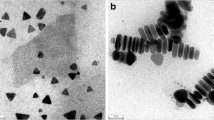
Abstract
In pH 6.0 Na2HPO4-NaH2PO4 buffer solution and in the presence of cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide, nanosilver particles were aggregated to a stable suspension. Therein, rhodamine 6G (Rh6G) exhibited three strong surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) peaks at 613, 1,363, and 1,510 cm−1, and their SERS intensities were enhanced when the concentration of Rh6G increased. In the presence of Hg2+, the SERS intensity decreased greatly owing to formation of stable Rh6G-HgBr 2−4 ternary association complex molecules as well as its particles. In the optimal condition, the decreased SERS intensity at 613 cm−1 responds linearly with the concentration of Hg2+ over 25–2,000 nmol/L. Thus, a new sensitive SERS method has been proposed for the determination of trace Hg2+ in the water sample, with satisfactory results.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scheuhammer AM, Meyer MW, Sandheinrich MB, Murray MW (2007) Effects of environmental methylmercury on the health of wild birds, mammals, and fish. AMBIO J Human Env 36(1):12–19
Hontelez J (2005) Zero mercury: key issues and policy recommendations for the EU strategy on mercury. UK: European Environmental Bureau 29.
Mergler D, Anderson HA, Chan LHM, Mahaffey KR, Murray M, Sakamoto M, Stern AH (2007) AMBIO J Human Env 36(1):3–11
Resano M, Briceno J, Belarra MA (2009) Direct determination of Hg in polymers by solid sampling-graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry: a comparison of the performance of line source and continuum source instrumentation. Spectrochem Acta Part B 64:520–529
Romero V, Costas-Mora I, Lavilla I, Bendicho C (2011) Cold vapor-solid phase microextraction using amalgamation in different Pd-based substrates combined with direct thermal desorption in a modified absorption cell for the determination of Hg by atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochem Acta Part B 66:156–162
Sardans J, Montes F, Penuelas J (2010) Determination of As, Cd, Cu, Hg and Pb in biological samples by modern electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochem Acta Part B 65:97–112
Gil S, Lavilla I, Bendicho C (2006) Green method for ultrasensitive determination of Hg in natural waters by electrothermal–atomic absorption spectrometry following sono-induced cold vapor generation and ‘in-atomizer trapping’. Spectrochem Acta Part B 62:69–75
Capelo JL, Riva GM, Oliveira LG, Vilhena C, Santos AC, Valada T, Galesio M, Oliveira P, Gomes da Silva MDR, Gaspar EM, Alves S, Fernandez C, Vaz C (2006) Mercury determination by FI-CV-AAS after the degradation of organomercurials with the aid of an ultrasonic field: the important role of the hypochlorite ion. Talanta 68:813–818
Lopez-Rouco A, Stanisz E, Matusiewicz H, Lavilla I, Bendicho C (2008) UV reduction with ultrasound-assisted gas-liquid separation for the determination of mercury in biotissues by atomic absorption spectrometry. J Anal Atom Spectr 23:1026–1029
Li ZX, Yang XM, Guo YA, Li HT, Feng YH (2008) Simultaneous determination of arsenic, antimony, bismuth and mercury in geological materials by vapor generation-four-channel non-dispersive atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Talanta 74:915–921
Leopold K, Foulkes M, Worsfold PJ (2009) Gold-coated silica as a preconcentration phase for the determination of total dissolved mercury in natural waters using atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Anal Chem 81:3421–3428
Li X, Wang ZH (2007) Determination of mercury by interminttent flow electrochemical cold vapor generation coupled to atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 588:179–183
Yin YM, Qiu JH, Yang LM, Wang QQ (2007) A new vapor generation system for mercury species based on the UV irradiation of mercaptoethanol used in the determination of total and methyl mercury in environmental and biological samples by atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 388:831–836
Lee JS, Han MS, Mirkin CA (2007) Colorimetric detection of mercuric ion (Hg2+) in aqueous media using DNA-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Edi 46:4093–4096
Li T, Dong SJ, Wang EK (2009) Label-free colorimetric detection of aqueous mercury ion (Hg2+) using Hg2+-modulated G-quadruplex-based DNAzymes. Anal Chem 81:2144–2194
Wang H, Wang YX, Jin JY, Yang RH (2008) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric and “Turn-On” fluorescent probe for mercury(II) ions in aqueous solution. Anal Chem 80:9021–9028
Ito R, Kawaguchi M, Sakui N, Okanouchi N, Saito K, Seto Y, Nakazawa H (2009) Stir bar sorptive extraction with in situ derivatization and thermal desorption-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for trace analysis of methylmercury and mercury(II) in water sample. Talanta 77:1295–1298
Beceiro-Gonzalez E, Guimaraes A, Alpendurada MF (2009) Optimisation of a headspace-solid-phase micro-extraction method for simultaneous determination of organometallic compounds of mercury, lead and tin in water by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1216(29):5563–5569
