Abstract
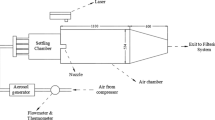
The present study experimentally investigated the near-field flow mixing characteristics of two turbulent jets issuing from equilateral triangular and circular orifice plates into effectively unbounded surroundings, respectively. Planar particle image velocimetry (PIV) was applied to measure the velocity field at the same Reynolds number of Re=50,000, where Re = U e D e/ν with U e being the exit bulk velocity and ν the kinematic viscosity of fluid, D e the equivalent diameters. The instantaneous velocity, mean velocity, Reynolds stresses were obtained. From the mean velocity field, the centreline velocity decay rate and half-velocity width were derived. Comparing the mixing characteristics of the two jets, it is found that the triangular jet has a faster mixing rate than the circular counterpart. The triangular jet entrainments with the ambient fluid at a higher rate in the near field. This is evidenced by a shorter unmixed core, faster Reynolds stress and centreline turbulence intensity growth. The primary coherent structures in the near field are found to break down more rapidly in the triangular jet as compared to the circular jet. Over the entire measurement region, the triangular jet maintained a higher rate of decay and spread. Moreover, all components of Reynolds stress of the triangular jet appear to reach their peaks earlier, and then decay more rapidly than those of the circular jet. In addition, the axis-switching phenomenon is observed in the triangular jet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gutmark E, Grinstein F. Flow control with noncircular jets. Annu Rev Fluid Mech, 1999, 31(1): 239–272
Zaman K B M Q. Axis switching and spreading of an asymmetric jet: The role of coherent structure dynamics. J Fluid Mech Digital Archive, 1996, 316(1): 1–27
Gutmark E, Schadow K, Parr T, et al. Noncircular jets in combustion systems. Expt Fluids, 1989, 7(4): 248–258
Koshigoe S, Gutmark E, SCHADOW K, et al. Initial development of noncircular jets leading to axis switching. AIAA J, 1989, 27: 411–419
Grinstein F, Gutmark E, Parr T. Near field dynamics of subsonic free square jets: A computational and experimental study. Phys Fluids, 1995, 7(6): 1483–1497
Miller R, Madnia C, Givi P. Numerical simulation of non-circular jets. Compt Fluids, 1995, 24(1): 1–25
Quinn W. Mean flow and turbulence measurements in a triangular turbulent free jet. Int J Heat Fluid Fl, 1990, 11(3): 220–224
Quinn W. Measurements in the near flow field of an isosceles triangular turbulent free jet. Expt Fluids, 2005, 39(1): 111–126
Mi J, Nathan G. Statistical properties of turbulent free jets issuing from nine differently-shaped nozzles. Flow Turbul Combust, 2010, 84(4): 583–606
Iyogun C, Birouk M. Effect of sudden expansion on entrainment and spreading rates of a jet issuing from asymmetric nozzles. Flow Turbul Combust, 2009, 82(3): 287–315
Mi J, Kalt P, Nathan G J, et al. PIV measurements of a turbulent jet issuing from round sharp-edged plate. Expt Fluids, 2007, 42(4): 625–637
Bruun H H. Hot-wire Anemometry, Principles and Data Analysis. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1994
Mi J, Xu M, Du C. Digital filter for hot-wire measurements of small-scale turbulence properties. Meas Sci Technol, 2011, 22: 125401
Xu M, Du C, Mi J. Centerline statistics of the small-scale trubulence of a circular jet and their dependence on high frequency noise. Acta Phy Sin, 2011, 60(3): 345353
He L, Yi S H, Zhao Y X, et al. Experimental study of a supersonic turbulent boundary layer using PIV. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2012, 54(9): 1702–1709
Yang S Q, Jiang N. Tomographic TR-PIV measurement of coherent structure spatial topology utilizing an improved quadrant splitting method. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2012, 55(10): 1863–1872
Pan C, Wang J J, Zhang C. Identification of Lagrangian coherent structures in the turbulent boundary layer. Sci China Ser G-Phys Mech Astron, 2009, 52(2): 248–257
Tang Z Q, Jiang N. Dynamic mode decomposition of hairpin vortices generated by a hemisphere protuberance. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2012, 55(1): 118–124
Liu Z F, Wang L Z, Fu S. Study of flow induced by sine wave and saw tooth plasma actuators. Sci China-Phys Mech Astron, 2012, 54(11): 2033–2039
Mi J, Kalt P, Nathan G. On Turbulent jets issuing from notched-rectangular and circular orifice plates. Flow Turbul Combust, 2010, 84(4): 565–582
Xu M, Zhang J, Mi J, et al. Mean and fluctuating velocity fields of a diamond turbulent jet. Chin Phys B, 2013, 22(3): 034701
Hussain A, Clark A. On the coherent structure of the axisymmetric mixing layer: A flow-visualization study. J Fluid Mech, 1981, 104: 263–294
Schadow K, Gutmark E, Parr D, et al. Selective control of flow coherence in triangular jets. Expt Fluids, 1988, 6(2): 129–135
Ho C, Gutmark E. Vortex induction and mass entrainment in a small-aspect-ratio elliptic jet. J Fluid Mech, 1987, 179: 383–405
Hussain F, Husain H. Elliptic jets, Part 1. Characteristics of unexcited and excited jets. J Fluid Mech, 1989, 208: 257–320
Husain H, Hussain A. Controlled excitation of elliptic jets. Phys Fluids, 1983, 26: 2763–2765
Du C, Xu M, Mi J. Effect of exit Reynolds number on a turbulent round jet. Acta Phy Sin, 2010, 59(9): 6323–6330
Deo R C, Mi J, Nathan G J. The influence of Reynolds number on a plane jet. Phys Fluids, 2008, 20(7): 075108
Xu M, Pollard A, Mi J, et al. Effects of Reynolds number on some properties of a turbulent jet from a long square pipe. Phys Fluids, 2013, 25: 035102
Widnall S E. The structure and dynamics of vortex filaments. Annu Rev Fluid Mech, 1975, 7(1): 141–165
Hussein H, Capp S, George W. Velocity measurements in a high-Reynolds-number, momentum-conserving, axisymmetric, turbulent jet. J Fluid Mech, 1994, 258: 31–75
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, M., Zhang, J., Mi, J. et al. PIV measurements of turbulent jets issuing from triangular and circular orifice plates. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56, 1176–1186 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5099-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-013-5099-0