Abstract
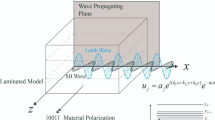
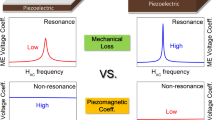
Magnetoelectric equivalent circuit analytical method is presented for laminate composites of magneto-strictive Terfenol-D (Tb x Dy1−x Fe2) and piezoelectric Pb(Zr1−x Ti x )O3 (PZT) operated in longitudinal magnetized and transverse polarized (or L-T), and transverse magnetized and transverse polarized (or T-T) modes. Magnetoelectric (ME) couplings both at low-frequency and resonance-frequency have been studied, and our analysis predicts that (i) the ME voltage coefficients of both L-T and T-T modes increase with increasing the thickness of the piezoelectric phase whereas magnetostrictive phase thickness keeps constant, and then tend to saturation when the thickness ratio of piezoelectric phase to magnetic phases is >3; (ii) there are the optimum thickness ratios that maximize magnetoelectric (ME) voltage coefficients for the two modes, which are dependent on elastic compliances ratio of piezoelectric phase and magnetostrictive phase; and (iii) the ME voltage coefficients are dramatically increased by a factor of ∼Q m, when operated at resonance frequency. A series of Terfenol-D/PZT laminates were fabricated, and the results were compared with the theoretical ones. Experiments confirmed that equivalent circuit method is a useful tool for optimum designs of ME laminates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Landau L D, Lifshitz E. Electrodynamics of Continuous Media. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1960. 119
Dong S X, Li J F, Viehland D. Ultrahigh magnetic field sensitivity in laminates of TERFENOL-D and Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 crystals. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83: 2265–2267
Dong S X, Li J F, Viehland D. Vortex magnetic field sensor based on ring-type magnetoelectric laminate. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85: 2307
Dong S X, Zhai J Y, Bai F M, et al. Push-pull mode magnetostrictive/piezoelectric laminate composite with an enhanced magnetoelectric voltage coefficient. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 87: 062502
Li Y Q. An innovative passive solid-state magnetic sensor. Sensors, 2000, 10: 17
Dong S X, Zhai J Y, Li J F, et al. Magnetoelectric gyration effect in Tb1−x DyxFe2−y /Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 laminated composites at the electromechanical resonance. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89: 243512
Zhai J Y, Li J F, Dong S X, et al. Enhanced magnetoelectric effect in three-phase MnZnFe2O4/Tb1−x DyxFe2−y /Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 composites. J Appl Phys, 2006, 100: 124108
Dong S X, Li J F, Viehland D. Voltage gain effect in a ring-type magnetoelectric laminate. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84: 4188
Dong S X, Li J F, Viehland D. A strong magnetoelectric voltage gain effect in magnetostrictive-piezoelectric composite. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85: 3534
Tatarenko A S, Srinivasan G, Bichurin M I. Magnetoelectric microwave phase shifter. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88: 183507
Festisov Y, Srinivasan G. Electric field tuning characteristics of a ferrite-piezoelectric microwave resonator. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88: 143503
Matteo S Di, Jansen A G M. Magnetoelectricity in V2O3. Phys Rev B, 2002, 66: 100402
Dzyaloshinskii I E. On the magnetoelectric effect in antiferromagnets. Sov Phys J Exp Theor Phys, 1960, 37: 628
Ryu J, Carazo A V, Uchino K, et al. Piezoelectric and magnetoelectric properties of lead zirconate titanate/Ni-ferrite particulate composites. J Electroceramics, 2001, 7: 24
Nan C W, Liu L, Cai N, et al. A three-phase magnetoelectric composite of piezoelectric ceramics, rare-earth iron alloys, and polymer. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 81: 3831
Suchetelene V. Product properties: A new application of composite materials. Philips Res Rep, 1972, 27: 28
Ryu J, Carazo A V, Uchino K, et al. Magnetoelectric properties in piezoelectric and magnetostrictive laminate composites. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2001, 40: 4948
