Abstract
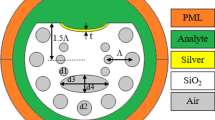
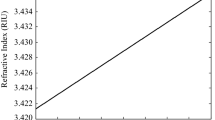
We propose a highly sensitive temperature sensor based on photonic crystal surface plasmon waveguides comprising different plasmonic active metals such as gold, silver, and aluminum, utilizing surface plasmon resonance phenomenon. We found that the resonance wavelength can be easily and substantially tuned over a broad spectral range by changing the temperature and also by judiciously choosing the different plasmonic metals. Employing coupled mode theory, we found that the proposed sensor can be used in harsh environment with sensitivity as high as ∼70 pm/K around telecommunication window.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee B (2003) Review of the present status of optical fiber sensors. Opt Fiber Technol 9(2):57–79
Remouche M, Mokdad R, Chakari A, Meyrueis P (2007) Intrinsic integrated optical temperature sensor based on waveguide bend loss. Optics & Laser Technology 39:1454–1460
Chomát M, Čtyroký J, Berková D, Matějec V, Kaňka J, Skokánková J, Todorov F, Jančárek A, Bittner P (2006) Temperature sensitivity of long-period gratings inscribed with a CO2 laser in optical fiber with graded-index cladding. Sensor and Actuator B Chem 119(2):642–650
Sharma AK, Jha R, Gupta BD (2007) Fiber-optic sensors based on surface plasmon resonance: a comprehensive review. IEEE Sens J 7(8):1118–1129
Choi HY, Park KS, Park SJ, Paek UC, Lee BH, Choi ES (2008) Miniature fiber-optic high temperature sensor based on a hybrid structured Fabry–Perot interferometer. Opt Lett 33:2455–2457
Jha R, Villatoro J, Badenes G, Pruneri V (2009) Refractometery based on photonic crystal fiber modal interferometer. Opt Lett 34:617–619
Homola J, Čtyroký J, Skalsky M, Hradilova J, Kolarova P (1997) A surface plasmon resonance based integrated optical sensor. Sensors Actuator B Chem 38–39:286–290
Srivastava T, Das R, Jha R (2010) Design consideration and propagation characteristic of channel Bragg plasmon coupled waveguide. Appl Phys Lett 97:213104–3
Dostalek J, Ctyroky J, Himola J, Brynda E, Skalsky M, Nekvindova P, Spirkova J, Skvor J, Schrofel J (2001) Surface plasmon resonance biosensor based on integrated optical waveguide. Sens Actuators B 76:8
West BR, Helmy AS (2006) Properties of the quarter-wave Bragg reflection waveguide: theory. J Opt Soc Am B 23:1207
Srivastava T, Jha R, Das R (2011) High performance bimetallic SPR sensor based on periodic multilayer waveguide. IEEE Photon Tech Lett 23:1448
Srivastava T, Das R, Jha R (2011) Highly accurate and sensitive surface plasmon resonance sensor based on channel photonic crystal waveguide. Sensors and Actuator B 157:246
Toyoda T, Yabe M (1983) The temperature dependence of the refractive indices of SrTiO3 and TiO2. J Phys D: Appl Phys 16:L251–L255
Ghosh G, Endo M, Iwasaki T (1994) Temperature dependent Sellmeier coefficients and chromatic dispersions for some optical fiber glasses. Journ Lightwave Technol 12(8):1338–1342
Sharma AK, Pattanaik HS, Mohr GJ (2009) On temperature sensing capability of a fibre optic SPR mechanism based on bimetallic alloy nanoparticles. J Phys D: Appl Phys 42:045104
Chiang HP, Leung PT, Tse WS (1998) The surface plasmon enhancement effect on absorbed molecules at elevated temperatures. J Chem Phys 108:2659–2660
Holstein T (1954) Optical and infrared volume absorptivity of metals. Phys Rev 96:535–536
Lawrence WE (1976) Electron–electron scattering in the low temperature resistivity of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 13:5316–5319
Schiebener P, Straub J, Levelt Sengers JMH, Gallaghen JS (1990) Refractive index of water and steam as function of wavelength, temperature and density. J Phys Chem Ref Data 19:677–717
Yariv A (1973) Coupled-mode theory for guided-wave optics. J Quant Electron QE-9(9):919–933
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, T., Das, R. & Jha, R. Highly Sensitive Plasmonic Temperature Sensor Based on Photonic Crystal Surface Plasmon Waveguide. Plasmonics 8, 515–521 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-012-9421-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-012-9421-x