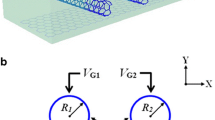
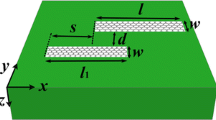
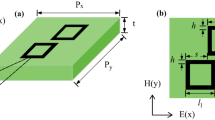
Abstract
Wavelength-tunable plasmon-induced transparency (PIT) in coupled graphene gratings was theoretically investigated in mid-infrared region. Both direct and phase-coupled PITs were considered in the proposed structure. In both schemes, a proper wavelength detuning between two graphene gratings was required for PIT observations. The effect of graphene quality on the PIT was also investigated. Graphene quality of μ = 50,000 cm2/Vs was sufficient for achieving a distinct PIT peak while a weak PIT was observed for μ = 10,000 cm2/Vs. PIT peak amplitude modulation and tunability of operating wavelength were demonstrated by adjusting the Fermi level of graphene. Compared with previously studied graphene-based PITs, the proposed PIT based on the coupled graphene gratings is much easier to design and fabricate.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boller KJ, Imamolu A, Harris SE (1991) Observation of electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 66(20):2593–2596
Harris S, Hau L (1999) Nonlinear optics at low light levels. Phys Rev Lett 82(23):4611–4614
Wu Y, Saldana J, Zhu Y (2003) Large enhancement of four-wave mixing by suppression of photon absorption from electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys Rev A 67(1):013811
Hau LV, Harris SE, Dutton Z, Behroozi CH (1999) Light speed reduction to 17 metres per second in an ultracold atomic gas. Nature 397(6720):594–598
Krauss TF (2008) Why do we need slow light. Nat Photon 2(8):448–450
Smith DD, Chang H, Fuller KA, Rosenberger AT, Boyd RW (2004) Coupled resonator induced transparency. Phys Rev A 69(6):063804
Xu Q, Sandhu S, Povinelli ML, Shakya J, Fan S, Lipson M (2006) Experimental realization of an on-chip all-optical analogue to electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 96(12):123901
Song HY, Kim S, Magnusson R (2009) Tunable guided-mode resonances in coupled gratings. Opt Express 17(26):23544–23555
Zhang S, Genov DA, Wang Y, Liu M, Zhang X (2008) Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys Rev Lett 101(4):047401
Li Z, Ma Y, Huang R, Singh R, Gu J, Tian Z, Han J, Zhang W (2011) Manipulating the plasmon-induced transparency in terahertz metamaterials. Opt Express 19(9):8912–8919
Taubert R, Hentschel M, Kastel J, Giessen H (2012) Classical analog of electromagnetically induced absorption in plasmonics. Nano Lett 12(3):1367–1371
Liu X, Gu J, Singh R, Ma Y, Zhu J, Tian Z, He M, Han J, Zhang W (2012) Electromagnetically induced transparency in terahertz plasmonic metamaterials via dual excitation pathways of the dark mode. Appl Phys Lett 100(13):131101
Liu N, Weiss T, Mesch M, Langguth L, Eigenthaler U, Hirscher M, Sonnichsen C, Giessen H (2009) Planar metamaterials analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency for plasmonic sensing. Nano Lett 10(4):1103–1107
Dong ZG, Liu H, Mu MX, Mu T, Wang SM, Zhu SN, Zhang X (2010) Plasmonically induced transparent magnetic resonance in a metallic metamaterials composed of asymmetric double bars. Opt Express 18(17):18229–18234
Biswas S, Duan J, Nepal D, Park K, Pachter R, Vaia RA (2013) Plasmon-induced transparency in the visible region via self-assembled gold nanorod heterodimers. Nano Lett 13(12):6287–6291
Gu J, Singh R, Liu X, Zhang X, Ma Y, Zhang S, Maier SA, Tian Z, Azad AK, Chen HT, Taylor AJ, Han J, Zhang W (2012) Active control of electromagnetically induced transparency analogue in terahertz metamaterials. Nat Commun 3:1151
Zhang J, Xiao S, Jeppesen C, Kristensen A, Mortensen NA (2010) Electromagnetically induced transparency in metamaterials at near-infrared frequency. Opt Express 18(16):17187–17192
Liu N, Langguth I, Weiss T, Kastel J, Flesichhauer M, Pfau T, Giessen H (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat Mat 8(9):758–762
Xu H, Lu Y, Lee Y, Ham BS (2010) Studies of electromagnetically induced transparency in metamaterials. Opt Express 18(17):17736–17747
R. D. Kekatpure, E. S. barnard, W. Cai, and M. L. Brongersma, Phase-coupled plasmon-induced transparency, Phys. Rev. Lett. 104(24), 243902 (2010).
