Abstract
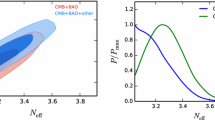
In this work, we constrain the spectral index n t of the primordial gravitational wave power spectrum in a universe with sterile neutrinos by using the Planck temperature data, the WMAP 9-year polarization data, the baryon acoustic oscillation data, and the BICEP2 data. We call this model the ΛCDM+r+ν s +n t model. The additional massive sterile neutrino species can significantly relieve the tension between the Planck and BICEP2 data, and thus can reduce the possible effects of this tension on the fit results of n t . To constrain the parameters of sterile neutrino, we also utilize the Hubble constant direct measurement data, the Planck Sunyaev-Zeldovich cluster counts data, the Planck CMB lensing data, and the cosmic shear data. We find that due to the fact that the BICEP2 data are most sensitive to the multipole ℓ ∼ 150 corresponding to k ∼ 0.01 Mpc−1, there exists a strong anticorrelation between n t and r 0.002 in the BICEP2 data, and this further results in a strongly blue-tilt spectrum. However, a slightly red-tilt tensor power spectrum is also allowed by the BICEP2 data in the region with larger value of r 0.002. By using the full data sets, we obtain m eff v,sterile = 0.48 0.11−0.13 eV, N eff = 3.73 +0.34−0.37 , and n t = 0.96 +0.48−0.63 for the ΛCDM + r + v s + n t model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BICEP2 Collaboration. BICEP2 I: Detection of B-mode polarization at degree angular scales. arXiv:1403.3985 [astro-ph.CO]
Planck Collaboration. Planck 2013 results. XVI. Cosmological parameters. arXiv:1303.5076 [astro-ph.CO]
Zhang J F, Li Y H, Zhang X. Sterile neutrinos help reconcile the observational results of primordial gravitational waves from Planck and BICEP2. arXiv:1403.7028 [astro-ph.CO]
Zhang J F, Li Y H, Zhang X. Cosmological constraints on neutrinos after BICEP2. arXiv:1404.3598 [astro-ph.CO]
Dvorkin C, Wyman M, Rudd D H, et al. Neutrinos help reconcile Planck measurements with both early and local universe. arXiv:1403.8049 [astro-ph.CO]
Liu H, Mertsch P, Sarkar S. Fingerprints of galactic loop I on the cosmic microwave background. arXiv:1404.1899 [astro-ph.CO]
Harigaya K, Yanagida T T. Discovery of large scale tensor mode and chaotic inflation in supergravity. arXiv:1403.4729 [hep-ph]
Nakayama K, Takahashi F. Higgs chaotic inflation and the primordial B-mode polarization discovered by BICEP2. arXiv:1403.4132 [hep-ph]
Brandenberger R H, Nayeri A, Patil S P. Closed string thermodynamics and a blue tensor spectrum. arXiv:1403.4927 [astro-ph.CO]
Contaldi C R, Peloso M, Sorbo L. Suppressing the impact of a high tensor-to-scalar ratio on the temperature anisotropies. arXiv:1403.4596 [astro-ph.CO]
Miranda V, Hu W, Adshead P. Steps to reconcile inflationary tensor and scalar spectra. arXiv:1403.5231 [astro-ph.CO]
Gerbino M, Marchini A, Pagano L, et al. Blue gravity waves from BICEP2? arXiv:1403.5732 [astro-ph.CO]
McDonald J. Negative running of the spectral index, hemispherical asymmetry and consistency of Planck with BICEP2. arXiv:1403.6650 [astro-ph.CO]
Kehagias A, Riotto A. Remarks about the tensor mode detection by the BICEP2 Collaboration and the super-Planckian excursions of the inflaton field. arXiv:1403.4811 [astro-ph.CO]
Lyth D H. BICEP2, the curvature perturbation and supersymmetry. arXiv:1403.7323 [hep-ph]
Bonvin C, Durrer R, Maartens R. Can primordial magnetic fields be the origin of the BICEP2 data? arXiv:1403.6768 [astro-ph.CO]
Lizarraga J, Urrestilla J, Daverio D, et al. Can topological defects mimic the BICEP2 B-mode signal? arXiv:1403.4924 [astro-ph.CO]
Moss A, Pogosian L. Did BICEP2 see vector modes? First B-mode constraints on cosmic defects. arXiv:1403.6105 [astro-ph.CO]
Chluba J, Dai L, Jeong D, et al. Linking the BICEP2 result and the hemispherical power asymmetry through spatial variation of r. arXiv:1404.2798 [astro-ph.CO]
Cai Y F, Wang Y. Testing quantum gravity effects with latest CMB observations. arXiv:1404.6672 [astro-ph.CO]
Li M. Generating scale-invariant tensor perturbations in the noninflationary universe. arXiv:1405.0211 [hep-th]
Wang Y, Xue W. Inflation and alternatives with blue tensor spectra. arXiv:1403.5817 [astro-ph.CO]
Wu F Q, Li Y C, Lu Y J, et al. Cosmological parameter fittings with the BICEP2 data. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2014, 57(8): 1449–1454
Li H, Xia J Q, Zhang X M. Global fitting analysis on cosmological models after BICEP2. arXiv:1404.0238 [astro-ph.CO]
Hu B, Hu J W, Guo Z K, et al. Reconstruction of the primordial power spectra with Planck and BICEP2. arXiv:1404.3690 [astro-ph.CO]
Cheng C, Huang Q G. The tilt of primordial gravitational waves spectra from BICEP2. arXiv:1403.5463 [astro-ph.CO]
Cheng C, Huang Q G. Constraints on the cosmological parameters from BICEP2, Planck and WMAP. arXiv:1403.7173 [astro-ph.CO]
WMAP Collaboration. Nine-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) observations: Cosmological parameter results. Astrophys J Suppl, 2013, 208: 19
BOSS Collaboration. The clustering of galaxies in the SDSS-III baryon oscillation spectroscopic survey: Baryon acoustic oscillations in the data release 10 and 11 galaxy samples. arXiv:1312.4877 [astro-ph.CO]
Riess A G, Macri L, Casertano S, et al. A 3% solution: Determination of the Hubble constant with the Hubble space telescope and wide field Camera 3. Astrophys J, 2011, 730: 119; Erratum-ibid. Astrophys J, 2011, 732: 129
Planck Collaboration. Planck 2013 results. XX. Cosmology from Sunyaev-Zeldovich cluster counts. arXiv:1303.5080 [astro-ph.CO]
Planck Collaboration. Planck 2013 results. XVII. Gravitational lensing by large-scale structure. arXiv:1303.5077 [astro-ph.CO]
Benjamin J, Van Waerbeke L, Heymans C, et al. CFHTLenS tomographic weak lensing: Quantifying accurate redshift distributions. arXiv:1212.3327 [astro-ph.CO]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhang, J. & Zhang, X. Tilt of primordial gravitational wave spectrum in a universe with sterile neutrinos. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 57, 1455–1459 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5509-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5509-y