Srinivasan G, Rasmussen E, Levin B, et al. Magnetoelectric effects in bilayers and multilayers of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric perovskite oxides. Phys Rev B, 2002, 65: 134402
Srinivasan G, Rasmussen E, Gallegos J, et al. Magnetoelectric bilayer and multilayer structures of magnetostrictive and piezoelectric oxides. Phys Rev B, 2001, 64: 214408
Srinivasan G, Laletin V M, Hayes R, et al. Giant magnetoelectric effects in layered composites of nickel zinc ferrite and lead zirconate titanate. Solid State Comm, 2002, 124: 373–378
Bichurin M I, Petrov V M, Srinivasan G. Theory of low-frequency magnetoelectric effects in ferromagnetic-ferroelectric layered composites. J Appl Phys, 2002, 92: 7681
Mori K, Wuttig M. Magnetoelectric coupling in Terfenol-D/polyvinylidenedifluoride composites. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 81: 100
Dong S X, Li J F, Viehland D. Longitudinal and transverse magnetoelectric voltage coefficients of magnetostrictive/piezoelectric laminate composite: Theory. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferr Freq Contr, 2003, 50: 1253
Dong S X, Li J F, Viehland D. Longitudinal and transverse magnetoelectric voltage coefficients of magnetostrictive/piezoelectric laminate composite: Experiments. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferr Freq Contr, 2004, 51: 794
Dong S X, Li J F, Viehland D. Enhanced magnetoelectric effects in laminate composites of Terfenol-D/Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 under resonant drive. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83: 4812
Dong S X, Li J F, Viehland D. A longitudinal-longitudinal mode TERFENOL-D/Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-PbTiO3 laminate composite. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85: 5305
Dong S X, Li J F, Viehland D. Characterization of magnetoelectric laminate composites operated in longitudinal-transverse and transverse-transverse modes. J Appl Phys, 2004, 95: 2625
Dong S X, Li J F, Viehland D. Circumferentially magnetized and circumferentially polarized magnetostrictive/piezoelectric laminated rings. J Appl Phys, 2004, 96: 3382
Nan C W. Magnetoelectric effect in composites of piezoelectric and piezomagnetic phases. Phys Rev B, 1994, 50: 6082
Nan C W, Li M, Huang J H. Calculations of giant magnetoelectric effects in ferroic composites of rare-earth-iron alloys and ferroelectric polymers. Phys Rev B, 2001, 63: 144415
Avellaneda M, Harshe G. Magnetoelectric effect in piezoelectric/magnetostrictive multilayer (2-2) composites. J Intel Mater Syst Struct, 1994, 5: 501–513
Wu T, Huang J. Closed-form solutions for the magnetoelectric coupling coefficients in fibrous composites with piezoelectric and piezomagnetic phases. Intern J Solids Struct, 2000, 37: 3009
Dong S X, Zhai J Y, Li J F, et al. Near-perfect magnetoelectricity in high-permeability magnetostrictive/piezoelectric-fiber laminates. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89: 252904
Dong S X, Viehland D, Xing Z P, et al. Giant magnetoelectric effect (under a dc magnetic bias of 2 Oe) in laminate composites of FeBSiC alloy ribbons and Pb(Zn1/3,Nb2/3)O3-7%PbTiO3 fibers. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 91: 022915
Mason W. Physical Acoustics, Principle and Methods. New York: Academic Press, 1964. 263
Cady W G. Piezoelectricity: An introduction to theory and applications of electromechanical phenomena in crystal. New York: Dover Publications, 1964
Katz H W. Solid State Magnetic and Dielectric Devices. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 1959. 119
Amin A, Newnham R E, Cross L E. Effect of elastic boundary conditions on morphotropic Pb(Zr,Ti)O3 piezoelectrics. Phys Rev B, 1986, 34: 1595
Yang F, Wen Y M, Li P, et al. The resonant magnetoelectric response of magnetostrictive/piezoelectric laminated composite under the consideration of losses. Acta Phys Sin, 2007, 56: 3539
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Office of Naval Research in USA
Electronic supplementary material
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, S., Zhai, J. Equivalent circuit method for static and dynamic analysis of magnetoelectric laminated composites. Chin. Sci. Bull. 53, 2113–2123 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0304-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-008-0304-7