Abstract
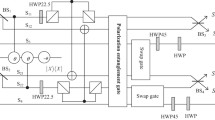
In the regime of weak nonlinearity we present two general, feasible schemes for manipulating photon states. One is an entangler for generating any one of the n-photon Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger (GHZ) states. Interactions of the incoming photons with cross-Kerr media followed by a phase shift gate and a measurement on a probe beam plus appropriate local operations using classical feed-forward of the measurement results allow one to obtain the desired states in a nearly deterministic manner. The second scheme discussed is an analyzer for multiphoton maximally entangled states, which is derived from the above entangler. In this scheme, all of the 2n n-photon GHZ states can, nearly deterministically, be discriminated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekert A K. Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys Rev Lett, 1991, 67: 661–663
Wen K, Long G L. Modified Bennett-Brassard 1984 quantum key distribution protocol with two-way classical communications. Phys Rev A, 2005, 72: 022336
Bennett C H, Wiesner S J. Communication via one- and two-particle operators on Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen states. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 69: 2881–2884
Bennett C H, Brassard G, Crépeau C, et al. Teleporting an unknown quantum state via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys Rev Lett, 1993, 70: 1895–1899
Yan F L, Yan T. Probabilistic teleportation via a non-maximally entangled GHZ state. Chin Sci Bull, 2010, 55: 902–906
Raussendorf R, Briegel H J. A one-way quantum computer. Phys Rev Lett, 2001, 86: 5188–5191
Horodecki R, Horodecki P, Horodecki M, et al. Quantum entanglement. Rev Mod Phys, 2009, 81: 865–942
Li M, Fei S M. Bell inequalities for multipartite qubit quantum systems and their maximal violation. Phys Rev A, 2012, 86: 052119
Ding D, Yan F L, Gao T. Bell-type inequality and quantum nonlocality in four-qubit systems. arXiv:quant-ph/1310.6300
Klyshko D N. The Bell and GHZ theorems: A possible three-photon interference experiment and the question of nonlocality. Phys Lett A, 1993, 172: 399–403
Greenberger D M, Horne M A, Shimony A, et al. Bell’s theorem without inequalities. Am J Phys, 1990, 58: 1131–1143
Dür W, Vidal G, Cirac J I. Three qubits can be entangled in two inequivalent ways. Phys Rev A, 2000, 62: 062314
Gühne O, Tóth G. Entanglement detection. Phys Rep, 2009, 474: 1–75
Yan F L, Gao T, Chitambar E. Two local observables are sufficient to characterize maximally entangled states of N qubits. Phys Rev A, 2011, 83: 022319
Milburn G J, Walls D F. State reduction in quantum-counting quantum nondemolition measurements. Phys Rev A, 1984, 30: 56–60
Imoto N, Haus H A, Yamamoto Y. Quantum nondemolition measurement of the photon number via the optical Kerr effect. Phys Rev A, 1985, 32: 2287–2292
Braginsky V B, Khalili F Y. Quantum nondemolition measurements: The route from toys to tools. Rev Mod Phys, 1996, 68: 1–11
Grangier P, Levenson J A, Poizat J P. Quantum non-demolition measurements in optics. Nature (London), 1998, 396: 537–542
Barrett S D, Kok P, Nemoto K, et al. Symmetry analyzer for nondestructive Bell-state detection using weak nonlinearities. Phys Rev A, 2005, 71: 060302
Munro WJ, Nemoto K, Beausoleil R G, et al. High-efficiency quantumnondemolition single-photon-number-resolving detector. Phys Rev A, 2005, 71: 033819
Nemoto K, Munro W J. Nearly deterministic linear optical controlled-NOT gate. Phys Rev Lett, 2004, 93: 250502
Sheng Y B, Deng F G, Zhou H Y. Efficient polarization-entanglement purification based on parametric down-conversion sources with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys Rev A, 2008, 77: 042308
Deng F G. Efficient multipartite entanglement purification with the entanglement link from a subspace. Phys Rev A, 2011, 84: 052312
Wang C, Li Y S, Hao L. Optical implementation of quantum random walks using weak cross-Kerr media. Chin Sci Bull, 2011, 56: 2088–2091
Zou X B, Pahlke K, Mathis W. Conditional generation of the Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state of four distant atoms via cavity decay. Phys Rev A, 2003, 68: 024302
Duan L M, Kimble H J. Efficient engineering of multiatom entanglement through single-photon detections. Phys Rev Lett, 2003, 90: 253601
Jin L, Song Z. Generation of Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger and W states for stationary qubits in a spin network via resonance scattering. Phys Rev A, 2009, 79: 042341
