911 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0342-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0342-y