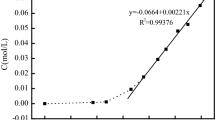
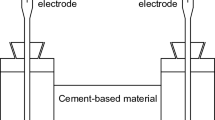
Abstract
Chemical titration method and lab-made chloride probes were jointly adopted to investigate the effects of water-to-cement (W/C) ratio and the impressed current density on chloride transport for cement-based materials during electrochemical chloride extraction (ECE) process. The dissolution of bound chlorides and the effect of current density on dissolution were analyzed. The variations of chloride concentration at different depths and the chloride transference process were monitored. Test results show that W/C ratios adopted have slight influence on chloride extraction, while chloride extraction efficiency is mainly determined by the impressed current density. During ECE process a portion of bound chloride ions dissolved and the amount of bound chlorides released is directly proportional to current density.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orellan J C, Escadeillas G, Arliguie G. Electrochemical chloride extraction efficiency and side effects. Cem Concr Res, 2004, 34: 227–234
Orellan J C, Escadeillas G, Arliguie G. Electrochemical chloride extraction: Influence of C3A of the cement on treatment efficiency. Cem Concr Res, 2006, 36: 1939–1946
Elsener B, Molina M, Bohni H. Electrical removal of chlorides from reinforced concrete. Corros Sci, 1993, 35: 1563–1570
Swamy R N, McHugh S. Effectiveness and structural implications of electrochemical chloride extraction from reinforced concrete beams. Cem Concr Compos, 2006, 28: 722–733
Fajardo G, Escadeillas G, Arliguie G. Electrochemical chloride extraction (ECE) from steel reinforced concrete specimens contaminated by “artificial” sea-water. Corros Sci, 2006, 48: 110–125
Elsener B, Angst U. Mechanism of electrochemical chloride removal. Corros Sci, 2007, 49: 4504–4522
Ministry of Communications of the People’s Republic of China. JTJ 270-98, Testing Code of Concrete for Port and Waterway Engineering (in Chinese), 1998
Mindness S, Young J F, Darwin D. Concrete. 2nd ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education, 2003
Liu W, Xing F, Xie Y J. Effect of water to cement ratio and mineral admixtures on the porosity of concrete (in Chinese). Low Temp Arch Tech, 2006, 109: 9–11
Weng Z C, Yu H F, Sun W, et al. Influence of water-cement ratio and cement content on chloride binding capacity of concrete (in Chinese). J Wuhan Univ Tech, 2006, 28: 47–50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (Grant No. 2009CB623105), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (Grant No. 20070247063), the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Costal and Offshore Engineering (Grant No. LP0707) and the Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars of Ministry of Education of China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, W., Zhao, Z. Chloride transference during electrochemical chloride extraction process. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 53, 1466–1470 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-3135-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-010-3135-0