Wang X T, Bayat A, Bose S, et al. Global control methods for Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger-state generation on a one-dimensional Ising chain. Phys Rev A, 2010, 82: 012330
Feng W, Wang P Y, Ding X M, et al. Generating and stabilizing the Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state in circuit QED: Joint measurement, Zeno effect, and feedback. Phys Rev A, 2011, 83: 042313
Zheng A S, Liu J B. Generation of an N-qubit Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state with distant atoms in bimodal cavities. J Phys B-At Mol Opt Phys, 2011, 44: 165501
Lin Q. Efficient generation of multi-photon W state (in Chinese). Sci Sin-Phys Mech Astron, 2012, 42: 54–60
Zeilinger A, Horne M A, Weinfurter H, et al. Three-particle entanglements from two entangled pairs. Phys Rev Lett, 1997, 78: 3031–3034
Bouwmeester D, Pan JW, Daniell M, et al. Observation of three-photon Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger entanglement. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 82: 1345–1349
Pan J W, Daniell M, Gasparoni S, et al. Experimental demonstration of four-photon entanglement and high-fidelity teleportation. Phys Rev Lett, 2001, 86: 4435–4438
Sagi Y. Scheme for generating Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger-type states of n photons. Phys Rev A, 2003, 68: 042320
Louis S G R, Nemoto K, Munro W J, et al. The efficiencies of generating cluster states with weak nonlinearities. New J Phys, 2007, 9: 193
Jin G S, Lin Y, Wu B. Generating multiphoton Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger states with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Phys Rev A, 2007, 75: 054302
Wang Y, Ye L, Fang B L. A nearly deterministic scheme for generation of multiphoton GHZ states with weak cross-Kerr nonlinearity. Chin Phys B, 2011, 20: 100313
Kok P. Effects of self-phase-modulation on weak nonlinear optical quantum gates. Phys Rev A, 2008, 77: 013808
Munro W J, Nemoto K, Spiller T P. Weak nonlinearities: a new route to optical quantum computation. New J Phys, 2005, 7: 137
Lin Q, He B, Bergou J A, et al. Processing multiphoton states through operation on a single photon: Methods and applications. Phys Rev A, 2009, 80: 042311
Ding D, Yan F L. Efficient scheme for three-photon Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state generation. Phys Lett A, 2013, 377: 1088–1094
Schuck C, Huber G, Kurtsiefer C, et al. Complete deterministic linear optics Bell state analysis. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 96: 190501
Pavičić M. Near-deterministic discrimination of all Bell states with linear optics. Phys Rev Lett, 2011, 107: 080403
Hong C K, Ou Z Y, Mandel L. Measurement of subpicosecond time intervals between two photons by interference. Phys Rev Lett, 1987, 59: 2044–2046
Pan J W, Zeilinger A. Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger-state analyzer. Phys Rev A, 1998, 57: 2208–2211
Qian J, Feng X L, Gong S Q. Universal Greenberger-Horne-Zeilingerstate analyzer based on two-photon polarization parity detection. Phys Rev A, 2005, 72: 052308
Sheng Y B, Deng F G, Long G L. Complete hyperentangled-Bell-state analysis for quantum communication. Phys Rev A, 2010, 82: 032318
Guo Q, Cheng L Y, Wang H F, et al. Complete N photon GHZ state analyzer and its applications to quantum communication. Opt Commun, 2012, 285: 1571–1575
Ding D, Yan F L. Quantum nondemolition measurement of two-photon Bell-state and three-photon Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger-state based on weak nonlinearities (in Chinese). Acta Phys Sin, 2013, 62: 100304
Wang C, He L Y, Zhang Y, et al. Complete entanglement analysis on electron spins using quantum dot and microcavity coupled system. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2013, 56: 2054–2058
Ding D, Yan F L, Gao T. Preparation of km-photon concatenated GHZ states for observing distinct quantum effects at macroscopic scale. J Opt Soc Am B, 2013, 30: 3075–3078
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, D., Yan, F. & Gao, T. Entangler and analyzer for multiphoton Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger states using weak nonlinearities. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 57, 2098–2103 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5498-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-014-5498-x