Abstract
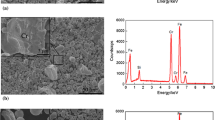
In order to gain a sufficient wear resistance for applications, the biomimetic non-smooth units in concave were fabricated on the surfaces of 20CrMnTi steel using a biomimetic laser remelting technology. The diameter and distribution of the concaves were optimized using orthogonal experiment. The microstructures of the biomimetic non-smooth units were examined. The anti-wear behaviors were investigated by the rolling wear test with lubricant. The results of wear tests indicated that the biomimetic surfaces exhibit a higher anti-wear ability than the smooth surfaces. The biomimetic surface with concaves of 250 μm in diameter and transverse distance of 270 μm and longitudinal distance of 400 μm exhibits the best anti-wear property. The enhancement of wear resistance can be mainly attributed to the action of biomimetic non-smooth units and the super fined microstructure and hardness in the biomimetic unit zones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Q X, Ren X J, Gao Y K, et al. Effect of carburization on residual stress field of 20CrMnTi specimen and its numerical simulation. Mat Sci Eng A, 2005, 392: 240–247
Yan M F, Liu Z R. Study on microstructure and microhardness in surface layer of 20CrMnTi steel carburised at 880°C with and without RE. Mater Chem Phys, 2001, 72: 97–100
Yu Z W, Xu X L. Failure analysis of an idler gear of diesel engine gearbox. Eng Fail An, 2006, 3: 1092–1100
Liu L G, Li Q, Liu X H, et al. Stress field simulation of carburized specimens with different carbon content during quenching process. Mater Lett, 2007, 61: 1251–1255
Rigney D A. Comments on the sliding wear of metals. Trbol Int, 1997, 30: 361–368
Hirasata K, Hayashi K, Inamoto Y. Friction and wear of several kinds of cast irons under severe sliding conditions. Wear, 2007, 263: 790–800
Osterle W, Klaffke D, Griepentrog M. Potential of wear resistant coatings on Ti-6Al-4V for artificial hip joint bearing surfaces. Wear, 2008, 264: 505–517
Ren L Q. Progress in the study on anti-adhesion and resistance reduction of terrain machines. Sci China Ser E-Tech Sci, 2009, 52: 273–284
Wu J H, Phillips B S, Jiang W P, et al. Bio-inspired surface engineering and tribology of MoS2 over coated CBN-TiN composite coating. Wear, 2006, 261: 592–599
Tong J, Li T B, Ma Y H. Two-body abrasive wear of the surfaces of pangolin scales. J Bionic Eng, 2007, 4: 77–84
Tong J, Moayad B Z, Ma Y H. Effects of biomimetic surface designs on furrow opener performance. J Bionic Eng, 2009, 6: 280–289
Wu J H, Phillips B S, Jiang W P, et al. Bio-inspired surface engineering and tribology of MoS2 overcoated CBN-TiN composite coating. Wear, 2006, 261: 592–599
Ren L Q, Tong J, Zhang S J, et al. Reducing sliding resistance of soil against bulldozing plates by unsmoothed bionics surfaces. J Terramech, 1995, 32: 303–309
Shan H Y, Zhou H, Sun N, et al. Study on adhesion resistance behavior of sample with striated non-smooth surface by laser processing technique. J Mater Pro, 2008, 199: 221–229
Zhou H, Tong X, Ren L Q. The thermal fatigue resistance of cast iron with biomimetic non-smooth surface processed by laser with different parameters. Mat Sci Eng A, 2006, 428: 141–147
Zhou H, Sun N, Shan H Y, et al. Bio-inspired wearable characteristic surface: Wear behavior of cast iron with biomimetic units processed by laser. Appl Surf Sci, 2007, 253: 9513–9520
Meng Y M, Chen Y L, Li S P, et al. Research on the orthogonal experiment of numeric simulation of macromolecule-cleaning element for sugarcane harvester. Mater Desig, 2009, 30: 2250–2258
Du X K, Wang J J, Wang T M, et al. Orthogonal experiment and microstructure analysis on TiC-TiB2 multi-phase ceramic coating prepared by SHS reactive spraying. Tans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2007, 17: 847–850
Vilar R, Colaço R. Laser-assisted combinatorial methods for rapid design of wear resistant iron alloys. Surf Coat, 2009, 203: 2878–2885
Zhang Z H, Zhou H, Ren L Q, et al. Surface morphology of laser tracks used for forming the non-smooth biomimetic unit of 3Cr2W8V steel under different processing parameters. Appl Surf Sci, 2008, 254: 2548–2555
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Han, Z., Xu, M. et al. Anti-wear properties on 20CrMnTi steel surfaces with biomimetic non-smooth units. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 53, 2920–2924 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-4130-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-4130-1