Abstract
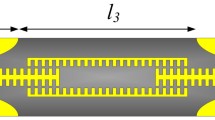
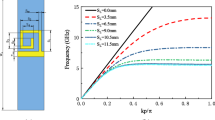
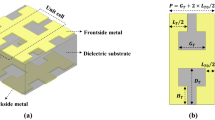
A new type of stripline-based microwave transmission, which has relatively lower crosstalk compared with the conventional striplines, is proposed. The structure is formed by corrugated inward slit that is subwavelength scale on the edge of the stripline via the photolithography techniques. Numerical simulation is used to analyze the transmission and dispersion properties of this new stripline structure, and the results are experimentally verified in the frequency range from 200 MHz to 8 GHz. We found that spoof surface plasmon polaritons are supported on the new stripline structure whose electromagnetic fields are highly localized near the stripline, and hence the coupling is suppressed between the present type of stripline and the conventional stripline. For a structured stripline and a conventional stripline which are parallelly placed and separated by a distance of the stripline width, the crosstalk between them ranges from −17.13 to −64.89 dB, which is much lower than the crosstalk between two coupled conventional striplines. As this new type of stripline has such an important advantage, it would be applicable to high-density microwave circuits or high-speed circuits.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raether H (1988) Surface Plasmons. Springer, Berlin
Pendry JB, Martin-Moreno L, Garcia-Vidal FJ (2004) Mimicking surface plasmons with structured surfaces. Science 305:847–848
Garcia-Vidal FJ, Martin-Moreno L, Pendry JB (2005) Surfaces with holes in them: new plasmonic metamaterials. J Opt A Pure Appl Opt 7:S97–S101
Jiang T, Shen LF, Zhang X, Ran L (2009) High-order modes of spoof surface Plasmon polaritons on periodically corrugated metal surface. Progress In Electromagnetics Research M 8:91–102
Garcia de Abajo FJ, Saenz JJ (2005) Electromagnetic surface modes in structured perfect-conductor surfaces. Phys Rev Lett 95:233901
Wu JJ, Yang TJ, Shen LF (2009) Subwavelength microwave guiding by a periodically corrugated metal wire. J of Electromagn Waves and Appl 23:11–19
Hibbins P, Evans BR, Sambles JR (2005) Experimental verification of designer surface plasmons. Science 308:670–672
Zhang XF, Shen LF, Wu J-J, Yang T-J (2009) “Terahertz surface plasmon polaritons on a periodically structed metal film with high confinement and low loss”. J of Electromagn Waves and Appl 23:2451–2460
Wu JJ (2010) Subwavelength microwave guiding by periodically corrugated strip line. Prog Electromagn Res 104:113–123
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the National Science Council of ROC under grant no. NSC 98-2221-E-216-001 and the Project of Ministry of Education under grant no. 98-2811-M-216-002 for the financial supports. We are grateful to Dr. Jian Qi Shen and Linfang Shen for stimulating discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J.J., Lin, H.E., Yang, TJ. et al. Low-Frequency Surface Plasmon Polaritons Guided on a Corrugated Metal Striplines with Subwavelength Periodical Inward Slits. Plasmonics 6, 59–65 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-010-9169-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-010-9169-0