Han Z, Bozhevolnyi SI (2011) Plasmon-induced transparency with detuned ultracompact Fabry-Perot resonators in integrated plasmonic devices. Opt Express 19(4):3251–3257
Zhu Y, Hu X, Yang H, Gong Q (2014) On-chip plasmon-induced transparency based on plasmonic coupled nanocavities. Sci Rep 4:3752
Cheng H, Chen S, Yu P, Duan X, Xie B, Tian J (2013) Dynamically tunable plasmonically induced transparency in periodically patterned graphene nanostrips. Appl Phys Lett 130(20):203112
Shi X, Han D, Dai Y, Yu Z, Sun Y, Chen H, Liu X, Zi J (2013) Plasmonic analog of electromagnetically induced transparency in nanostructure graphene. Opt Express 21(23):28438–28443
Ding J, Arigong B, Ren H, Zhou M, Shao J, Lu M, Chai Y, Lin Y, Zhang H (2014) Tunable complementary metamaterials structures based on graphene for single and multiple transparency windows. Sci Rep 4:6128
Jablan M, Buljan H, Solijacic M (2009) Plasmonics in graphene at infrared frequencies. Phys Rev B 80(24):245435
Koppens FHL, Chang DE, Garcia de Abajo FJ (2011) Graphene plasmonics: a platform for strong light-matter interactions. Nano Lett 11(8):3370–3377
Grigorenko AN, Polini M, Novoselov KS (2012) Graphene plasmonics. Nat Photon 6(11):749–758
Ju N, Geng B, Horng J, Girit C, Martin M, Hao Z, Bechtel HA, Liang X, Zettl A, Shen YR, Wang F (2011) Graphene plasmonics for tunable terahertz metamaterials. Nat Nanotech 6(10):630–643
Nikitin AY, Guinea F, Garcia-Vidal FJ, Martin-Moreno L (2012) Surface plasmon enhanced absorption and suppressed transmission in periodic arrays of graphene ribbons. Phys Rev B 85(8):081405
Hanson GW (2008) Dyadic Green’s functions and guided surface waves for a surface conductivity model of graphene. J Appl Phys 103(6):064302
Emani NK, Chung T-F, Ni X, Kildishev AV, Chen YP, Boltasseva A (2012) Electrically tunable damping of plasmonic resonances with graphene. Nano Lett 12(10):5202–5206
Bolotin KI, Sikes KJ, Jiang Z, Klima M, Fudenberg G, Hone J, Kim P, Stormer HL (2008) Ultrahigh electron mobility in suspended graphene. Solid State Commun 146(9):351–355
Wang L, Meric I, Huang PY, Gao Q, Gao Y, Tran H, Taniguchi T, Watanabe K, Campos LM, Muller DA, Guo J, Kim P, Hone J, Shepard KL, Dean CR (2013) One-dimensional electrical contact to a two-dimensional material. Science 342(6158):614–617
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grants (NRF-2014-R1A2A2A01006720, NRF-2009-0094046, and NRF-2015M3C1A3022539).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M., Lee, S. & Kim, S. Plasmon-Induced Transparency in Coupled Graphene Gratings. Plasmonics 10, 1557–1564 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9965-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9965-7