Abstract
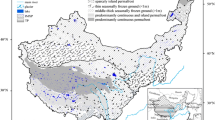
According to the analysis of the climate materials including the topographic map in 1975, the TM and CBERS satellite remote sensing materials from the 1980s to 2005 as well as the air temperature, precipitation, evaporation rate, maximum depth of snow and the biggest depth of frozen soil in the past 45 years, the water level area of four lakes at the southeast of Nagqu, Tibet including Bam Co, Pung Co, Dung Co and Nuripung Co show a distinct trend of expansion in the past 30 years. In 2005, the water level area of the above four lakes increased by 48.2 km2, 38.2 km2, 19.8 km2 and 26.0 km2 respectively compared to 1975, with the respective increase rate of 25.6%, 28.2%, 16.2% and 37.6%. That is closely related to the warming and humidified climate change in the recent years such as rise of the air temperature, increase of the precipitation, decrease of the evaporation rate and permafrost degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding Yongjian, Liu Fengjing, 1995. Effect of climatic change of water balance of Qinghai Lake basin for recent thirty years and possible tendency. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 15(2): 124–135. (in Chinese)
Gao Qingzhu, Li Yue, Lin Erda et al., 2005. Temporal and spatial distribution of grassland degradation in northern Tibet. Acta Geographica Sinica, 60(6): 965–973. (in Chinese)
Ge Shaoxia, Zong Ga, 2005. Preliminary study on change of lakes area in west Naqu, Tibet. Tibet’s Science and Technology, (4): 14–18. (in Chinese)
Hou Shugui, Qin Dahe, Yao Tandong et al., 2002. Recent change of the ice core accumulation rates on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(20): 1588–1591. (in Chinese)
Jin Huijun, Li Shuxun, Wang Shaoling et al., 2000. Impacts of climatic change on permafrost and cold regions environments in China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 55(2): 161–173. (in Chinese)
Ke Changqing, 2004. A review of monitoring lake environment change by means of remote sensing. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (4): 81–86. (in Chinese)
Li Bingyuan, 2000. The last greatest lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geographica Sinica, 55(2): 174–182. (in Chinese)
Li Lin, Zhu Xide, Wang Qingchun et al., 2005. Mapping and analyses of permafrost change in Qinghai Plateau using GIS. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 27(3): 320–328. (in Chinese)
Liu Xuesong, Ma Yucai, La Ba et al., 2003. Climatic Regionalization of Animal Husbandry of Naqu Region. Beijing: China Meteorological Press. (in Chinese)
Ren Jiawen, Qin Dahe, Jing Zhefan, 1998. Climatic warming causes the glacier retreat in Mt.Qomolangma. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 20(2): 17–18. (in Chinese)
Shi Yafeng, 2003. An Assessment of the Issues of Climatic Shift from Warm-dry to Warm-wet in Northwest China. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 1–3. (in Chinese)
Wang Sumin, 1993. The Principle and Research Advances of Lake Sediments: Study on Historical Evolution Law of Environment in China. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 22–31. (in Chinese)
Wang Yuefeng, Xiao Shu, Zeng Tao, 2005. An analysis of TM image in Tibet’s lakes. Tibet’s Science and Technology, (5): 23–26. (in Chinese)
Wu Shaohong, Yi Yunhe, Zheng Du et al., 2005.Climate changes in the Tibetan Plateau during the last three decades. Acta Geographica Sinica, 60(1): 3–11. (in Chinese)
Yao Tandong, Jiao Keqin, Yang Meixue, 1999. A study on the precipitation variance in Guliya Ice Core in the past 400 years. Progress in Natural Science, 9(12): 1161–1165. (in Chinese)
Zheng Du, Lin Zhenyao, Zhang Xueqin, 2002. Progress in studies of Tibetan Plateau and global environmental change. Earth Science Frontiers, 9(1): 95–102. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation: National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.40761005
Author: Bian Duo (1966–), Professor, specialized in application of remote sensing and GIS on environment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bianduo, Bianbaciren, Li, L. et al. The response of lake change to climate fluctuation in north Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in last 30 years. J. Geogr. Sci. 19, 131–142 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-009-0131-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-009-0131-z