Abstract
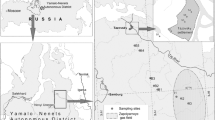
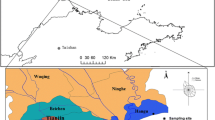
The concentrations of heavy metals Ba, Pb, Cu, Zn and Co in snow pit collected in September, 2005 from the accumulation area of the East Rongbuk Glacier (6523 m a.s.l.), which lies on the northern slope of Mt. Qomolangma, were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Concentrations (pg/ml) of heavy metals are Ba2-227, Co2.8-15.7, Cu10-120, Zn29-4948 and Pb14-142, respectively. The δ18O was determined by MAT-252. The time period of the snow pit spans from autumn 2005 to summer 2004. Seasonal variations of the concentrations and δ18O are observed, of which Pb, Cu, Zn and Co are much lower in summer monsoon season than that in non summer monsoon season, suggesting that different sources of heavy metals contributed to the site. EFc (crustal enrichment factors) is Co3.6, Cu27, Pb33 and Zn180, respectively. Higher EFc values of Pb, Cu and Zn suggest that Pb, Cu especially Zn are mainly contributed by anthropogenic sources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbante C, Cozzi G, Capodaglio G et al., 1999. Trace element determination in alpine snow and ice by double focusing inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with microconcentric nebulization. J. At. Spectrom., 14: 1433–1438.
Barbante C, Schikowski M, Doering T et al., 2004. Historical record of European emissions of heavy metals to the atmosphere since the 1650s from alpine snow/ice cores drilled near Monte Rosa. Environmental and Science & Technology, 38: 4084–4090.
Berg T, Royset O, Steinnes E, 1994. Trace metals in atmospheric precipitation at Norwegian background stations (1989–1990) measured by ICP-MS. Atmospheric Environment, 28(21): 3519–3536.
Boutron C F, Gorlach U, Candelone J P et al., 1991. Decrease in anthropogenic lead, cadmium, and zinc in Greenland snows since 1960’s. Nature, 353: 153–156.
Boyle E A, Sherrell R M, Bacon M P, 1994. Lead variability in the western North Atlantic and central Greenland ice: Implications for the search for decadal trends in anthropogenic emissions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 58: 3227–3238.
Candelone J P, Hong S, 1995. Post-industrial revolution changes in large-scale atmospheric pollution of the North Hemisphere by heavy metals as documented in central Greenland snow and ice. Geophys. Res., 100(8): 16605–16616.
Candelone J P, Jaffrezo J L, Hong S et al., 1996. Seasonal variations in heavy metals concentrations in present day Greenland snow. The Science of the Total Environment, 193: 101–110.
Dansgaard W, 1964. Stable isotope in precipitation. J. Tellus, 14(4): 436–468.
Ferraria C P, Clotteaua T, Thompson L G et al., 2001. Heavy metals in ancient tropical ice: Initial results. Atmospheric Environment, 35: 5809–5815.
Hong S, Boutron C F, Edwardw R et al., 1998. Heavy metals in Antarctic ice from Law Dome: Initial results. Environmental Research, 78: 94–103.
Hong S et al., 2000. A clean protocol for determining ultralow heavy metals concentrations: Its application to the analysis of Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn, and Mn in Antarctic snow. Korean J. Polar Res., 11(1): 35–47.
Hou S G, Qin D H, Zhang D Q et al., 2002. Comparison of two ice core chemical records recovered from the Qomolangma (Mount Everest) region. Annals of Glaciology, 35: 266–272.
Hou S G, Qin D H, Zhang D Q et al., 2003. A 154a high-resolution ammonium record from the Rongbuk Glacier, north slope of Mt. Qomolangma (Everest), Tibet-Himal region. Atmospheric Environment, 37(5): 721–729.
Jenkins M, James D, 1987. Chemical composition of fresh snow on Mount Everest. Journal of Geophysical Research, D9: 10999–11002.
Kang S C, Mayewski P A, Qin D H et al., 2002. Glaciochemical records from a Mt. Everest ice core: Relationship to atmospheric circulation over Asia. Atmospheric Environment, 36(21): 3351–3361.
Kang S C, Mayewski P A, Qin D H et al., 2004. Seasonal differences in snow chemistry from the vicinity of Mt. Everest, central Himalayas. Atmospheric Environment, 38: 2819–2829.
Muhlbaier D J, Wolff T J, 1989. Trace inorganic species in precipitation and their potential use in source apportionment studies. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 42: 401–412.
Nriagu J O. 1989. A global assessment of natural sources of atmospheric trace metals. Nature, 338: 47–49.
Planchon F A M, Boutron C F, Barbante C et al., 2002. Changes in heavy metals in Antarctic snow from Coats Land since the mid-19th to the late-20th century. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 200: 207–222.
Qin D H, Mayewski P A, Wake C P et al., 2000. Evidence for recent climate change from ice cores in the Himalayas. Annals of Glaciology, 31: 153–158.
Schikowski M, Barbante C, Doering T et al., 2004. Post-17th-century changes of European lead emissions recorded in high-altitude Alpine snow and ice. Environmental and Science & Technology, 38: 957–964.
Vallelonga P, Velde K Van de et al., 2002. The lead pollution history of Law Dome, Antarctic, from isotopic measurements on ice core: 1500AD to 1989 AD. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 204: 291–306.
Van de Velde K, Boutron C F, Ferrari C et al., 1998. Seasonal variations of heavy metals in the 1960s alpine ice: Source versus meteorological factors. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 164: 521–533.
Veysseyre A, Moutard K, Ferrari C et al., 2001. Heavy metals in fresh snow collected at different altitudes in the Chamonix and Maurienne valleys, French Alps: Initial results. Atmospheric Environment, 35: 415–425.
Wedepohle K H, 1995. The composition of the continental crust. Geochimica Acta, 59: 1217–1232.
Wushiki H, 1977. Deuterium content in the Himalayan precipitation at Khumbu district, observed in 1974/1975. Journal of the Japanese Society of Snow and Ice, 39(Special Issue): 50–56.
Xie Zichu, Su Zhen, 1975. The development condition, quantity and distribution of glacier in Mount Qomolangma. The report of scientific expedition in Mount Qomolangma (1966–1968), Modern Glacier and Geomorphology. Beijing: Science Press, 1–13. (in Chinese)
Zhang Dongqi, Qin Dahe, Hou Shugui et al., 2002. Chemical characteristic study of snow and snow pit in Mount Qomolangma region. Journal of Lanzhou University, 38(4): 119–124. (in Chinese)
Zhang Dongqi, Qin Dahe, Ren Jiawen et al., 2001. Chemical characteristics of fresh snow in Mount Everest Region. Environmental Science, 22(2): 123–125. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation: National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.40501014; No.40871058
Author: Duan Jianping (1981–), Ph.D. Candidate, specialized in climate and environmental change.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, J., Wang, L., Ren, J. et al. Seasonal variations in heavy metals concentrations in Mt. Qomolangma Region snow. J. Geogr. Sci. 19, 249–256 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-009-0249-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-009-0249-z