Abstract
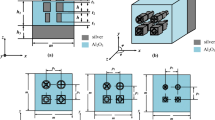
We present a meta-cone absorber based on metamaterials which can absorb nearly all incident light in the near-infrared spectrum. The absorber has an ultrahigh absorption with a broad receiving angle and independence of polarization state. This absorption enhancement can be attributed to the excitation of slow light mode and localized surface plasmon resonances (LSPR). In addition, we use slow light theory to explain why incident light with different wavelengths are trapped at different positions. We believe our work will provide a promising candidate as absorbing elements in technical applications and scientific research.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu XL, Starr T, Starr AF, Padilla WJ (2010) Infrared spatial and frequency selective metamaterial with near unity absorbance. Phys Rev Lett 104(20):207403
Landy N, Bingham C, Tyler T, Jokerst N, Smith D, Padilla W (2009) Design, theory, and measurement of a polarization-insensitive absorber for terahertz imaging. Phys Rev B 79(12):125104
Diem M, Koschny T, Soukoulis CM (2009) Wide-angle perfect absorber/thermal emitter in the terahertz regime. Phys Rev B 79(3):033101
Zhu J, Yu Z, Burkhard GF, Hsu C-M, Connor ST, Xu Y, Wang Q, Fan S, Cui Y (2009) Optical absorption enhancement in amorphous silicon nanowire and nanocone arrays. Nano Lett 10:1021
Chalabi H, Schoen D, Brongersma ML (2014) Hot-electron photodetection with a plasmonic nanostripe antenna. Nano Lett 14:1374–1380
Yen-Hsun S, Ke Y-F, Cai S-l, Yao Q-Y (2012) Surface plasmon resonance of layer-by-layer gold nanoparticles induced photoelectric current in environmentally-friendly plasmon-sensitized solar cell. Light Sci Appl 10:1038
Te Lin K, Chen H-L, Lai Y-S, Yu C-C (2014) Silicon-based broadband antenna for high responsivity and polarization-insensitive photodetection at telecommunication wavelengths. Nat Commun 5:3288
Schurig D, Mock J, Justice B, Cummer S, Pendry J, Starr A, Smith D (2006) Metamaterial electromagnetic cloak at microwave frequencies. Science 314:5801
Pendry J (2000) Negative refraction makes a perfect lens. Phys Rev Lett 85:3966
Fok L, Zhang X (2011) Negative acoustic index metamaterial. Phys Rev B 83:214304
Almoneefand TS, Ramahi OM (2015) Metamaterial electromagnetic energy harvester with near unity efficiency. Appl Phys Lett 106:153902
Shen X, Cui TJ, Zhao J, Ma HF, Jiang WX, Li H (2011) Polarization-independent wide-angle triple-band metamaterial absorber. Opt Express 19:009401
Wang B-X, Wang G-Z, Wang L-L (2015) Design of a novel dual-band terahertz metamaterial absorber. Plasmonics 14:114012
Dong X, Tao K, Wang Q (2015) Ultrabroadband mid-infrared light absorption based on a multi-cavity plasmonic metamaterial array. Plasmonics 10:1007
Grześkiewicz B, Sierakowski A, Marczewski J, Pałka N, Wolarz E (2014) Polarization-insensitive metamaterial absorber of selective response in terahertz frequency range. J Opt 16:105104
Sun C, Su J, Wang X (2015) A design of thin film silicon solar cells based on silver nanoparticle arrays. Plasmonics 10:1007
Cao S, YU W, Wang T, Xu Z, Wang C, Fu Y, Liu Y (2013) Two-dimensional subwavelength meta-nanopillar array for efficient visible light absorption. Appl Phys Lett 102:161109
TC Choy (1999) Effective medium theory: principles and applications. Oxford University Press on Demand 102
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370
ED Palik (1998) Handbook of optical constants of solids. Academic press
Baba T (2008) Slow light in photonic crystal. Nat Photonics 2:146
T Jiang, YJ Feng (2008) In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology
Jiang T, Zhao J, Feng Y (2009) Stopping light by an air waveguide with anisotropic metamaterial cladding. Opt Express 19:170–177
Hu H, Ji D, Xie Z, Liu K, Gan Q (2013) Rainbow trapping in hyperbolic metamaterial waveguide. Sci Rep 3:1249
Acknowledgments
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61306125 and U1435210), the Science and Technology Innovation Project (Y3CX1SS143) of CIOMP, the Science and Technology Innovation Project of Jilin Province (Nos. Y3293UM130, 20130522147JH, and 20140101176JC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Gao, J., Yang, H. et al. A Super Meta-Cone Absorber for Near-Infrared Wavelengths. Plasmonics 11, 1067–1072 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0143-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0143-8