Chen JG, Chen HW, Jin CHT (2009) Determination of ultra-trace amount methyl-, phenyl- and inorganic mercury in environmental and biological samples by liquid chromatography with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after cloud point extraction preconcentration. Talanta 77:1281–1287
Rodrigues JL, de Souza SS, de Oliveira Souza VC, Barbosa F Jr (2009) Methlmercury and inorganic mercury determination in blood by using liquid chromatography with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and a fast sample preparation procedure. Talanta 80:1158–1163
Jiang ZL, Fan YY, Chen ML, Liang AH, Liao XJ, Wen GQ, Shen XC, He XC, Pan HC, Jiang HS (2009) Resonance scattering spectral detection of trace Hg2+ using aptamer-modified nanogold as probe and nanocatalyst. Anal Chem 81:5439–5445
Liang AH, Zhang J, Cai W, Jiang ZL, Li TS, Yao JE, Shang GY (2011) A highly sensitive resonance scattering spectral assay for Hg2+ based on the aptamer-modified AuRu nanoparticle-NaClO3-NaI-Cationic surfactant catalytic reaction. Anal Lett 44:1442–1453
Wen GQ, Liang AH, Fan YY, Jiang ZL, Jiang CN (2009) A simple and rapid resonance scattering spectral method for detection of trace Hg2+ using aptamer-nanogold as probe. Plasmonics 5:1–6
Wang GQ, Chen LX (2009) Aptameric SERS sensor for Hg2+ analysis using silver nanoparticles. Chin Chem Lett 20:1475–1477
Wang GQ, Lim C, Chen LX, Chon H, Choo J, Hong J, Demello AJ (2009) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering in nanoliter droplets: towards high-sensitivity detection of mercury(II) ions. Anal Bioanal Chem 39:1827–1832
Senapati T, Senapati D, Singh AK, Fan Z, Kanchanapally R, Ray PC (2011) Highly selective SERS probe for Hg(II) detetion using tryptophan-protected popcorn shaped gold nanoparticles. Chem Commun 47:10326–10328
Han D, Lim SY, Kim BJ, Piao L, Chung TD (2010) Mercury(II) detection by SERS based on a single gold microshell. Chem Commun 46:5587–5589
Wang XF, Shen YH, Xie AJ, Li SK, Cai Y, Wang Y, Shu HY (2011) Assembly of dandelion-like Au/PANI nanocomposites and their application as SERS nanosensors. Biosen Bioelectron 26:3063–3067
Fleischmann M, Hendra PJ, McQuillan AJ (1974) Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chem Phy Lett 26(2):163–166
Jeanmaire DL, Van Duyne RP, Sloan AP (1977) Surface Raman spectroelectrochemistry: Part I. Heterocyclic, aromatic, and aliphatic amines adsorbed on the anodized silver electrode. J Electroanal Chem Inter Electrochem 84(1):1–20
Albrecht MG, Creighton JA (1977) Anomalously intense Raman of pyridine at a silver electrode. J Am Chem Soc 99:5215–5217
Kennedy DC, McKay CS, Tay LL, RouleauY PJP (2011) Carbon-bonded silver nanopatricles: alkyne-functionalized ligands for SERS imaging ofmammalian cells. Chem Commun 47:3156–3158
Lee S, Gu GH, Suh JS (2011) A simple method to fabricate silver colloid clusters for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Chem Phy Lett 511(1–3):121–125
Costa JCS, Corio P (2010) Star-shaped silver nanoparticles as SERS substrates for trace analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. XXII International Conference on Raman Spectroscopy 1267:940–941
Dieringer JA, Wustholz KL, Masiello DJ, Camden JP, Kleinman SL, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP (2009) Surface-enhanced Raman excitation spectroscopy of a single rhodamine 6G molecule. J Am Chem Soc 131:849–854
Chen JN, Martensson T, Dick KA, Deppert K, Xu HQ, Samuelson L, Xu HX (2008) Surface-enhanced Ramanscattering of rhodamine 6G on nanowire arrays decorated with gold nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 19(27):1–5
Gong JL, Lv P, Zeng GM (2009) Recent advancements in environmental analysis based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem Sensors 29(3):8–12
Zhang L, Zhang YL, Zhang W, Wang WM, Du YP, Yukihiro O (2009) The study on linear relationship between concentration and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) signal of thymine in improved Ag Sol. Spectrosc Spect Anal 29:1889–1891
Hidebrand P, Stockburger M (1984) Surface-enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopy of Rhodamine 6G adsorbed on colloidal silver. J Phy Chem 88:5935–5944
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21075023, 20865002, 20965002), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (no. 0991021z), the Research Funds of Key Laboratory of Ecology of Rare and Endangered Species and Environmental Protection, Ministry of Education, and the Research Funds of Guangxi Education Office.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
DOC 49 kb
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Y., Li, K., Wen, G. et al. A Rapid Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Method for the Determination of Trace Hg2+ Using Rhodamine 6G-Aggregated Nanosilver as Probe. Plasmonics 7, 461–468 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-012-9329-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-012-9329-5