Abstract
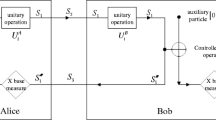
A quasi-secure quantum dialogue protocol using single photons was proposed. Different from the previous entanglement-based protocols, the present protocol uses batches of single photons which run back and forth between the two parties. A round run for each photon makes the two parties each obtain a classical bit of information. So the efficiency of information transmission can be increased. The present scheme is practical and well within the present-day technology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett C H, Brassard G. Quantum cryptography: Public-key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing. Bangalore: IEEE Press, 1984. 175–179
Ekert A. Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys Rev Lett, 1991, 67: 661–664
Bennett C H. Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 68: 3121–3124
Deng F G, Long G L. Bidirectional quantum key distribution protocol with practical faint laser pulses. Phys Rev A, 2004, 70: 012311
Deng F G, Long G L. Controlled order rearrangement encryption for quantum key distribution. Phys Rev A, 2003, 68: 042315
Boström K, Felbinger T. Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 89: 187902
Shimizu K, Imoto N. Single-photon-interference communication equivalent to Bell-state-basis cryptographic quantum communication. Phys Rev A, 2000, 62: 054303
Deng F G, Long G L, Liu X S. Two-step quantum direct communication protocol using the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pair block. Phys Rev A, 2003, 68: 042317
Deng F G, Long G L. Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad. Phys Rev A, 2004, 69: 052319
Zhu A D, Xia Y, Fan Q B, et al. Secure direct communication based on secret transmitting order of particles. Phys Rev A, 2006, 73: 022338
Cao H J, Song H S. Quantum secure direct communication with W state. Chin Phys Lett, 2006, 23: 290–292
Li X H, Zhou P, Liang Y J, et al. Quantum secure direct communication network with two-step protocol. Chin Phys Lett, 2006, 23: 1080–1083
Wang C, Deng F G, Li Y S, et al. Quantum secure direct communication with high-dimension quantum superdense coding. Phys Rev A, 2005, 71: 044305
Lee H, Lim J, Yang H. Quantum direct communication with authentication. Phys Rev A, 2006, 73: 042305
Beige A, Englert B-G, Kurtsiefer C, et al. Secure communication with a publicly known key. Acta Phys Pol A, 2002, 101: 357–363
Cai Q Y, Li B W. Deterministic secure communication without using entanglement. Chin Phys Lett, 2004, 21: 601–603
Cai Q Y. A one-time-pad key communication protocol with entanglement. Arxiv: quant-ph/0309108
Li X H, Deng F G, Li C Y, et al. Deterministic secure quantum communication without maximally entangled states. J Korean Phys Soc, 2006, 49: 1354–1359
Nguyen B A. Quantum dialogue. Phys Lett A, 2004, 328: 6–10
Wójcik A. Eavesdropping on the “Ping-Pong” quantum communication protocol. Phys Rev Lett, 2003, 90: 157901
Zhang Z J, Man Z X, Li Y. Improving Wójcik’s eavesdropping attack on the ping-pong protocol. Phys Lett A, 2004, 333: 46–50
Zhang Z J. Deterministic secure direct bidirectional communication protocol. arxiv: quant-ph/0403186
Zhang Z J, Man Z X. Secure bidirectional quantum communication protocol without quantum channel. Arxiv: quant-ph/0403217
Zhang Z J, Man Z X. Secure direct bidirectional communication protocol using the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen pair block. Arxiv: quant-ph/0403215
Man Z X, Zhang Z J, Li Y. Quantum dialogue revisited. Chin Phys Lett, 2005, 22: 22–24
Man Z X. The ‘quantum dialogue’ can be eavesdropped under the intercept-and-resend attack. arxiv: quant-ph/0406230
Xia Y, Fu C B, Zhang S. Quantum dialogue by using the GHZ state. Arxiv: quant-ph/0601127
Cleve R, Gottesman D, Lo H K. How to share a quantum secret. Phys Rev Lett, 1999, 83: 648–651
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2006AA01Z419), the Major Research Plan of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 90604023), the National Research Foundation for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (Grant No. 20040013007), the National Laboratory for Modern Communications Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 9140C1101010601) and the Open Foundation of the State Key Laboratory of Information Security, Graduate University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Wen, Q. Quasi-secure quantum dialogue using single photons. SCI CHINA SER G 50, 558–562 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-007-0057-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-007-0057-3