Abstract
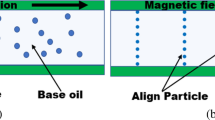
This paper describes an application study of Magneto-Rheological (MR) grease damper to a structure with three stories. MR fluid is known as one of successful smart materials whose rheological properties can be varied by magnetic field strength, and has been applied to various kinds of device such as dampers, clutches, engine mounts, etc. However, ferromagnetic particles dispersed in MR fluid settle out of the suspension after a certain interval due to the density difference between the particles and their career fluid. To overcome this defect, we have developed a new type of controllable working fluid using grease as the career of magnetic particles. Network of thickener in grease is expected to hold the magnetic particles and prevent them from settled down. No or little sedimentation was observed in MR grease whose characteristics could be controlled by the magnetic field strength. MR grease was introduced into a cylindrical damper and its performance was studied. As a result, it was confirmed that the damping force of MR grease damper could be controlled by the applied electric current to the coil in the cylinder of damper. Furthermore, vibration response of a three-story model structure equipped with MR grease damper was investigated experimentally, and it was shown that MR grease damper worked effectively as a semi-active damper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rabinow J. The magnetic fluid clutch. Transactions of AIEE, 1948, 67(12): 1308–1315
Carlson J D, Catanzarite D M, St. Clair K A. Commercial magnetorheological fluid devices. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 1996, 10(23–24): 2857–2865
Jiang Z, Christenson R E. A fully dynamic magneto-rheological fluid damper model. Smart Materials and Structures, 2012, 21(6): 065002
Cha Y J, Agrawal A K, Dyke S J. Time delay effects on large-scale MR damper based semi-active control strategies. Smart Materials and Structures, 2013, 22(1): 015011
Nagano Y, Nakagawa T, Suzuki K. A basic study for an elevator emergency stop device utilizing MR fluid. In: Proceedings of 15th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, 2012, 1–4
Hoshino M. Theory of grease lubrication. JAST Journal of Japanese Society of Tribologists, 2002, 47(1): 8–14
Lugt P M. A review on grease lubrication in rolling bearings. Tribology Transactions, 2009, 52(4): 470–480
Oya Y, Miyamoto S, Morishita S, Shiraishi T. Experimental study on visualization of grease flow. JAST Journal of Japanese Society of Tribologists, 2011, 56(4): 248–255
Karnopp D, Crosby MJ, Harwood R A. Vibration control using semiactive force generators. Journal of Engineering for Industry, 1974, 96(2): 619–626
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugiyama, S., Sakurai, T. & Morishita, S. Vibration control of a structure using Magneto-Rheological grease damper. Front. Mech. Eng. 8, 261–267 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-013-0268-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-013-0268-4