Abstract
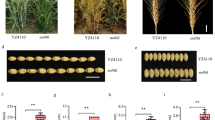
Gl e 2 is a mutant gene that controls glandless trait in cotton plants and seeds. It is an important gene resource to gossypol-free cottonseed breeding. The objective of this research was to develop SSR markers tightly linked with Gl e 2 by using the F2 segregating population containing 1599 plants derived from the cross of G. hirsutum genetic standard line TM-1 and G. barbadense glandless mutant line Hai-1. Genetic analysis suggested that the Gl e 2 was an incomplete dominant gene. Based on the backbone of genetic linkage map from G. hirsutum × G. barbadense BC1 published by our laboratory, Gl e 2 was located between CIR362 and NAU2251b, NAU3860b, STV033, with a genetic distance 9.27 and 0.96 cM, respectively. This result is useful for cloning Gl e 2 gene by map-based cloning method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cotton Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Genetics and Breeding of Cotton in China. Shandong: Shandong Science & Technology Press, 2003. 562
Bell A A, Stipanovic R D. The chemical composition biological activity and genetics of pigment glands in cotton. Proc Beltwide Cotton Prod Res Conf, 1977. 244–258
Afifi A, Bary A A, Kamel S A, et al. Bahtim 110, a new strain of Egyptian cotton free from gossypol. Emp Cot Grow Rew, 1966, 43: 112–120
Kohel R J, Lee J A. Genetic analysis of Egyptian glandless seeds cotton. Crop Sci, 1984, 24: 1119–1121
Tang C M, Min L F, Zhang T Z, et al. Genetic analysis for hai 1 strain of glandless cotton (G. barbadence L.) interaction between Gl e 2 and Gl 1. Cotton Sci Sin, 1996, 8: 138–140
Yuan Y L, Jing S R, Zhang T Z, et al. Studies on dominant glandless marker trait applied to heterosis in upland cotton. Seed, 1997, 6: 15–17
Lee J A. The genomic allocation of the principal foliar-gland loci in Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense. Evolution, 1965, 19: 182–188
Yu J, Kohel R J, Dong J M, et al. Toward positional cloning of a major glandless gene in cotton. Proc Beltwide Cotton Conf, National Cotton Council, Memphis, TN, 2000. 516–517
Guo W Z, Cai C P, Wang C B, et al. A microsatellite-based, gene-rich linkage map reveals genome structure, function, and evolution in Gossypium. Genetics, 2007, 176: 527–541
Kohel R J, Lewis C F, Richmond T R. Texas marker-1: Description of a genetic standard for Gossypium hirsutum L. Crop Sci, 1970, 10: 670–671
Paterson A H, Brubaker C L, Wendel J F. A rapid method for extraction of cotton (Gossypium spp.) genomic DNA suitable for RFLP and PCR analysis. Plant Mol Biol Rep, 1993, 11: 122–127
Reddy O U K, Pepper A E, Saha S. New dinucleotide and trinucleotide microsatellite marker resources for cotton genome research. J Cotton Sci, 2001, 5: 103–113
Nguyen T B, Giband M, Brottier P. Wide coverage of the tetraploid cotton genome using newly developed microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet, 2004, 109: 167–175
Taliercio E, Allen R D, Essenberg M, et al. Analysis of ESTs from multiple Gossypium hirsutum tissues and identification of SSRs. Genome, 2006, 49: 306–319
Han Z G, Guo W Z, Song X L, et al. Genetic mapping of EST-derived microsatellites from the diploid Gossypium arboreum in allotetraploid cotton. Mol Gen Genomics, 2004, 272: 308–327
Han Z G, Wang C B, Song X L, et al. Characteristics, development and mapping of Gossypium hirsutum derived EST-SSRs in allotetraploid cotton. Theor Appl Genet, 2006, 112: 430–439
Zhang J, Wu Y T, Guo W Z, et al. Fast screening of microsatellite markers in cotton with PAGE/silver staining. Cotton Sci Sin, 2000, 12: 267–269
Li Z H, Luo P. SPSS for Windows. 2rd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005. 87–89
van Ooijen J W, Voorrips R E. JoinMap Version 3.0: Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. CPRO-DLO, Wageningen. 2001
Fryxell P A. A revision of Australian species of Gossypium with observation on occurrence of Thespesia in Australia (Malvaceae). Austr J Bot, 1965, 18: 71–102
Zhu S J, Jiang Y R, Reddy N, et al. Breeding, introgression and inheritance of delayed gland morphogenesis trait from Gosspium bickii into upland cotton germplasm. Chin Sci Bull, 2004, 49: 2470–2476
Chen X Y, Chen Y, Heinstein P, et al. Cloning, expression and characterization of (+)-δ-cadinene synthase: A catalyst for cotton phytoalexin biosynthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys, 1995, 324: 255–266
Liu C J, Heinstein P, Chen X Y. Expression pattern of genes encoding farnesyl diphosphate synthase and sesquiterpcne cyclase in cotton suspension cultured cells treated with fungal elicitors. Mol Plant-Microbe Inter, 1999, 12: 1095–1104
Meng Y L, Jia J W, Liu C J, et al. Coordinated accumulation of (+)-8-cadinene synthase mRNAs and gossypol in developing seeds of Gossypium hirsurum and a new member of the cad1 family from G. arboreum. J Nat Prod, 1999, 62: 248–252
Tan X P, Liang W Q, Liu C J, et al. Expression pattern of (+)-δ-cadinene synthase genes and biosyn thesis of sesquiterpcne aldehydes in plants of Gossypium arboreum L. Planta, 2000, 210: 644–651
Luo P, Wang Y H, Wang G D, et al. Molecular cloning and functional identification of (+)-δ-cadinene-8-hydroxylase, a cytochrome P450 momooxygenase (CYP70-6B1) of cotton sesquiterpene biosynthesis. Plant J, 2001, 28: 95–104
Xu Y H, Wang J W, Wang S, et al. Characterization of GaWRKY1, a cotton transcription factor that regulates the sesquiterpene synthase gene (+)-δ-cadinene synthase-A1. Plant Physiol, 2004, 135(1): 507–515
Chang P A, Li B, Ni X M, et al. Molecular cloning and expression analysis of a RanBP2 zinc finger protein gene in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, 2007, 55: 153–158
Sunilkumar G, Campbell L M, Puckhaber L, et al. Engineering cottonseed for use in human nutrition by tissue-specific reduction of toxic gossypol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2006, 103: 18054–18059
Li W T, Zeng R Z, Zhang Z M, et al. Fine mapping of locus S-b for F1 pollen sterility in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Chin Sci Bull, 2006, 51: 675–680
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2007CB108805) and Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (Grant No. IRT0432)
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, C., Ding, Y., Guo, W. et al. Fine mapping of the dominant glandless Gene Gl e 2 in Sea-island cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.). Chin. Sci. Bull. 52, 3105–3109 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0468-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0468-6