Abstract
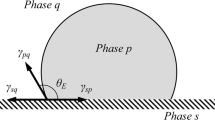
The factors influencing the state and wetting transition of droplets on a rough surface are both complex and obscure. The change in wetting is directly reflected by changes under the contact condition of the droplets with the surface. The recent study about the wettability of the superhydrophobic surface under the condensing condition arouses the new understanding about the apparent state of droplets on a rough surface. In this work, to validate the existence of droplets in an intermediate state, a microscale pillar topological polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) surface was manufactured and its wettability under various conditions was studied. According to the experimental data, it is proposed that the wetting state of a rough surface may be embodied using the contact area ratio of a solid/liquid/gas droplet with the projective plane. A general calculation model for the apparent contact angle of droplets is given and expressed diagrammatically. It is found that the measured apparent contact angles of droplets at different states on the surface falls within the range predicted by our proposed equation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wier K A, McCarthy T J. Condensation on ultrahydrophobic surfaces and its effect on droplet mobility: Ultrahydrophobic surfaces are not always water repellant. Langmuir, 2006, 22: 2433–2436[DOI]
Dorrer C, Ruhe J. Condensation and wetting transitions on microstructured ultrahydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir, 2007, 23: 3820–3824[DOI]
Narhe R D, Beysens D A. Growth dynamics of water drops on a square-pattern rough hydrophobic surface. Langmuir, 2007, 23:6486–6489[DOI]
Narhe R D, Beysens D A. Water condensation on a super-hydrophobic spike surface. Europhys Lett, 2006, 75: 98–104[DOI]
Cheng Y T, Rodak D E. Is the lotus leaf superhydrophobic. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86: 144101-1-3
Cheng Y T, Rodak D E, Angelopoulos A, et al. Microscopic observations of condensation of water on lotus leaves. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 87: 194112-1-3
Cassie A B D, Baxter S. Contact angles. Trans Faraday Soc, 1948, 3: 11–16
Wenzel T N J. Surface roughness and contact angle. Phys Colloid Chem, 1949, 53: 1466–1467[DOI]
Chen H H, Cai Q J, Tsai C, et al. Dropwise condensation on superhydrophobic surfaces with two-tier roughness. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90: 173108-1–3
Lafuma L, Quere D. Superhydrophobic states. Nature Mater, 2003, 2: 457–460[DOI]
Bico J, Marzolin C, Quere D. Pearl drops. Europhys Lett, 1999, 47: 220–226[DOI]
He B, Patankar N A, Lee J. Multiple equilibrium droplet shapes and design criterion for rough hydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir, 2003, 19: 4999–5003[DOI]
Quere D, Lafuma A, Bico J. Slippy and sticky microtextured solids. Nanotechnology, 2003, 14: 1109–1112[DOI]
Cao L, Hu H-H, Gao D. Design and fabrication of micro-textures for inducing a superhydrophobic behavior on hydrophilic materials. Langmuir, 2007, 23: 4310–4314[DOI]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 50606025)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Lu, T. The apparent state of droplets on a rough surface. Sci. China Ser. G-Phys. Mech. Astron. 52, 233–238 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-009-0041-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-009-0041-1