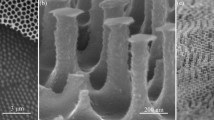
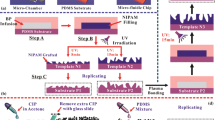
Abstract
Ultra hydrophobic surfaces take on better hydrophobicity and exhibit a water contact angle larger than 150°. In this paper the ultra hydrophobicity is analyzed and common fabrication methods are summarized in detail. The applications of micro topography in both the fabrication of hydrophobic surface and the experiments of drag reduction are addressed. Finally, the development trend and foreground of ultra hydrophobic surface are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swain P S, Lipowsky R. Contact angles on heterogeneous surfaces. A new look at Cassie’s and Wenzel’s laws. Langmuir, 1998, 14 6772–6780
Wang R, Hashimoto K, Fujishima A, et al. Light-induced amphiphilic surfaces. Nature, 1997, 388: 431–432
Chen W, Fadeev A Y, Hsieh M C, et al. Ultrahydrophobic and ultralyophobic surfaces: Some comments and examples. Langmuir, 1999, 15: 3395–3399
Jia O, Blair P, Jonathan P R, et al. Laminar drag reduction in microchannels using ultrahydrophobic surfaces. Phys Fluids, 2004, 16: 4635–4644
Barthlott W, Neinhuis C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta, 1997, 202: 1–8
Neinhuis C, Barthlott W. Characterization and distribution of water-repellent, self-cleaning plant surfaces. Annals Botany, 1997, 79: 667–677
Feng L, Li S H, Li Y S, et al. Super-hydrophobic surfaces: From natural to artificial. Adv Mater, 2002, 14(24): 1857–1860
Zhai J, Li H J, Li Y S, et al. Discovery of super amphiphobic properties of aligned carbon nanotube films. Physics (in Chinese), 2002, 8: 483–486
Onda T, Shibuichi S, Satoh N, et al. Super-water-repellent fractal surfaces. Langmuir, 1996, 12: 2125–2127
Veeramasuneni S, Drelich J, Miller J D, et al. Hydrophobicity of ion-plated PTFE coatings. Prog Org Coat, 1997, 31: 265–270
Hozumi A, Takai O. Preparation of ultra water-repellent films by microwave plasma-enhanced CVD. Thin Solid Films, 1997, 303: 222–225
Wolfram E, Faust R. Wetting, Spreading and Adhesion. Padday J F, ed London: Academic Press, 1978, 213–218
Oner D, McCarthy T J. Effects of topography length scales on wettability. Langmuir, 2000, 16: 7777–7782
Kim J, Kim C J. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference MEMS. Las Vegas, NV, 2002
Tian J, Xu J F, Xue Q J. An experimental study on the drag reduction of low surface energy coatings. J Hydrodyn (in Chinese), 1997, 1: 27–32
Watanabe K, Yanuar, Udagawa H. Drag reduction of Newtonian fluid in a circular pipe with highly water-repellent wall. J Fluid Mech, 1999, 381: 225–238
Watanabe K, Takayama T, Ogata S, et al. Flow between two coaxial rotating cylinders with a highly water-repellent wall. AIChE J, 2003, 49: 1956–1963
Pit R, Hervet H, Leger L. Friction and slip of a simple liquid at a solid surface. Tribol Lett, 1999, 7: 147–152
Pit R, Hervet H, Lege L. Direct experimental evidence of slip in hexadecane: Solid interfaces. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 85: 980–983
Mhetar V, Archer L A. Slip in entangled polymer solutions. Macromolecules, 1998, 31: 6639–6649
Tretheway D C, Meinhart C D. Apparent fluid slip at hydrophobic microchannel walls. Phys Fluids, 2002, 14(3): L9–L12
Barrat J L, Bockquet L. Large slip effect at a nonwetting fluid-solid interface. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 82: 4671–4674
Baudry J, Charlaix E, Tonck A, et al. Experimental evidence for a large slip effect at a nonwetting fluid-surface interface. Langmuir, 2001, 17: 5232–5236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Yu, Y. & Chen, D. Research progress on the ultra hydrophobic surface topography effect. CHINESE SCI BULL 51, 2297–2300 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-2129-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-2129-6