Abstract
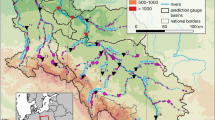
Based on the daily runoff data from 20 hydrological stations above the Bengbu Sluice in the Huaihe River Basin during 1956–2010, run test, trend test and Mann-Kendall test are used to analyze the variation trend of annual maximum runoff series. The annual maximum series (AM) and peaks over threshold series (POT) are selected to describe the extreme distributions of generalized extreme value distribution (GEV) and generalized Pareto distribution (GPD). Temporal and spatial variations of extreme runoff in the Huaihe River Basin are analyzed. The results show that during the period 1956–2010 in the Huaihe River Basin, annual maximum runoff at 10 stations have a decreasing trend, while the other 10 stations have an unobvious increasing trend. The maximum runoff events almost occurred in the flood period during the 1960s and 1970s. The extreme runoff events in the Huaihe River Basin mainly occurred in the mainstream of the Huaihe River, Huainan mountainous areas, and Funiu mountainous areas. Through Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, GEV and GPD distributions can be well fitted with AM and POT series respectively. Percentile value method, mean excess plot method and certain numbers of peaks over threshold method are used to select threshold, and it is found that percentile value method is the best of all for extreme runoff in the Huaihe River Basin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brabson B B, Palutikof J P, 2000. Tests of generalized Pareto distribution for predicting extreme wind speeds. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 39: 1627–1640.
Cai Min, Ding Yuguo, Jiang Zhihong, 2007. Extreme precipitation experimentation over eastern China based on L-moment estimation. Plateau Meteorology, 26(2): 309–318. (in Chinese)
Coles S, 2001. An Introduction to Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values. New York: Springer Verlag, 36–78.
Ding Yuguo, 2006. Theoretical basis for discussing disaster disciplinarian: The probability of extreme climate event. Meteorology and Disaster Reduction Research, 29(1): 44–50. (in Chinese)
Ding Yuguo, Jiang Zhihong, 2009. Extreme Climate Research Methods. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 79–80. (in Chinese)
Dong Quan, Chen Xing, Chen Tiexi et al., 2009. Relationship between extremes of precipitation and discharge in the Huaihe River Basin. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 45(6): 790–801. (in Chinese)
Dong Shuanglin, 2001. Gust extremes in China and its statistical study. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 59(3): 327–333. (in Chinese)
Fisher R A, 1925. Theory of statistical estimation. Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, (22): 700–715.
Fisher R A, Tippett, 1928. Limiting forms of the frequency distribution of the largest or smallest member of a sample. Proceedings of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 24: 180–190.
IPCC, 2007. Climate Change 2007: The physical science basis//Contribution of Working Group 1 to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, USA: Cambridge University Press.
Jenkinson A F, 1955. The frequency distribution of the annual maximum (or minimum) values of meteorological elements. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 81: 158–171.
Kunkel, Kenneth E, Karen Andsager et al., 1999. Long-term trends in extreme precipitation events over the conterminous United States and Canada. Journal of Climate, 12: 2515–2527.
Manton M J, Della-Marta P M, Haylock M R et al., 2001. Trends in extreme daily rainfall and temperature in Southeast Asia and the South Pacific: 1961–1998. International Journal of Climatology, 21(3): 269–284.
Nandintsetseg B, Greene J S, Goulden C E, 2007. Trends in extreme daily precipitation and temperature near lake Hövsgöl, Mongolia. International Journal of Climatology, 27(3): 341–347.
Rajeevan M, Bhate J, Jaswal A K, 2008. Analysis of variability and trends of extreme rainfall events over India using 104 years of gridded daily rainfall data. Geophysical Research Letters, 35: L18707, doi:10.1029/2008GL035143.
Xia Jun, She Dunxian, Zhang Yongyong et al., 2012. Spatio-temporal trend and statistical distribution of extreme precipitation events in Huaihe River Basin in during 1960–2009. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 22(2): 195–208.
Shi Daoji, 2006. Practical Methods of Extreme Value Statistics. Tianjin: Tianjin Science and Technology Press. (in Chinese)
Su Buda, Jiang Tong, Dong Wenjie, 2008. Probabilistic characteristics of precipitation extremes over the Yangtze River Basin. Scientia Meteorologica Sinica, 28(6): 625–629. (in Chinese)
Trenberth K E, Coauthors, 2007. Observations: Atmospheric surface and climate change. In: Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Cambridge University Press, 235–336.
Wan Shiquan, Zhou Guohua, Pan Zhu et al., 2010. A simulative study of extreme daily rainfall in Nanjing for the past 100 years. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 68(6): 790–799. (in Chinese)
Wang Fang, Tian Hong, 2010. Characteristics of extreme precipitation events in Huaihe River Basin in 1960–2007. Advances in Climate Change Research, 6(3): 228–229. (in Chinese)
Wei Fengying, Zhang Ting, 2009. Oscillation characteristics of summer precipitation in the Huaihe River Valley and relevant climate background. Science in China (Series D), 39(10): 1360–1374. (in Chinese)
Xia Jun, Liu Chunzhen, Ren Guoyu, 2011. Opportunity and challenge of the climate change impact on the water resource of China. Advances in Earth Science, 26(1): 1–12. (in Chinese)
Zhai Panmao, Ren Fumin, Zhang Qiang, 1999. Detection of trends in China’s precipitation extremes. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 57(2): 208–216. (in Chinese)
Zhang Jinling, Wang Ji, Gan Qinghui, 2009. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of extreme precipitation events in the Yangtze and Huaihe River Basin of China from 1961 to 2006. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 37(7): 3089–3091, 3146. (in Chinese)
Zhang Ting, Wei Fengying, 2009. Probability distribution of precipitation extremes during raining seasons in South China. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 67(3): 442–450. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation: National Basic Research Program of China, No.2010CB428406; The Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No.20102060201000066
Author: Xia Jun (1954–), Professor, specialized in hydrology and water resources.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, J., Du, H., Zeng, S. et al. Temporal and spatial variations and statistical models of extreme runoff in Huaihe River Basin during 1956–2010. J. Geogr. Sci. 22, 1045–1060 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-012-0982-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-012-0982-6